Artículos SCI
2024
2024
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
DC magnetron sputter deposition in pure helium gas: formation of porous films or gas/solid nanocomposite coatings
Ibrahim, S; Fernández, A; Brault, P; Sauldubois, A; Desgardin, P; Caillard, A; Hufschmidt, D; De Haro Jiménez, MC, Sauvage, T; Barthe, MF, Thomann, ALVacuum, 224 (2024) 113184 DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2024.113184
Abstract
Magnetron sputtering of two materials (Aluminum and Silicon) was performed in He gas and led to the formation of very different porous thin films: a fiberform nanostructure or a gas/solid nanocomposite. The composition of the thin films obtained was analyzed by means of ion beam techniques: Rutherford backscattering and proton elastic backscattering spectroscopies to measure the amount of Al(Si) deposited atoms and that of He atoms inserted inside the films. Microstructural and crystalline properties were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. Transmission electron microscopy coupled with electron energy loss spectroscopy were used to investigate the presence of empty or He filled pores or even bubbles. Correlating the Al(Si) film properties with the deposition conditions evaluated by SRIM (sputtering process at the target) and by a homemade collision code (species transport to the substrate) gave a better insight into the reason for the formation of such different films. The role of both He ions backscattered at the target and surface mobility during the growth is discussed. Comparison with low kinetic energy He + implantation experiments indicates that similar mechanisms, such as He insertion, diffusion inside the lattice, release or accumulation into pores and bubbles, are certainly taking place.
Junio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2024.113184
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of graphene-based nanostructures processing routes and aspect ratio in flexural strength and fracture mechanisms of 3Y-TZP-matrix composites
Moriche, R; Guisado-Arenas, E; Muñoz-Ferreiro, C; López-Pernía, C; Morales-Rodríguez, A; Jiménez-Piqué, E; Gallardo-López, A; Poyato, RCeramics International, 50(11) (2024) 19217-19227 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.03.021
Abstract
In this work, the influence of the aspect ratio of graphene-based nanostructures (GBNs) and content on the mechanical properties of 3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystalline 3Y-TZP matrix composites was analysed. The influence of the dispersion method and sintering parameters on the flexural strength and elastic modulus of the composites was studied, and the fracture surfaces were characterized to determine the fracture mechanisms that occur. The results showed that small amounts of exfoliated graphene nanoplatelets, with reduced lateral size, and few layer graphene, up to 1.0 and 2.5 vol%, respectively, slightly increase the 3Y-TZP flexural strength. This has been attributed to the tortuosity of the crack propagation pathways and strengthening mechanisms. Higher contents cause a decrease in flexural strength and stiffness because of overlapped GBNs, which can promote the crack propagation. The pull-out of GBN was more significant in composites with non-exfoliated graphene nanoplatelets, where no increase on the flexural or biaxial strength was measured.
Junio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.03.021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Biomass gasification, catalytic technologies and energy integration for production of circular methanol: New horizons for industry decarbonisation
Bobadilla, Luis F; Azancot, Lola; González-Castaño, Miriam; Ruíz-López, Estela; Pastor-Pérez, Laura; Durán-Olivencia, Francisco J.; Ye, Runping; Chong, Katie; Blanco-Sánchez, Paula H; Wu, Zenthao; Reina, TR; Odriozola, JAJournal of Environmental Sciences, 140 (2024) 306-318 DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.09.020

Abstract
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) recognises the pivotal role of renewable energies in the future energy system and the achievement of the zero-emission target. The implementation of renewables should provide major opportunities and enable a more secure and decentralised energy supply system. Renewable fuels provide long-term solutions for the transport sector, particularly for applications where fuels with high energy density are required. In addition, it helps reducing the carbon footprint of these sectors in the long-term. Information on biomass characteristics feedstock is essential for scaling-up gasification from the laboratory to industrial-scale. This review deals with the transformation biogenic residues into a valuable bioenergy carrier like biomethanol as the liquid sunshine based on the combination of modified mature technologies such as gasification with other innovative solutions such as membranes and microchannel reactors. Tar abatement is a critical process in product gas upgrading since tars compromise downstream processes and equipment, for this, membrane technology for upgrading syngas quality is discussed in this paper. Microchannel reactor technology with the design of state-of-the-art multifunctional catalysts provides a path to develop decentralised biomethanol synthesis from biogenic residues. Finally, the development of a process chain for the production of (i) methanol as an intermediate energy carrier, (ii) electricity and (iii) heat for decentralised applications based on biomass feedstock flexible gasification, gas upgrading and methanol synthesis is analysed.
Junio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.09.020
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Nickel-based cerium zirconate inorganic complex structures for CO2 valorisation via dry reforming of methane
Martín-Espejo, Juan Luis; Merkouri, Loukia-Pantzechroula; Gándara-Loe, Jesús; Odriozola, José AntonioJournal of Environmental Sciences, 140 (2024) 12-23 DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.01.022
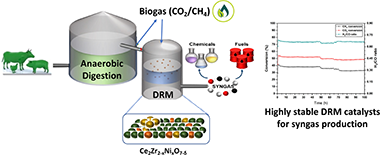
Abstract
The increasing anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases (GHG) is encouraging extensive research in CO2 utilisation. Dry reforming of methane (DRM) depicts a viable strategy to convert both CO2 and CH4 into syngas, a worthwhile chemical intermediate. Among the different active phases for DRM, the use of nickel as catalyst is economically favourable, but typically deactivates due to sintering and carbon deposition. The stabilisation of Ni at different loadings in cerium zirconate inorganic complex structures is investigated in this work as strategy to develop robust Ni-based DRM catalysts. XRD and TPR-H2 analyses confirmed the existence of different phases according to the Ni loading in these materials. Besides, superficial Ni is observed as well as the existence of a CeNiO3 perovskite structure. The catalytic activity was tested, proving that 10 wt.% Ni loading is the optimum which maximises conversion. This catalyst was also tested in long-term stability experiments at 600 and 800°C in order to study the potential deactivation issues at two different temperatures. At 600°C, carbon formation is the main cause of catalytic deactivation, whereas a robust stability is shown at 800°C, observing no sintering of the active phase evidencing the success of this strategy rendering a new family of economically appealing CO2 and biogas mixtures upgrading catalysts.
Junio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.01.022
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Enhanced low-temperature CO2 methanation over La-promoted NiMgAl LDH derived catalyst: Fine-tuning La loading for an optimal performance
Wang, ZL; Zhang, TY; Reina, TR; Huang, L; Xie, WF; Musyoka, NM; Oboirien, B; Wang, QFuel, 366 (2024) 131383 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2024.131383
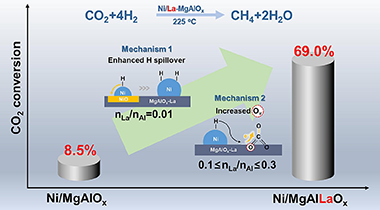
Abstract
LDH-derived Ni-based catalysts are gathering momentum due to their excellent thermal stability but their lowtemperature CO2 methanation is limited. In this study, various concentrations of La were introduced into the LDH-derived Ni-based catalysts for CO2 methanation, and the underlying mechanisms were investigated. The optimal Ni/La-0.2-MgAlOx catalyst presented a CO(2)conversion level of 69.0 % at 225 C-degrees, which is over 7 times higher than that of conventional Ni/MgAlOx. The addition of small amounts of La could significantly enhance H spillover to promote the reduction of Ni species, but the oxygen vacancy concentration became the dominant factor causing changes in low -temperature activity as the La contents continue to increase. CO2 was found to be adsorbed at the oxygen vacancies in the form of bidentate carbonates, which are more reactive under an enhanced electron -rich environment. The research offers guidance to design effective and sustainable catalysts for low -temperature CO2 methanation.
Junio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2024.131383
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Hydrochar and synthetic natural gas co-production for a full circular economy implementation via hydrothermal carbonization and methanation: An economic approach
González-Arias, J; Torres-Sempere, G; González-Castaño, M; Baena-Moreno, FM; Ramirez Reina, TJournal of Environmental Sciences, 140 (2024) 69-78 DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.04.019
Abstract
Herein we study the economic performance of hydrochar and synthetic natural gas co-production from olive tree pruning. The process entails a combination of hydrothermal carbonization and methanation. In a previous work, we evidenced that standalone hydrochar production via HTC results unprofitable. Hence, we propose a step forward on the process design by implementing a methanation, adding value to the gas effluent in an attempt to boost the overall process techno-economic aspects. Three different plant capacities were analyzed (312.5, 625 and 1250 kg/hr). The baseline scenarios showed that, under the current circumstances, our circular economy strategy in unprofitable. An analysis of the revenues shows that hydrochar selling price have a high impact on NPV and subsidies for renewable coal production could help to boost the profitability of the process. On the contrary, the analysis for natural gas prices reveals that prices 8 times higher than the current ones in Spain must be achieved to reach profitability. This seems unlikely even under the presence of a strong subsidy scheme. The costs analysis suggests that a remarkable electricity cost reduction or electricity consumption of the HTC stage could be a potential strategy to reach profitability scenarios. Furthermore, significant reduction of green hydrogen production costs is deemed instrumental to improve the economic performance of the process. These results show the formidable techno-economic challenge that our society faces in the path towards circular economy societies.
Junio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.04.019
Reactividad de Sólidos
Ca-based materials derived from calcined cigarette butts for CO2 capture and thermochemical energy storage
Amghar, N; Moreno, V; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; Perejón, A; Pérez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Environmental Sciences, 140 (2024) 230-241 DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.07.028
Abstract
Cigarette butts (CBs) are one of the most common types of litter in the world. Due to the toxic substances they contain, the waste generated poses a harmful risk to the environment, and therefore there is an urgent need for alternative solutions to landfill storage. Thus, this work presents a possible revalorization of this waste material, which implies interesting environmental benefits. CBs were used as sacrificial templates for the preparation of CaO-based materials by impregnation with calcium and magnesium nitrates followed by flaming combustion. These materials presented enhanced porosity for their use in the Calcium Looping process applied either to thermochemical energy storage or CO2 capture applications. The influence of the concentration of Ca and Mg in the impregnating solutions on the multicycle reactivity of the samples was studied. An improved multicycle performance was obtained in terms of conversion for both applications.
Junio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.07.028
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Novel heterostructured NaTaO3/WO3 systems with improved photocatalytic properties for water decontamination under UV and Visible illumination
Hernández-Laverde, M; Murcia, JJ; Navío, JA; Hidalgo, MCJournal of Materials Science, 59 (2024) 8669-8681 DOI: 10.1007/s10853-024-09699-x
Abstract
In this work, we present the preparation of NaTaO3/WO3 systems, a broad-bandgap and a narrow-bandgap semiconductor, respectively, for photocatalytic applications. The samples were prepared by two different methods, microwave-assisted and conventional hydrothermal method, with different NaTaO3/WO3 molar ratios. All samples were extensively characterized, and the photocatalytic behavior was studied in the degradation reaction of rhodamine B under simulated solar illumination. A significant synergistic effect in the coupling of the two components could be observed, with an important improvement in the rhodamine degradation rate, especially for the microwave-prepared sample with 1:1 (NaTaO3/WO3) molar ratio. The enhancement of the activity can be explained by the formation of type II and Z-Scheme heterojunctions. The obtained results are promising for the development of more efficient photocatalyst materials under solar or visible illumination.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1007/s10853-024-09699-x
Materiales Coloidales
Nanoparticulated Bimodal Contrast Agent for Ultra-High-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectral X-ray Computed Tomography
González-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Caro, C; Gómez-González, E; Luisa, GMM; Ocaña, MInorganic Chemistry, 63(23) (2024) 10648-10656 DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.4c01114
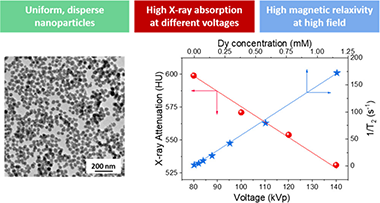
Abstract
Bimodal medical imaging based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) is a well-known strategy to increase the diagnostic accuracy. The most recent advances in MRI and CT instrumentation are related to the use of ultra-high magnetic fields (UHF-MRI) and different working voltages (spectral CT), respectively. Such advances require the parallel development of bimodal contrast agents (CAs) that are efficient under new instrumental conditions. In this work, we have synthesized, through a precipitation reaction from a glycerol solution of the precursors, uniform barium dysprosium fluoride nanospheres with a cubic fluorite structure, whose size was found to depend on the Ba/(Ba + Dy) ratio of the starting solution. Moreover, irrespective of the starting Ba/(Ba + Dy) ratio, the experimental Ba/(Ba + Dy) values were always lower than those used in the starting solutions. This result was assigned to lower precipitation kinetics of barium fluoride compared to dysprosium fluoride, as inferred from the detailed analysis of the effect of reaction time on the chemical composition of the precipitates. A sample composed of 34 nm nanospheres with a Ba0.51Dy0.49F2.49 stoichiometry showed a transversal relaxivity (r(2)) value of 147.11 mM(-1)s(-1) at 9.4 T and gave a high negative contrast in the phantom image. Likewise, it produced high X-ray attenuation in a large range of working voltages (from 80 to 140 kVp), which can be attributed to the presence of different K-edge values and high Z elements (Ba and Dy) in the nanospheres. Finally, these nanospheres showed negligible cytotoxicity for different biocompatibility tests. Taken together, these results show that the reported nanoparticles are excellent candidates for UHF-MRI/spectral CT bimodal imaging CAs.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.4c01114
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic activity enhancement by noble metal deposition on faceted F-TiO2 synthesised by microwave assisted method. A study of selective oxidation of gas-phase ethanol in a FBPR reactor
Hernández-Laverde, M; Murcia, JJ; Morante, N; Sannino, D; Vaiano, V; Navío, JA; Hidalgo, MCCatalysis Today, 433 (2024) 114645 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2024.114645
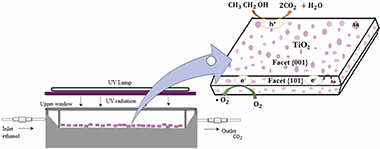
Abstract
In the present work, fluorinated titanium dioxide (TiO2-F) with high exposition of facet {001} was prepared by following a facile and high yield hydrothermal method assisted by microwave. This faceted TiO2 was then modified by Au or Ag deposition at two different metal loadings (0.125 and 0.25 wt%). A wide physicochemical characterisation of the materials was performed. X-ray difractograms showed high {001} facet exposition in all materials. By X-ray fluorescence it was found that the different samples contained about 5% of fluor. All samples presented high surface area and high uniformity and homogeneity of particles, which highlights the good properties that can be achieved by the microwave synthesis method compared to conventional hydrothermal methods. Oxidation state of the noble metals was studied by XPS. On the other side, TiO2-F and the metallised titania powders were immobilised on polystyrene pellets (PS) for evaluating their gas photocatalytic activity in volatile organic compounds (VOCs) decontamination by following the reaction of photoxidation of ethanol in gas phase. It was found that activity was considerably improved by the addition of noble metals, obtaining high conversion and selectivity to CO2. It is remarkable that the selectivity to CO is almost zero. The highest efficiency was found for the faceted TiO2-F sample with the lowest Au loading (0.125 wt%) immobilised on PS where 91% ethanol conversion and 100% CO2 selectivity were achieved. Different reaction variables were also studied.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2024.114645
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Evaluation of Pt/TiO2-Nb2O5 systems in the photocatalytic reforming of glucose for the generation of H2 from industrial effluents
Lara Sandoval, AE; Serafin, J; Murcia Mesa, JJ; Rojas Sarmiento, HA; Hernandez Niño, JS; Llorca, J; Navío Santos, JA; Hidalgo Lõpez; MCFuel, 363 (2024) 130932 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2024.130932
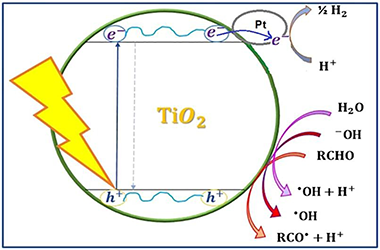
Abstract
Different Pt-TiO2-Nb2O5 systems were synthesized and studied in the photocatalytic reforming of glucose for the generation of H2. The physicochemical properties of the synthesized photocatalysts were analyzed using different characterization techniques from which it was found that fluoridation and sulphation have different effects on the oxides under study such as a protective effect on the crystalline phase in anatase, and greater response in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The addition of fluorine or sulfates favors the reduction of platinum species on the surface of the semiconductor oxides and a better homogeneity of size and distribution of the particles of this metal. Studies were carried out in the gas phase that allowed the monitoring and quantification of the hydrogen produced from aqueous glucose solutions and it was determined that Pt-F-Nb2O5 and Pt-F-TiO2 are the most efficient materials for the production of hydrogen from this substrate. Similarly, liquid phase studies were carried out with a real sample from a confectionery industry where it was determined that with the material Pt-F-Nb2O5 the highest transformation of glucose is obtained, without the formation of any other sugar or intermediate compound, indicating the preferential production of hydrogen during the photocatalytic reaction. The foregoing demonstrates the potential of the evaluated process in obtaining this gas from the recovery of polluting residues derived from the samples under study.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2024.130932
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Materials for 3D Printed Metal and Metal-Ion Batteries
García Rodríguez, T; Medina Santos, JI; Coelho,m J; Pinilla, SChemElectroChem (2024) e202400206 DOI: 10.1002/celc.202400206
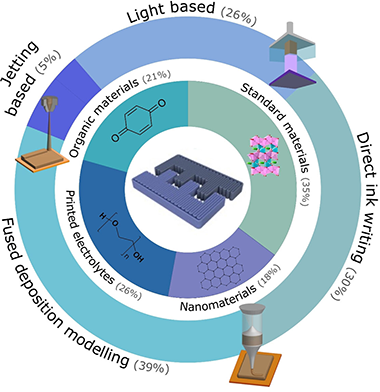
Abstract
The review provides an overview of the latest innovations, trends, and challenges in the field of 3D-printed metal and metal-ion batteries. It focuses on the materials used in the printing of batteries, including electrodes, electrolytes, and other electroactive components. Compared to other high-quality reviews on the topic, this review provides a broader selection of materials that are expected to gain attention in the next few years, such as redox-active polymers and metal-organic frameworks. This work gives an overview and insight into the latest trends in printing techniques as well as a statistical review of their uses and strengths. We have also gathered the latest works done for each of the material types, and we have taken the opportunity to put them in context and use them to exemplify in which direction is the field going. The review concludes with a critical view of the challenges ahead and a discussion of the direction that the field is taking as well as the external factors that might help to define its future.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1002/celc.202400206
Reactividad de Sólidos
Complex TiC-Ni-based composites joined to steel support by thermal explosion under load: synthesis, microstructure and tribological behavior
Lemboub, S; Boadebane, A; Boudebane, S; Bourbia, A; Mezrag, S; Gotor, FJComposites Interfaces, 31(5) (2024) 537-557 DOI: 10.1080/09276440.2023.2268968
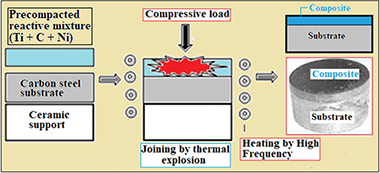
Abstract
The combustion in thermal explosion mode of reactive mixtures of Ti-Ni-graphite(carbides, borides, oxides), under load, was used to produce complex composite materials, densified and joined to a C55 carbon steel support. The ignition of the exothermic reaction, carried out thanks to the rapid high-frequency heating of a green compact up to 1573 K, was followed by an isothermal holding at 1373 K for 360 s. This procedure ensured a perfect mechanical assembly between the composite material and the steel substrate. SEM analysis and concentration profiles carried out at the interface testified to the interdiffusion of iron and titanium atoms between the two materials. The maximum combustion temperature (T-max.) exceeding 2200 K induced the appearance of a liquid phase that assisted densification and joining, and in which a part of the additions was dissolved before cooling. The starting chemical composition of reactive mixtures largely determined the microstructure, hardness and tribological behavior of the composites after the process. Thereby, the maximum hardness (1235 HV0.15) and the lowest wear rate (1.824 x 10(-6) mm(3).N-1.m(-1)) were obtained in the sample containing TiC, Al2O3 and TiB2 hard phases. The manufactured samples exhibit no deterioration of the composite by spalling, regardless of the starting composition.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1080/09276440.2023.2268968
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Green Fabrication of Stackable Laser-Induced Graphene Micro-Supercapacitors under Ambient Conditions: Toward the Design of Truly Sustainable Technological Platforms
Silvestre, SL; Morais, M; Soares, RRA; Johnson, Z; Benson, E; Ainsley, E; Pham, V; Claussen, JC; Gomes, CL; Martins, R; Fortunato, E; Pereira, L; Coelho, JAdvanced Materials Technologies, (2024) 2365709X DOI: 10.1002/admt.202400261
Abstract
Extensive research into green technologies is driven by the worldwide push for eco-friendly materials and energy solutions. The focus is on synergies that prioritize sustainability and environmental benefits. This study explores the potential of abundant, non-toxic, and sustainable resources such as paper, lignin-enriched paper, and cork for producing laser-induced graphene (LIG) supercapacitor electrodes with improved capacitance. A single-step methodology using a CO2 laser system is developed for fabricating these electrodes under ambient conditions, providing an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional carbon sources. The resulting green micro-supercapacitors (MSCs) achieve impressive areal capacitance (≈7–10 mF cm−2) and power and energy densities (≈4 μW cm-2 and ≈0.77 µWh cm−2 at 0.01 mA cm−2). Stability tests conducted over 5000 charge–discharge cycles demonstrate a capacitance retention of ≈80–85%, highlighting the device durability. These LIG-based devices offer versatility, allowing voltage output adjustment through stacked and sandwich MSCs configurations (parallel or series), suitable for various large-scale applications. This study demonstrates that it is possible to create high-quality energy storage devices based on biodegradable materials. This development can lead to progress in renewable energy and off-grid technology, as well as a reduction in electronic waste.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1002/admt.202400261
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Highly Stable Photoluminescence in Vacuum-Processed Halide Perovskite Core–Shell 1D Nanostructures
Castillo-Seoane, J; Contreras-Bernal, L; Rojas, TC; Espinós, JP; Castro-Méndez, AF; Correa-Baena, JP; Barranco, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Borras, AAdvances Functional Materials, 34 (2024) 2403763 DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202403763
Abstract
Hybrid organometal halide perovskites (HP) present exceptional optoelectronic properties, but their poor long-term stability is a major bottleneck for their commercialization. Herein, a solvent-free approach to growing single-crystal organic nanowires (ONW) is presented, along with nanoporous metal oxide scaffolds and HP, to form a core@multishell architecture. The synthesis is carried out under mild vacuum conditions employing thermal evaporation for the metal-free phthalocyanine (H2Pc) nanowires, which are the core, plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) for the TiO2 shell, and co-evaporation of lead iodide (PbI2) and methylammonium iodide (CH3NH3I/MAI) for the CH3NH3PbI3 (MAPbI3/MAPI) perovskite shell. A detailed characterization of the nanostructures by electron microscopy, (S)-TEM, and X-ray diffraction, XRD, is presented, revealing a different crystallization of the HP depending on the template: while the growth on H2Pc nanowires induces the typical MAPI tetragonal structure, a low-dimensional phase (LDP) is observed on the 1D-TiO2 nanotubes. Such a combination yields an unprecedentedly stable photoluminescence emission over 20 h and over 300 h after encapsulation in polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) under different atmospheres including N2, air, and high moisture levels. Moreover, the unique 1D morphology of the system, together with the high refractive index, allows for a strong waveguiding effect along the HP nanowire length.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202403763
Reactividad de Sólidos
Al2O3/Y3Al5O12 (YAG)/ZrO2 composites by single-step powder synthesis and spark plasma sintering
Vakhshouri, M; Najafzadehkhoee, A; Talimian, A; López-Pernia, C; Poyato, R; Gallardo-López, A; Gutiérrez-Mora, F; Prnova, A; Galusek, DJournal of the European Ceramic Societ (2024) DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2024.05.004
Abstract
Alumina-yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG)-zirconia composites are often produced by the melt solidification method. In the present study, we investigated the fabrication of α-Al2O3/Y3Al5O12 (YAG)/ZrO2 composite by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) of powders synthesized by Pechini’s sol-gel method. The ternary composites with homogenous microstructure and high density were produced by SPS at 1300 °C for 15 min. The addition of ZrO2 promoted the sintering of composites, resulting in a higher density and, in turn, higher hardness. A change in the indentation fracture behavior as the result of ZrO2 addition was observed.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2024.05.004
Reactividad de Sólidos
Ultraslow calorimetric studies of the martensitic transformation of NiFeGa alloys: detection and analysis of avalanche phenomena
Martín-Olalla, JM; Vidal-Crespo, A; Romero, FJ; Manchón-Gordón, A; Ipus, JJ; Blázquez, JS; Gallardo, MC; Conde, CFJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 149 (2024) 5165-5176 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-024-13206-4
Abstract
We study the thermal properties of a bulk Ni55Fe19Ga26 Heusler alloy in a conduction calorimeter. At slow heating and cooling rates (∼1Kh-1), we compare as-cast and annealed samples. We report a smaller thermal hysteresis after the thermal treatment due to the stabilization of the 14 M modulated structure in the martensite phase. In ultraslow experiments (40mKh-1), we detect and analyze the calorimetric avalanches associated with the direct and reverse martensitic transformation from cubic to 14 M phase. This reveals a distribution of events characterized by a power law with exponential cutoff p(u)∝u-εexp(-u/ξ) where ε∼2 and damping energies ξ=370μJ (direct) and ξ=27μJ (reverse) that characterize the asymmetry of the transformation.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-024-13206-4
Materiales Coloidales
B-site deficient hexagonal perovskites: Structural stability, ionic order-disorder and electrical properties
Yang, X; Fernández-Carrión, AJ; Geng, X; Kuang, XProgress in Solid State Chemistry, 74 (2024) 100459 DOI: 10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2024.100459
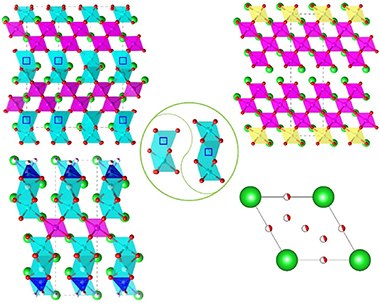
Abstract
This review presents an overview on the structures and electrical properties of B-site deficient hexagonal perovskite oxides, which have been receiving increasing attention as key components as dielectric resonators in microwave telecommunications, as well as solid-state oxide ion and proton conductors in solid oxide fuel cells. The structural evolution and stability, order-disorder of cation and anions, and mechanisms underlying the dielectric and ionic conduction behaviors for the B-site deficient hexagonal perovskites are summarized and the roles of the B-site deficiency on the structural stability and option, ion order-disorder and electrical performance are highlighted. This provides useful guidance for design of new hexagonal perovskite oxide materials and structural control to enhance their electrical properties and discover new functionality as dielectric resonators and solid-state ionic conductors.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2024.100459
Reactividad de Sólidos
Expanding the scope of multiphase-flash sintering: Multi-dogbone configurations and reactive processes
Manchón-Gordón, AF; Molina-Molina, S; Perejón, A; Alcalde-Conejo, A; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; Pérez-Maqueda, LACeramics International, 50 (2024) 25210-25215 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.04.250
Abstract
In this work, we have expanded the possibilities of the multiphase-flash sintering (MPFS) technique by investigating several configurations that involve multiple dogbone specimens (ranging from 1 to 3) and multiple phases (also ranging from 1 to 3). Unlike the traditional MPFS approach using complex 3D or cylindrical samples, this new method allows for a direct comparison with the established conventional flash sintering technique. Our experimental results with dense 8-mol% Yttria-stabilized zirconia demonstrate a significant reduction in the onset temperature as the number of phases and dogbones increases. Building on these findings, we achieved the preparation of pure bulk specimens of SrFe12O19 for the first time through reactive multiphase-flash sintering.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.04.250
Reactividad de Sólidos
Sodium acetate-based thermochemical energy storage with low charging temperature and enhanced power density
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Lizana, J; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; Perejón, A; Vañes-Vallejo, A; Pérez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Energy Storage, 86 (2024) 111310 DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2024.111310
Abstract
The electrification of heat necessitates the development of innovative domestic heat batteries to effectively balance energy demand with renewable power supply. Thermochemical heat storage systems show great promise in supporting the electrification of heating, thanks to their high thermal energy storage density and minimal thermal losses. Among these systems, salt hydrate-based thermochemical systems are particularly appealing. However, they do suffer from slow hydration kinetics in the presence of steam, which limits the achievable power density. Additionally, their relatively high dehydration temperature hinders their application in supporting heating systems. Furthermore, there are still challenges regarding the appropriate thermodynamic, physical, kinetic, chemical, and economic requirements for implementing these systems in heating applications. This study analyzes a proposal for thermochemical energy storage based on the direct hydration of sodium acetate with liquid water. The proposed scheme satisfies numerous requirements for heating applications. By directly adding liquid water to the salt, an unprecedented power density of 5.96 W/g is achieved, nearly two orders of magnitude higher than previously reported for other salt-based systems that utilize steam. Albeit the reactivity drops as a consequence of deliquescence and particle aggregation, it has been shown that this deactivation can be effectively mitigated by incorporating 10 % silica, achieving lower but stable energy and power density values. Furthermore, unlike other salts studied previously, sodium acetate can be fully dehydrated at temperatures within the ideal range for electrified heating systems such as heat pumps (40 °C – 60 °C). The performance of the proposed scheme in terms of dehydration, hydration, and multicyclic behavior is determined through experimental analysis.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2024.111310
Reactividad de Sólidos
Flash Joule Heating-Boro/Carbothermal Reduction (FJH-BCTR): An approach for the instantaneous synthesis of transition metal diborides
Taibi, A; Gil-González, E; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; Perejón, A; Pérez-Maqueda, LACeramics International (2024) DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.01.144
Abstract
Transition metal diborides (TMB2), such as ZrB2 and HfB2, are a class of ultra-high-temperature ceramics (UHTCs) that have attracted considerable attention due to their performance in extreme environments. Their implementation is burdened by the high energetic requirement of traditional synthetic procedures. Here, we report a novel methodology, termed as Flash Joule Heating-Boro/Carbothermal Reduction (FJH-BCTR), for the instantaneous synthesis of phase-pure sub-micron powders of several TMB2 and composite within seconds and without any external source of heating. The immediate synthesis is attributed to the Joule heat generated by the current, enabling extremely fast heating and cooling rates and, therefore, avoiding excessive grain growth. The advantages of FJH-BCTR are thoroughly displayed and can be summarized as; highly efficient, it allows a dramatic drop in terms of energy and time; universal, several TMB2 and composite can be prepared; and flexible, different experimental parameters can be tuned to achieve the desired phase.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.01.144
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effects of ZrO2 crystalline phase on oxygen vacancy of GaZr oxides and their properties for CO2 hydrogenation to light olefins
Meng, F; Gong, Z; Wang, Q; Xing, M; Nawaz, MA; Qiao, Z; Jing, J; Li, W; Li, ZCatalysis Today, 433 (2024) 114661 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2024.114661
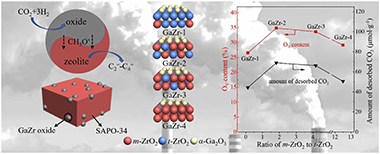
Abstract
A bifunctional catalyst, comprising GaZr oxide and SAPO-34 zeolite, manifests enhanced catalytic activity in CO2 hydrogenation to light olefins; nonetheless, the comprehensive analysis of the pivotal role played by the underlying structure of ZrO2 in Ga-Zr oxide has not been investigated. Herein, different crystalline structures of ZrO2 were prepared by the co-precipitation method and adopted as a support to deposit Ga to obtain ZrO2 with different ratios of monoclinic ZrO2 (m-ZrO2) to tetragonal ZrO2 (t-ZrO2) in GaZr oxides for CO2 hydrogenation to light olefins. Various characterizations demonstrated that the interface between Ga and the mixed phase of (m-t) ZrO2 produces more oxygen vacancies which favors the adsorption and activation of CO2, and the larger specific surface area and stronger H2 adsorption and dissociation capacity promote CO2 conversion. Interestingly, the GaZr oxide with high m-ZrO2 content exhibits superior catalytic activity than the GaZr oxide with high content of t-ZrO2. The highest light olefins yield (9.0%) and selectivity (77.9%) (CO free) with 27.9% CO2 conversion was achieved. In-situ DRIFT spectra further elaborated that the GaZr oxides with different ZrO2 crystalline phases follow the same reaction pathway to hydrogenate CO2 first to HCOO* and then to CH3O* on GaZr oxide surface. While compared with sole ZrO2, the introduction of Ga significantly promotes the hydrogenation of HCOO* to CH3O*, acting as a crucial reaction intermediate that subsequently diffuses into SAPO-34 pores to enhance the desired light olefins selectivity.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2024.114661
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Highly active and selective ZIF-derived cobalt catalyst for methanol conversion to dimethyl carbonate
Wang, LP; Meng, FH; Ding, PF; Nawaz, MA; Li, ZApplied Organometallic Chemistry (2024) e7537 DOI: 10.1002/aoc.7537
Abstract
The oxidative carbonylation of methanol to synthesize dimethyl carbonate (DMC) has been extensively studied over Cu-based catalysts, but the activity and selectivity are not high. The Co catalysts exhibit high DMC selectivity, but the difficulty in recycling homogeneous Co catalyst and the low conversion of heterogeneous Co catalyst limit the application of Co catalysts. Here, the core–shell ZIFs materials were synthesized and carbonized to obtain solid core–shell cobalt catalysts, and then the catalytic performance for methanol conversion to DMC was investigated. The CoNC@NC catalyst, carbonized from Z67@Z8 with Z67 as the core and Z8 as the shell, shows that the carbonized NC shell effectively suppressed the aggregation of Co NPs and the Co NPs were only 15.4 nm, which was much smaller than those of NC@CoNC (34.5 nm) and CoNC (48.1 nm) catalysts. Compared with the CoNC catalyst, CoNC@NC significantly improved the pulse chemisorption of CH3OH and CO, leading to a significant increase in methanol conversion from 6.9% to 17.1%. Furthermore, the deactivation rate of the CoNC@NC catalyst (22.8%) was much lower than that of CoNC (59.4%) after five reaction cycles. The results of this work provide a new strategy for the design and preparation of solid cobalt catalysts for the oxidative carbonylation of methanol to DMC.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1002/aoc.7537
Materiales Semiconductores para la Sostenibilidad
Multifold Enhanced Photon Upconversion in a Composite Annihilator System Sensitized by Perovskite Nanocrystals
Chua, XW; Dai, LJ; Anaya, M; Salway, H; Ruggeri, E; Bi, PQ; Yang, ZH; Stranks, SD; Yang, LACS Nano, 18 (2024) 15229-15238 DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.4c03753
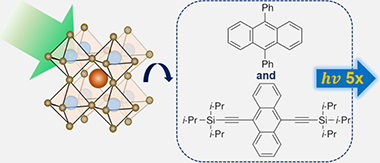
Abstract
Photon upconversion via triplet-triplet annihilation (TTA-UC) provides a pathway to overcoming the thermodynamic efficiency limits in single-junction solar cells by allowing the harvesting of sub-bandgap photons. Here, we use mixed halide perovskite nanocrystals (CsPbX3, X = Br/I) as triplet sensitizers, with excitation transfer to 9,10-diphenylanthracene (DPA) and/or 9,10-bis[(triisopropylsilyl)ethynyl]anthracene (TIPS-An) which act as the triplet annihilators. We observe that the upconversion efficiency is five times higher with the combination of both annihilators in a composite system compared to the sum of the individual single-acceptor systems. Our work illustrates the importance of using a composite system of annihilators to enhance TTA upconversion, demonstrated in a perovskite-sensitized system, with promise for a range of potential applications in light-harvesting, biomedical imaging, biosensing, therapeutics, and photocatalysis.
Mayo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.4c03753
Unlocking archaeological data online via the PEPAdb (Prehistoric Europe’s Personal Adornment Database) initiative for Open Science
Romero-García, G; Sánchez-Gómez, D; Garrido-Cordero, JA; Martínez-Blanes, JM; Sousa, AC; Odriozola, PAntiquity, 98 (2024) 398 DOI: 10.15184/aqy.2024.2
Abstract
PEPAdb (Prehistoric Europe's Personal Adornment Database) is a long-term, open-ended project that aims to improve access to archaeological data online. Its website (https://pepadb.us.es) publishes and analyses datasets about prehistoric personal adornment, drawing on the results of various research projects and bibliographic references.
Abril, 2024 · DOI: 10.15184/aqy.2024.2
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
H2 production based on a ternary mixture of commercial CuO-NiO-TiO2 in a solar pilot plant
Villachica-Llamosas, JG; Ruiz-Aguirre, A; Colón, G; Peral, J; Malato, SCatalysis Today, 431 (2024) 114608 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2024.114608
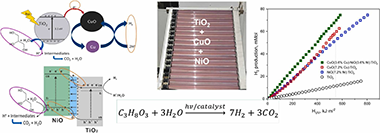
Abstract
Glycerol is a by-product in biodiesel production (in the range of g·L−1), so its photoreforming by photocatalysis is a way of valorising it. TiO2 in photocatalysis has been widely studied, although its efficiency is limited by the high energy band gap, and the electron-hole recombination. Its combination with different semiconductors should improve charge separation, extending also the absorption from UV to visible light. Cu and Ni oxides are two of the most efficient low-cost transition metal oxide catalysts. Experiments were carried out in a 25 L pilot plant connected to a compound parabolic solar collector. Different combinations of the three semiconductors, based on the concentration of each metal on TiO2 (Me, 5%, 7.2% and 10%) were evaluated. Evonik P25-TiO2, CuO and NiO were combined by mechanical mixing. Hydrogen was quantified by a micro gas chromatograph, and copper and nickel leaching by ICP-MS. The best hydrogen production (0.060 mMol kJ−1) was attained with a proportion of 10:1 of TiO2:MeO, that corresponds to a total metal concentration of 7.2 wt%, being Cu and Ni in the same proportion. Metal content in solution increased as the reaction progressed, but Ni lixiviation of <0.012 mg L−1 was not significant. Significant Cu leaching (>1 mg L−1) was observed. This article presents novel results, in a solar pilot plant, for determining which ternary mixture can give better results, as well as metal leaching into water. Handling relevant volume of water in anoxic conditions can help to understand the application of this technology for the production of hydrogen.
Abril, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2024.114608
Reactividad de Sólidos
Magnesium calcites for CO2 capture and thermochemical energy storage using the calcium-looping process
Perejón, A; Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; Diánez, MJ; Pérez-Maqueda, LAEnvironmental Research, 246 (2024) 118119 DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118119
Abstract
In this study, a precipitation-based synthesis method has been employed to prepare magnesium calcites with the general formula Ca1-xMgxCO3, with the objective of use them in the calcium looping (CaL) process for CO2 capture (CaL-CCS) and thermochemical energy storage (CaL-CSP). The structure and microstructure of the samples have been characterized. It has been found by X-ray diffraction that the samples with a Ca:Mg molar ratio of 0.5:0.5 and 0.55:0.45 are phase pure, while the samples with molar ratios of 0.7:0.3 and 0.8:0.2 are composed by two phases with different stoichiometry. In addition, the sample prepared with calcium alone shows the aragonite phase. The microstructure of the magnesium-containing samples is composed of nanocrystals, which are aggregated in spherical particles whereas the aragonite sample presents a typical rod-like morphology. The multicycle tests carried out under CaL-CCS conditions show that an increase on the MgO content in the calcined samples results in a reduced value of effective conversion when compared to aragonite. On the other hand, under CaL-CSP conditions, the samples with the higher MgO content exhibit nearly stable effective conversion values around 0.5 after 20 cycles, which improve the results obtained for aragonite and those reported for natural dolomite tested under the same conditions.
Abril, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118119
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
MoS2 2D materials induce spinal cord neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity affecting locomotor performance in zebrafish
Di Mauro, G; González, VJ; Bambini, F; Camarda, S; Prado, E; Holgado, JP, Vázquez, E; Ballerini, L; Cellot, GNanoscale Horizons, 9(5)(2024) 785-798 DOI: 10.1039/d4nh00041b
Abstract
MoS2 nanosheets belong to an emerging family of nanomaterials named bidimensional transition metal dichalcogenides (2D TMDCs). The use of such promising materials, featuring outstanding chemical and physical properties, is expected to increase in several fields of science and technology, with an enhanced risk of environmental dispersion and associated wildlife and human exposures. In this framework, the assessment of MoS2 nanosheets toxicity is instrumental to safe industrial developments. Currently, the impact of the nanomaterial on the nervous tissue is unexplored. In this work, we use as in vivo experimental model the early-stage zebrafish, to investigate whether mechano-chemically exfoliated MoS2 nanosheets reach and affect, when added in the behavioral ambient, the nervous system. By high throughput screening of zebrafish larvae locomotor behavioral changes upon exposure to MoS2 nanosheets and whole organism live imaging of spinal neuronal and glial cell calcium activity, we report that sub-acute and prolonged ambient exposures to MoS2 nanosheets elicit locomotor abnormalities, dependent on dose and observation time. While 25 μg mL−1 concentration treatments exerted transient effects, 50 μg mL−1 ones induced long-lasting changes, correlated to neuroinflammation-driven alterations in the spinal cord, such as astrogliosis, glial intracellular calcium dysregulation, neuronal hyperactivity and motor axons retraction. By combining integrated technological approaches to zebrafish, we described that MoS2 2D nanomaterials can reach, upon water (i.e. ambient) exposure, the nervous system of larvae, resulting in a direct neurological damage.
Abril, 2024 · DOI: 10.1039/d4nh00041b
Materiales Avanzados
Preparation of Geopolymeric Materials from Industrial Kaolins, with Variable Kaolinite Content and Alkali Silicates Precursors
Martínez-Martínez, S; Bouguermouh, K; Bouzidi, N; Mahtout, L; Sánchez-Soto, PJ; Pérez-Villarejo, LMaterials, 17 (2024) 1839 DOI: 10.3390/ma17081839
Abstract
In the present work, the development of geopolymeric materials with Na or K based on industrial kaolin samples, with variable kaolinite content and alkaline silicates, is studied. XRF, XRD, FTIR and SEM-EDS have been used as characterization techniques. Three ceramic kaolin samples, two from Algeria and one from Charente (France), have been considered. In particular, chemical and mineralogical characterization revealed elements distinct of Si and Al, and the content of pure kaolinite and secondary minerals. Metakaolinite was obtained by grinding and sieving raw kaolin at 80 mu m and then by thermal activation at 750 degrees C for 1 h. This metakaolinite has been used as a base raw material to obtain geopolymers, using for this purpose different formulations of alkaline silicates with NaOH or KOH and variable Si/K molar ratios. The formation of geopolymeric materials by hydroxylation and polycondensation characterized with different Si/Al molar ratios, depending on the original metakaolinite content, has been demonstrated. Sodium carbonates have been detected by XRD and FTIR, and confirmed by SEM-EDS, in two of these geopolymer materials being products of NaOH carbonation.
Abril, 2024 · DOI: 10.3390/ma17081839
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Exciton-carrier coupling in a metal halide perovskite nanocrystal assembly probed by two-dimensional coherent spectroscopy
Rojas-Gatjens, E; Tiede, DO; Koch, KA; Romero-Perez, C; Galisteo-López, JF; Calvo, ME; Míguez, H; Kandada, ARSJournal of Physics-Materials, 7 (2024) 025002 DOI: 10.1088/2515-7639/ad229a
Abstract
The surface chemistry and inter-connectivity within perovskite nanocrystals play a critical role in determining the electronic interactions. They manifest in the Coulomb screening of electron-hole correlations and the carrier relaxation dynamics, among other many-body processes. Here, we characterize the coupling between the exciton and free carrier states close to the band-edge in a ligand-free formamidinium lead bromide nanocrystal assembly via two-dimensional coherent spectroscopy. The optical signatures observed in this work show: (i) a nonlinear spectral lineshape reminiscent of Fano-like interference that evidences the coupling between discrete electronic states and a continuum, (ii) symmetric excited state absorption cross-peaks that suggest the existence of a coupled exciton-carrier excited state, and (iii) ultrafast carrier thermalization and exciton formation. Our results highlight the presence of coherent coupling between exciton and free carriers, particularly in the sub-100 femtosecond timescales.
Abril, 2024 · DOI: 10.1088/2515-7639/ad229a
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Direct Laser Writing: From Materials Synthesis and Conversion to Electronic Device Processing
Pinheiro, T; Morais, M; Silvestre, S; Carlos, E; Coelho, J; Almeida, HV; Barquinha, P; Fortunato, E; Martins, RAdvanced Materials, 36 (2024) 26 DOI: 10.1002/adma.202402014
Abstract
Direct Laser Writing (DLW) has been increasingly selected as a microfabrication route for efficient, cost-effective, high-resolution material synthesis and conversion. Concurrently, lasers participate in the patterning and assembly of functional geometries in several fields of application, of which electronics stand out. In this review, recent advances and strategies based on DLW for electronics microfabrication are surveyed and outlined, based on laser material growth strategies. First, the main DLW parameters influencing material synthesis and transformation mechanisms are summarized, aimed at selective, tailored writing of conductive and semiconducting materials. Additive and transformative DLW processing mechanisms are discussed, to open space to explore several categories of materials directly synthesized or transformed for electronics microfabrication. These include metallic conductors, metal oxides, transition metal chalcogenides and carbides, laser-induced graphene, and their mixtures. By accessing a wide range of material types, DLW-based electronic applications are explored, including processing components, energy harvesting and storage, sensing, and bioelectronics. The expanded capability of lasers to participate in multiple fabrication steps at different implementation levels, from material engineering to device processing, indicates their future applicability to next-generation electronics, where more accessible, green microfabrication approaches integrate lasers as comprehensive tools.
This review covers recent progress and breakthroughs in direct laser writing for multimaterial synthesis and conversion, toward processing and fabrication of electronics. Predominant laser-material processing mechanisms for the writing of conductive and semiconductive materials are discussed, alongside important considerations on laser operation and implementation for both rigid and flexible electronics, including microelectronics, energy harvesting and storage, sensors, and bioelectronics. image
Abril, 2024 · DOI: 10.1002/adma.202402014
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Reforming of biomass-derived producer gas using toluene as model tar: Deactivation and regeneration studies in Ni and K-Ni catalysts
Azancot, L; González-Castaño, M; Bobadilla, LF; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAEnvironmental Research, 247 (2024) 118210 DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118210
Abstract
Within the syngas production from biomass gasification, tar removal constitutes a chief issue to overcome for advanced catalytic systems. This work investigates the performance of Ni and Ni-K catalysts for reforming of derived-biomass producer gas using toluene as model tar. At 750 degrees C and 60Lg(-1)h(-1), the stability test (70 h) revealed stable performances (CO2, CH4 and C7H8 conversions of 60, 95 and 100%, correspondingly) uniquely for the Ni-K catalyst. Although the efficient protection towards coking let by K was demonstrated, TPO studies over the post-reacted systems still evidenced the presence of carbon deposits for both samples. Conducting three successive reaction/regeneration cycles with different gasifying agents (air, steam and CO2) at 800 C for 1h, the capability towards regeneration of both catalytic systems was assessed and the spent catalysts were characterized by XRD, SEM and TEM. While none of the regeneration treatments recovered the performance of the unpromoted catalyst, the Ni-K catalysts demonstrated the capability of being fully regenerated by air and CO2 and exhibited analogous catalytic performances after a series of reaction/regeneration cycles. Hence, it is proved that the addition of K into Ni catalysts not only enhances the resistance against deactivation but enables rather facile regenerative procedures under certain atmospheres (air and CO2).
Abril, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118210
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Levulinic to succinic acid transformation over Ru based catalysts
Arriaga-Arellano, LA; Alvarez-Hernandez, D; Dominguez, MI; Martínez Tejada, M; Penkova, A; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MANext Materials, 3 (2024) 100059. DOI: 10.1016/j.nxmate.2023.100059
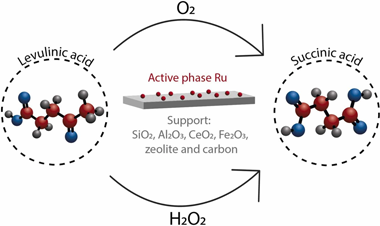
Abstract
In this work ruthenium based catalysts are tested as catalytic systems for the selective oxidation of levulinic to succinic acid. Very different in nature supports have been chosen in order to elucidate the effect of their textural and acidic properties on the final catalytic activity. The influence of Ru particle size is also discussed and proposed as one of the key factors. Medium range ruthenium particles supported on relatively acid supports are the best performing systems in terms of succinic acid yield, while the most active catalysts in terms of conversion result in important carbon loss due to reagent/products full oxidation.
Abril, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.nxmate.2023.100059
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Synergistic Effect of He for the Fabrication of Ne and Ar Gas-Charged Silicon Thin Films as Solid Targets for Spectroscopic Studies
Fernández, A; Godinho, V; Ávila, J; Jiménez de Haro, MC; Hufschmidt, D; López-Viejobueno, J; Almanza-Vergara, GE; Ferrer, FJ; Colaux, JL; Lucas, S; Asensio, MCNanomaterials, 14(8) (2024) 727 DOI: 10.3390/nano14080727
Abstract
Sputtering of silicon in a He magnetron discharge (MS) has been reported as a bottom-up procedure to obtain He-charged silicon films (i.e., He nanobubbles encapsulated in a silicon matrix). The incorporation of heavier noble gases is demonstrated in this work with a synergistic effect, producing increased Ne and Ar incorporations when using He–Ne and He–Ar gas mixtures in the MS process. Microstructural and chemical characterizations are reported using ion beam analysis (IBA) and scanning and transmission electron microscopies (SEM and TEM). In addition to gas incorporation, He promotes the formation of larger nanobubbles. In the case of Ne, high-resolution X-ray photoelectron and absorption spectroscopies (XPS and XAS) are reported, with remarkable dependence of the Ne 1s photoemission and the Ne K-edge absorption on the nanobubble’s size and composition. The gas (He, Ne and Ar)-charged thin films are proposed as “solid” targets for the characterization of spectroscopic properties of noble gases in a confined state without the need for cryogenics or high-pressure anvils devices. Also, their use as targets for nuclear reaction studies is foreseen.
Abril, 2024 · DOI: 10.3390/nano14080727
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Long-lasting low fluorinated stainless steel hierarchical surfaces for omniphobic, anti-fouling and anti-icing applications
Montes, L; Rico, V; Nuñez-Galvez, F; Arenas, MA; del Campo, AC; Lopez-Flores, V; Espinós, JP; Borrás, A; González-Elipe, AR; López-Santos, CSurfaces and Interfaces, 46 (2024) 104167 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfin.2024.104167

Abstract
Stainless steel (SS) alloys are prevalent in many industries, household appliances or other commodities, where a strict control of surface properties is required to tailor their interaction with the environment. In this work we report a new procedure of stainless steel surface processing that provides a multifunctional response including superhydrophobicity, omniphobicity, self-cleaning, anti-fouling and effective anti-icing capacity, while still preserving a corrosion resistance similar to that of this material in compact form. The method consists of a first nanostructuration step followed by a low fluorination. The nanostructured surfaces presented a dual scale roughness of hierarchical character. The liquid free approach developed in this work to get this singular surface nanostructuration entails a first laser treatment of stainless steel flat substrates, followed by the deposition of a nanostructured thin layer of this material by electron beam evaporation in an oblique angle configuration. The resulting hierarchical surfaces were subjected to fluorination by: (i) the plasma-assisted deposition of a thin Teflon-like coating or (ii) the grafting of fluorinated molecules. The self-cleanable, anti-adherent and ice repellent character of the resulting low fluorinated surfaces outperformed the behaviour of classical slippery surfaces obtained by the infusion of high amounts of fluorinated liquids. These hierarchical SS surfaces withstood mild abrasion tests and the effect of water jets. Moreover, the corrosion behaviour of the fluorinated surfaces determined through their potentiodynamic analysis revealed a similar corrosion resistance than the flat SS substrates. Outstandingly, after these corrosion tests, the fluorinated samples obtained by grafting preserved their surface functionalities without significant degradation. The high mechanical and chemical stability of these low fluorinated samples support their usage for a large variety of applications.
Marzo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfin.2024.104167
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
NiFeO/NiFe bilayer electrocatalyst for an efficient urea assisted water electrolysis
Gómez-Sacedon, C; López-Fernández, E; González-Elipe, AR; Espinós, JP; Yubero, F; Gil-Rostra, J; de Lucas-Consuegra, AInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 59 (2024) 604-613 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.02.079
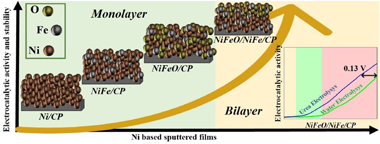
Abstract
In this work a set of mono- and bi-layered nanostructured Ni-Fe electrocatalysts prepared by magnetron sputtering deposition in an oblique angle configuration have been tested as anodes for urea assisted water electrolysis. In a three -electrode cell, it was found that an oxide/metal bilayer outperforms single metal or oxide layer configurations for the urea electro-oxidation. It is also found that the incorporation of Fe within the Ni structure stabilizes the electrodes likely because it produces a decrease in the surface poisoning of the electrocatalyst. The improved performance observed for the oxide/metal bilayer configuration has been attributed to a synergetic effect between the active (oxy)hydroxide Ni-Fe catalytic species at the outer layers and a high electrical conductivity through the underlying metallic layer. The bilayer electrocatalyst tested in an anion exchange membrane water electrolyser showed an overpotential decrease of 0.13 V when comparing urea oxidation vs. pure water electrolysis. Results prove a synergetic effect between the hydrogen production through water electrolysis and the removal of organic pollutants in water.
Marzo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.02.079
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Optimising anode supported BaZr1-xYxO3-δ electrolytes for solid oxide fuel cells: Microstructure, phase evolution and residual stresses analysis
Fernández Muñoz, S; Chacartegui, R; Alba, MD; Ramírez Rico, JJournal of Power Sources, 596 (2024) 234070 DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2024.234070
Abstract
Yttrium-doped BaZrO3 is a promising electrolyte for intermediate-temperature protonic ceramic fuel cells. In the anode-supported configuration, a slurry containing the electrolyte is deposited on the surface of a calcined porous anode and sintered. Differences in sintering behaviour and thermal expansion coefficients for the anode and electrolyte result in elastic residual stresses that can impact the long-term stability of the cell during cyclic operation. Half-cells using BaZr0.8Y0.2O3-δ as the electrolyte were fabricated using the solid-state reaction sintering method under various sintering conditions. Comprehensive microstructure and residual stress analyses as a function of processing parameters were performed using two-dimensional X-ray diffraction, Rietveld refinement, and scanning electron microscopy, before and after the half-cells were reduced under hydrogen, giving a complete picture of phase, microstructure, and stress evolution under thermal and reduction cycles like the actual operation of the cell. Our results reveal that a temperature of 1400 °C and shorter soaking times might be advantageous for obtaining phase-pure and thin yttrium-doped BaZrO3 electrolytes with improved microstructure and the presence of compressive residual stress. These findings offer valuable insights into optimising the fabrication process of BaZrO3-based electrolytes, leading to enhanced performance and long-term stability of anode-supported protonic ceramic fuel cells operating at intermediate temperatures.
Marzo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2024.234070
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Highly Effective Non-Noble MnO2 Catalysts for 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Oxidation to 2,5-Furandicarboxylic Acid
Alvarez-Hernández, D; Megías-Sayago, C; Penkova, A; Centeno, MA; Ivanova, SChemsuschem, 17 (2024) e202400115 DOI: 10.1002/cssc.202400115
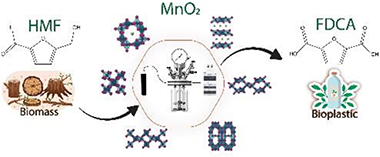
Abstract
Noble metal-free catalyst or catalytic oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid are proposed in this study as a proposal to solve one of the great disadvantages of this reaction of using preferably noble metal-based catalysts. The catalytic activity of six MnO2 crystal structures is studied as alternative. The obtained results showed a strong connection between catalytic activity the type of MnO2 structure organization and redox behavior. Among all tested catalysts, epsilon-MnO2 showed the best performance with an excellent yield of 74 % of 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid at full -hydroxymethylfurfural conversion.
Marzo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1002/cssc.202400115
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
A profitability study for catalytic ammonia production from renewable landfill biogas: Charting a route for the next generation of green ammonia
González-Arias, J; Nawaz, MA; Vidal-Barrero, F; Reina, TRFuel, 360 (2024) 130584 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.130584
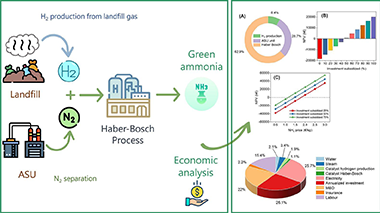
Abstract
This study introduces a novel techno-economic approach to renewable ammonia production using landfill biogas. The proposed process involves bio-hydrogen generation from landfill biogas, nitrogen production via air separation, and the Haber-Bosch process. Building on our prior research, which demonstrated the economic competitiveness of renewable hydrogen production from landfill gas, we extend our investigation to analyze the feasibility of producing renewable ammonia from biogas-derived bio-hydrogen. However, the economic analysis for the baseline scenario reveals the current lack of profitability (net present value of −18.3 M€), with ammonia prices needing to quadruple to achieve profitability. Major costs, including investment, maintenance, overhead expenses, and electricity, collectively account for over 70%, suggesting the potential efficacy of investment subsidies as a political tool. Only cases with subsidies exceeding 50% of total investment costs, under current ammonia market prices, would render the green ammonia route profitable. Our findings underscore the significant techno-economic challenges in realizing renewable ammonia production, emphasizing the need for innovation in process engineering and catalytic technologies to enable competitive and scalable green ammonia production.
Marzo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.130584
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Revalorization of Yerba Mate Residues: Biopolymers-Based Films of Dual Wettability as Potential Mulching Materials
Sánchez, LM; De Haro, J; Domínguez, E; Rodríguez, A; Heredia, A; Benítez, JJPolymers, 16 (2024) 815 DOI: 10.3390/polym16060815
Abstract
Biodegradable mulching films are a very attractive solution to agronomical practices intended to achieve more successful crop results. And, in this context, the employment of agricultural and industrial food residues as starting material for their production is an alternative with economic and environmental advantages. This work reports the preparation of bilayer films having two different wettability characteristics from three bio-derived biopolymers: TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers isolated from infused Yerba Mate residues, Chitosan and Polylactic acid. The infused Yerba Mate residues, the isolated and oxidized cellulose nanofibers, and the films were characterized. Nanofibrillation yield, optical transmittance, cationic demand, carboxyl content, intrinsic viscosity, degree of polymerization, specific surface area and length were studied for the (ligno)cellulose nanofibers. Textural and chemical analysis, thermal and mechanical properties studies, as well as water and light interactions were included in the characterization of the films. The bilayer films are promising materials to be used as mulching films.
Marzo, 2024 · DOI: 10.3390/polym16060815
Reactividad de Sólidos
A generalized interface reaction kinetic model for describing heterogeneous processes driven by contracting mechanisms
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; Rodríguez-Laguna, MR; Perejón, AJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 149(6) (2024) 2653-2663 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-023-12835-5
Abstract
The correct determination of the kinetic model and the kinetic parameters that describe a heterogeneous process is key to accurately predicting its progress within a wide range of conditions, which is one of the main purposes of kinetic analysis. Albeit ideal kinetic models continue to be used to gain insight about the process mechanism, they are constrained by certain assumptions that are rarely met in real experiments and limit their applicability. This is the case of contracting (or interface) kinetic models, which are one of the most commonly used. Thus, the ideal kinetic model R2 is derived by assuming a cylindrical contraction in the radial direction but not contemplating the possibility of a contraction in the direction of the axis of the cylinder. Moreover, in the case of the ideal model R3, it is assumed that contraction takes place simultaneously in particles of identical dimensions in all three directions of space (spheres or cubes). Here, it is revisited this type of model, and it is considered the contraction of particles with different geometries, namely cylinders with different aspect ratios and rectangular cuboids. Besides, a novel generalized interface reaction model is proposed, which covers all the studied cases and broadens the range of applicability to more complex situations involving different geometries and inhomogeneous particle sizes. Finally, the proposed model is applied to the analysis of the experimental thermal dissociation of ammonium nitrate, previously described in the literature as a sublimation process. It is proved that the novel kinetic model provides a more accurate description of the kinetics of the reaction and better prediction capabilities.
Marzo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-023-12835-5
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Surface Defect Engineered Nano-Cu/TiO2 Photocatalysts for Hydrogen Production
Liccardo, L; Moras, P; Shewerdyaeva, PM; Vomiero, A; Caballero, A; Colón, G; Moretti, EAdvanced Sustainable Systems, 8(3) (2024) 2300418 DOI: 10.1002/adsu.202300418
Abstract
Surface defects engineered nano-Cu/TiO2 photocatalysts are synthesized through an easy and cost-effective microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis, mixing commercial P25 titania (TiO2) and oxalic acid (Ox), followed by 2.0 wt% Cu co-catalyst (labeled as Cu2.0) loading through in situ photodeposition during reaction. The hydrothermal treatment does not affect the catalyst crystalline structure, morphology, nor the surface area. However, depending on the Ox/TiO2 molar ratio used an influence on the optical properties and on the reactivity of the system is detected. The presence of surface defects leads to intraband states formation between valence band and conduction band of bare titania, inducing an important enhancement in the photoactivity. Thus, Cu2.0/gOx/P25 200 (where g is the weight of Ox and 200 the temperature in Celsius degrees used during the synthesis) have been successfully tested as efficient photocatalysts for hydrogen production through methanol (MeOH) reforming under UV light in a MeOH/ H2O solution (10% v/v) by fluxing the system with N2, showing an increased reactivity compared to the bare Cu2.0/P25 system.
Marzo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1002/adsu.202300418
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Developing and understanding Leaching-Resistant cobalt nanoparticles via N/P incorporation for liquid phase hydroformylation
Galdeano-Ruano, C; Gutiérrez-Tarriño, S; Lopes, CW; Mazarío, J; Chinchilla, LE; Agostini, G; Calvino, JJ; Holgado, JP; Rodriguez-Castellón, E; Roldan, A; Oña-Burgos, PJournal of Catalysis, 431 (2024) 115374 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2024.115374
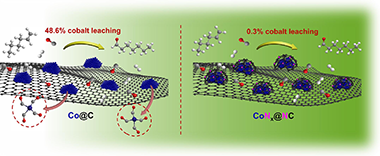
Abstract
The ultimate target in heterogeneous catalysis is the achievement of robust, resilient and highly efficient materials capable of resisting industrial reaction conditions. Pursuing that goal in liquid -phase hydroformylation poses a unique challenge due to carbon monoxide -induced metal carbonyl species formation, which is directly related to the formation of active homogeneous catalysts by metal leaching. Herein, supported heteroatomincorporated (P and N) Co nanoparticles were developed to enhance the resistance compared with bare Co nanoparticles. The samples underwent characterization using operando XPS, XAS and HR electron microscopy. Overall, P- and N -doped catalysts increased reusability and suppressed leaching. Among the studied catalysts, the one with N as a dopant, CoNx@NC, presents excellent catalytic results for a Co -based catalyst, with a 94% conversion and a selectivity to aldehydes of 80% in only 7.5 h. Even under milder conditions, this catalyst outperformed existing benchmarks in Turnover Numbers (TON) and productivity. In addition, computational simulations provided atomistic insights, shedding light on the remarkable resistance of small Co clusters interacting with N -doped carbon patches.
Marzo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2024.115374
Materiales Avanzados
Effect of olive-pruning fibres as reinforcements of alkali-activated cements based on electric arc furnace slag and biomass bottom ash
Gómez-Casero, MA; Sánchez-Soto, PJ; Castro, E; Eliche-Quesada, DArchives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 24(2) (2024) 84 DOI: 10.1007/s43452-024-00882-0
Abstract
In this work, alkali-activated composites using electric arc furnace slag (50 wt%) and biomass bottom ash (50 wt%) were manufactured, adding olive-pruning fibres as reinforcement. The objective of adding fibres is to improve the flexural strength of composites, as well as to prevent the expansion of cracks as a result of shrinkage. For this reason, composites reinforced with olive-pruning fibres (0.5-2 wt%) untreated and treated with three different solutions to improve matrix-fibre adhesion were manufactured. Treatments developed over fibres were a 10 wt% Na2SiO3 solution, 3 wt% CaCl2 solution and 5 wt% NaOH solution. Mechanical properties, physical properties, thermal properties and the microstructure of composites by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were studied to demonstrate the improvement. Alkaline treatment degraded fibre surface, increasing the matrix-fibre adhesion, and as a consequence, flexural strength increased up to 20% at 90 days of curing. Optimal results were obtained with composites reinforced with 1 wt% of olive-pruning fibre treated by a 10 wt% Na2SiO3 solution. Higher quantity of olive-pruning fibre leads to local agglomeration, which weakens the matrix-fibre adhesion. The effect on the compressive strength is less evident, since the addition of fibres produces an admissible decrease (between 0 and 9% using 0.5 or 1 wt% of fibres), except in composites that use olive pruning treated with 10 wt% Na2SiO3 solution, where values remain stable, similar or better to control paste. A greater ductility of the matrix in all composites was observed. Furthermore, the alkali-activated cement matrix was bonded to olive-pruning fibre better than untreated fibre, as it is shown in SEM images. Thus, the results showed that olive-pruning fibres could be used as reinforcement in the manufacturing of alkali-activated materials when they are treated with alkali solutions.
Marzo, 2024 · DOI: 10.1007/s43452-024-00882-0
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Insights into the physicochemical properties of Sugar Scum as a sustainable biosorbent derived from sugar refinery waste for efficient cationic dye removal
F. Atmani, M.M. Kaci, N. Yeddou-Mezenner, A. Soukeur, I. Akkari, J.A. NavíoBiomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 14 (2024) 4843-4857 DOI: 10.1007/s13399-022-02646-3
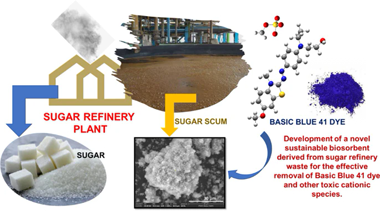
Abstract
The objective of this study was to determine the ability of sugar scum (SS), an industrial waste, as a novel biosorbent for the removal of Basic Blue 41 (BB 41) from aqueous solutions. The biosorbent was characterized by SEM/EDS, BET, FTIR, and pHpzc measurements, respectively. To reach a maximum adsorption capacity of 26.45 mg.g–1, impacting operational factors such as pH, biosorbent dose, contact duration, starting dye concentration, and temperature were adjusted, when the removal efficiency reached 84% during 60 min at pH 10, 1.5 g.L–1 of biosorbent and Co = 10 mg.L–1. The experimental data were modeled by various isotherm models, whereas the best fit was found for Freundlich with a high correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.991). Other kinetic models including pseudo-first, pseudo-second order, and intra-particle diffusion models were tested to fit the kinetic data. The biosorption of BB 41 onto SS was spontaneous (∆G° < 0) and exothermic (∆H° < 0), while the biosoprtion mechanism of BB41 over SS was proposed with repeated reuse showing that SS could be regenerated after four successive runs. Furthermore, this study revealed that sugar scum is an underutilized bioresource in Algeria, with the potential to provide low-cost environmental removal of additional contaminants in the wastewater treatment domain.
Febrero, 2024 · DOI: 10.1007/s13399-022-02646-3
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Synthesis and Characterization of Multilayered CrAlN/Al2O3 Tandem Coating Using HiPIMS for Solar Selective Applications at High Temperature
Sánchez-Pérez, M; Rojas, TR; Reyes, DF; Ferrer, FJ; Farchado, M; Morales, A; Escobar-Galindo, R; Sánchez-López, JCACS Applied Energy Materials, 7 (2024) 438-449 DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.3c02310
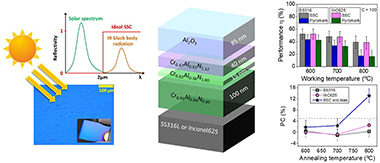
Abstract
The effect of applying a negative bias during deposition of a previously designed multilayer solar selective absorber coating was studied on two types of substrates (316L stainless steel and Inconel 625). The solar selective coating is composed of different chromium aluminum nitride layers deposited using a combination of radiofrequency (RF), direct current (DC), and high-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) technologies. The chemical composition is varied to generate an infrared reflective/absorber layer (with low Al addition and N vacancies) and two CrAlN intermediate layers with medium and high aluminum content (Al/Cr = 0.6 and 1.2). A top aluminum oxide layer (Al2O3) is deposited as an antireflective layer. In this work, a simultaneous DC-pulsed bias (−100 V, 250 kHz) was applied to the substrates in order to increase the film density. The optical performance, thermal stability, and oxidation resistance was evaluated and compared with the performance obtained with similar unbiased coating and a commercial Pyromark paint reference at 600, 700, and 800 °C. The coating remained stable after 200 h of annealing at 600 °C, with solar absorptance (α) values of 93% and 92% for samples deposited on stainless steel and Inconel, respectively, and a thermal emittance ε25°C of 18%. The introduction of additional ion bombardment during film growth through bias assistance resulted in increased durability, thermal stability, and working temperature limits compared with unbiased coatings. The solar-to-mechanical energy conversion efficiency at 800 °C was found to be up to 2 times higher than Pyromark at C = 100 and comparable at C = 1000.
Febrero, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.3c02310
Materiales Avanzados
Synthesis and characterization of porous and photocatalytic geopolymers based on natural clay: Enhanced properties and efficient Rhodamine B decomposition
Ettahiri, Y; Bouna, L: Brahim, A; Benlhachemi, A; Bakiz, B; Sánchez-Soto, PJ; Eliche-Quesada, D; Pérez-Villarejo, LApplied Materials Today, 36 (2024) 102048 DOI: 10.1016/j.apmt.2023.102048
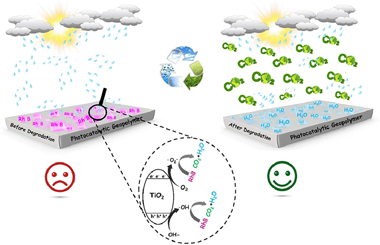
Abstract
In this work, the incorporation of anatase TiO2 semiconductor in the geopolymer matrix as catalytic materials has been studied. The most noteworthy results obtained from the synthesis of a novel TiO2/geopolymer nanocomposite as an effective ecological catalyst with high thermal stability and significant porosity is presented. The porous and photocatalytic geopolymers based natural clay rich in pyrophyllite and kaolinite minerals were prepared by simple method, the geopolymerization reaction was able to successfully load TiO2 nanoparticles into the geopolymer surface. Furthermore, the results indicate that the prepared catalyst achieved the best performance to degrade Rhodamine B (RhB) molecules present in aqueous solution under UV light irradiation. The geopolymer matrix proved to be a reusable support for TiO2 nanoparticles during the photocatalytic process, efficiently facilitating the separation of photogenerated charges. Finally, the physicochemical and morphological properties of the samples was characterized by several techniques, namely X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Thermogravimetric and Differential Thermal Analysis (TGA/DTA), N2 adsorption/desorption isotherm analysis (BET and BJH methods), UV–Vis Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy (DRS), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) coupled to an Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) analyzer and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM).
Febrero, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apmt.2023.102048
Materiales Semiconductores para la Sostenibilidad
Synergetic Near- and Far-Field Plasmonic Effects for Optimal All-Perovskite Tandem Solar Cells with Maximized Infrared Absorption
Bueno, J; Carretero Palacios, S; Anaya, MJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 15(9) (2024) 2632-2638 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c00194
Abstract
The efficiency and reliability of perovskite solar cells have rapidly increased in conjunction with the proposition of advanced single-junction and multi-junction designs that allow light harvesting to be maximized. However, Sn-based compositions required for optimized all-perovskite tandem devices have reduced absorption coefficients, as opposed to pure Pb perovskites. To overcome this, we investigate near- and far-field plasmonic effects to locally enhance the light absorption of infrared photons. Through optimization of the metal type, particle size, and volume concentration, we maximize effective light harvesting while minimizing parasitic absorption in all-perovskite tandem devices. Interestingly, incorporating 240 nm silver particles into the Pb-Sn perovskite layer with a volume concentration of 3.1% indicates an absolute power conversion efficiency enhancement of 2% in the tandem system. We present a promising avenue for experimentalists to realize ultrathin all-perovskite tandem devices with optimized charge carrier collection, diminishing the weight and the use of Pb.
Febrero, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c00194
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
New Nano-Crystalline Hydroxyapatite-Polycarboxy/Sulfo Betaine Hybrid Materials: Synthesis and Characterization
Díaz-Cuenca, A; Sezanova, K; Gergulova, R; Rabadjieva, D; Ruseva, KMolecules, 29(5) (2024) 930 DOI: 10.3390/molecules29050930
Abstract
Hybrid materials based on calcium phosphates and synthetic polymers can potentially be used for caries protection due to their similarity to hard tissues in terms of composition, structure and a number of properties. This study is focused on the biomimetic synthesis of hybrid materials consisting of hydroxiapatite and the zwitterionic polymers polysulfobetaine (PSB) and polycarboxybetaine (PCB) using controlled media conditions with a constant pH of 8.0–8.2 and Ca/P = 1.67. The results show that pH control is a dominant factor in the crystal phase formation, so nano-crystalline hydroxyapatite with a Ca/P ratio of 1.63–1.71 was observed as the mineral phase in all the materials prepared. The final polymer content measured for the synthesized hybrid materials was 48–52%. The polymer type affects the final microstructure, and the mineral particle size is thinner and smaller in the synthesis performed using PCB than using PSB. The final intermolecular interaction of the nano-crystallized hydroxyapatite was demonstrated to be stronger with PCB than with PSB as shown by our IR and Raman spectroscopy analyses. The higher remineralization potential of the PCB-containing synthesized material was demonstrated by in vitro testing using artificial saliva.
Febrero, 2024 · DOI: 10.3390/molecules29050930
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Renewable Carbonaceous Materials from Biomass in Catalytic Processes: A Review
Villora-Picó, JJ; González-Arias, J; Baena-Moreno, FM; Reina, TRMaterials, 17 (2024) 565 DOI: 10.3390/ma17030565
Abstract
This review paper delves into the diverse ways in which carbonaceous resources, sourced from renewable and sustainable origins, can be used in catalytic processes. Renewable carbonaceous materials that come from biomass-derived and waste feedstocks are key to developing more sustainable processes by replacing traditional carbon-based materials. By examining the potential of these renewable carbonaceous materials, this review aims to shed light on their significance in fostering environmentally conscious and sustainable practices within the realm of catalysis. The more important applications identified are biofuel production, tar removal, chemical production, photocatalytic systems, microbial fuel cell electrodes, and oxidation applications. Regarding biofuel production, biochar-supported catalysts have proved to be able to achieve biodiesel production with yields exceeding 70%. Furthermore, hydrochars and activated carbons derived from diverse biomass sources have demonstrated significant tar removal efficiency. For instance, rice husk char exhibited an increased BET surface area from 2.2 m2/g to 141 m2/g after pyrolysis at 600 °C, showcasing its effectiveness in adsorbing phenol and light aromatic hydrocarbons. Concerning chemical production and the oxidation of alcohols, the influence of biochar quantity and pre-calcination temperature on catalytic performance has been proven, achieving selectivity toward benzaldehyde exceeding 70%.
Febrero, 2024 · DOI: 10.3390/ma17030565
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth dynamics of nanocolumnar thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles
Alvarez, R; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Regodon, G; Ferrer, FJ; Rico, V; Garcia-Martin, JM; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, ANanotechnology, 35 (2024) 095705 DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/ad113d
Abstract
The morphology of numerous nanocolumnar thin films deposited by the magnetron sputtering technique at oblique geometries and at relatively low temperatures has been analyzed for materials as different as Au, Pt, Ti, Cr, TiO2, Al, HfN, Mo, V, WO3 and W. Despite similar deposition conditions, two characteristic nanostructures have been identified depending on the material: a first one defined by highly tilted and symmetric nanocolumnar structures with a relatively high film density, and a second one characterized by rather vertical and asymmetric nanocolumns, with a much lower film density. With the help of a model, the two characteristic nanostructures have been linked to different growth dynamics and, specifically, to different surface relaxation mechanisms upon the incorporation of gaseous species with kinetic energies above the surface binding energy. Moreover, in the case of Ti, a smooth structural transition between the two types of growths has been found when varying the value of the power used to maintain the plasma discharge. Based on these results, the existence of different surface relaxation mechanisms is proposed, which quantitatively explains numerous experimental results under the same conceptual framework.
Febrero, 2024 · DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/ad113d
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales - Materiales Semiconductores para la Sostenibilidad
Casimir-Lifshitz Optical Resonators: A New Platform for Exploring Physics at the Nanoscale
Esteso, V; Frustaglia, D; Carretero-Palacios, S; Míguez, HAdvanced Physics Research, 3 (2024) 2300065. DOI: 10.1002/apxr.202300065
Abstract
The Casimir-Lifshitz force, FC − L, has become a subject of great interest to both theoretical and applied physics communities due to its fundamental properties and potential technological implications in emerging nano-scale devices. Recent cutting-edge experiments have demonstrated the potential of quantum trapping at the nano-scale assisted by FC − L in metallic planar plates immersed in fluids through appropriate stratification of the inner dielectric media, opening up new avenues for exploring physics at the nano-scale. This review article provides an overview of the latest results in Casimir-Lifshitz based-optical resonator schemes and their potential applications in fields such as microfluidic devices, bio-nano and micro electromechanical systems (NEMS and MEMS), strong coupling, polaritonic chemistry, photo-chemistry, sensing, and metrology. The use of these optical resonators provides a versatile platform for fundamental studies and technological applications at the nano-scale, with the potential to revolutionize various fields and create new opportunities for research.
Febrero, 2024 · DOI: 10.1002/apxr.202300065
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Strong Light-Matter Coupling in Lead Halide Perovskite Quantum Dot Solids
Bujalance, C; Caliò, Dirin, DN; Tiede, DO; Gaisteo-López, JF; Feist, J; García-Vidal, FJ; Kovalenko, MV; Míguez, HACS Nano, 18(6) (2024) 4922-4931 DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.3c10358
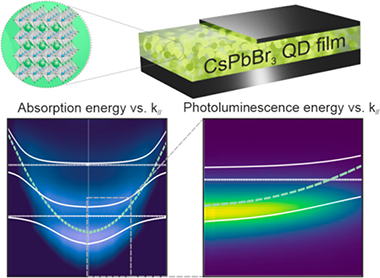
Abstract
Strong coupling between lead halide perovskite materials and optical resonators enables both polaritonic control of the photophysical properties of these emerging semiconductors and the observation of fundamental physical phenomena. However, the difficulty in achieving optical-quality perovskite quantum dot (PQD) films showing well-defined excitonic transitions has prevented the study of strong light-matter coupling in these materials, central to the field of optoelectronics. Herein we demonstrate the formation at room temperature of multiple cavity exciton-polaritons in metallic resonators embedding highly transparent Cesium Lead Bromide quantum dot (CsPbBr3-QD) solids, revealed by a significant reconfiguration of the absorption and emission properties of the system. Our results indicate that the effects of biexciton interaction or large polaron formation, frequently invoked to explain the properties of PQDs, are seemingly absent or compensated by other more conspicuous effects in the CsPbBr3-QD optical cavity. We observe that strong coupling enables a significant reduction of the photoemission line width, as well as the ultrafast modulation of the optical absorption, controllable by means of the excitation fluence. We find that the interplay of the polariton states with the large dark state reservoir plays a decisive role in determining the dynamics of the emission and transient absorption properties of the hybridized light-quantum dot solid system. Our results should serve as the basis for future investigations of PQD solids as polaritonic materials.
Febrero, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.3c10358
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Enhancing Essential Oil Extraction from Lavandin Grosso Flowers via Plasma Treatment
Molina, R; López-Santos, C; Balestrasse, K; Gómez-Ramírez, A; Sauló, JInternational Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25 (2024) 2383 DOI: 10.3390/ijms25042383
Abstract
This study explores the impact of plasma treatment on Lavandin Grosso flowers and its influence on the extraction of essential oils (EOs) via hydrodistillation. Short plasma treatment times enhance the yield of EO extraction from 3.19% in untreated samples to 3.44%, corresponding to 1 min of plasma treatment, while longer treatment times (10 min) show diminishing returns to 3.07% of yield extraction. Chemical characterization (GC/MS and ATR-FTIR) indicates that plasma treatments do not significantly alter the chemical composition of the extracted EOs, preserving their aromatic qualities. Investigations into plasma-surface interactions reveal changes at the nanometer level, with XPS confirming alterations in the surface chemistry of Lavandin Grosso flowers by reducing surface carbon and increasing oxygen content, ultimately resulting in an increased presence of hydrophilic groups. The presence of hydrophilic groups enhances the interaction between the surface membrane of the glandular trichomes on Lavandin Grosso flowers and water vapor, consequently increasing the extraction of EOs. Furthermore, microscopic SEM examinations demonstrate that plasma treatments do not affect the morphology of glandular trichomes, emphasizing that surface modifications primarily occur at the nanoscale. This study underscores the potential of plasma technology as a tool to enhance EO yields from botanical sources while maintaining their chemical integrity.
Febrero, 2024 · DOI: 10.3390/ijms25042383
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Harnessing a Vibroacoustic Mode for Enabling Smart Functions on Surface Acoustic Wave Devices - Application to Icing Monitoring and Deicing
Karimzadeh, A; Weissker, U; del Moral, J; Winkler, A; Borrás, A; González-Elipe, AR; Jacob, SAdvanced Materials Technologies, (2024) 2301749 DOI: 10.1002/admt.202301749
Abstract
Microacoustic wave devices are essential components in the radio frequency (RF) electronics and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) industry with increasing impact in various sensing and actuation applications. Reliable and smart operation of acoustic wave devices at low costs will cause a crucial advancement. Herein, this study presents the enablement of temperature and mechanical sensing capabilities in a Rayleigh-mode standing surface acoustic wave (sSAW) chip device by harnessing an acoustic shear-thickness dominant wave (SD) using the same set of electrodes. Most importantly, this mode is excited by switching the polarity of the sSAW transducer electrodes by simple electronics, allowing for direct and inexpensive compatibility with an existing setup. The method in the emergent topic of surface de-icing is validated by continuously monitoring temperature and liquid–solid water phase changes using the SD mode, and on-demand Rayleigh-wave deicing with a negligible energy cost. The flexibility for adapting the system to different scenarios, and loads and the potential for scalability opens the path to impact in lab-on-a-chip, internet of things (IoT) technology, and sectors requiring autonomous acoustic wave actuators.
Febrero, 2024 · DOI: 10.1002/admt.202301749
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Optimizing biogas methanation over nickel supported on ceria-alumina catalyst: Towards CO2-rich biomass utilization for a negative emissions society
González-Arias, J; Torres-Sempere, G; Arroyo-Torralvo, F; Reina, TR; Odriozola, JAEnrironmental Research, 242 (2024) 117735 DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.117735
Abstract
Biogas methanation emerges as a prominent technology for converting biogas into biomethane in a single step. Furthermore, this technology can be implemented at biogas plant locations, supporting local economies and reducing dependence on large energy producers. However, there is a lack of comprehensive studies on biogas methanation, particularly regarding the technical optimization of operational parameters and the profitability analysis of the overall process. To address this gap, our study represents a seminal work on the technical optimization of biogas methanation obtaining an empirical model to predict the performance of biogas methanation. We investigate the influence of operational parameters, such as reaction temperature, H2/CO2 ratio, space velocity, and CO2 share in the biogas stream through an experimental design. Based on previous research we selected a nickel supported on ceria-alumina catalyst; being nickel a benchmark system for methanation process such selection permits a reliable data extrapolation to commercial units. We showcase the remarkable impact of studied key operation parameters, being the temperature, the most critical factor affecting the reaction performance (ca. 2 to 5 times higher than the second most influencing parameter). The impact of the H2/CO2 ratio is also noticeable. The response surfaces and contour maps suggest that a temperature between 350 and 450 degrees C and an H2/CO2 ratio between 2.5 and 3.2 optimize the reaction performance. Further experimental tests were performed for model validation and optimization leading to a reliable predictive model. Overall, this study provides validated equations for technology scaling-up and techno-economic analysis, thus representing a step ahead towards real-world applications for bio-methane production.
Febrero, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.117735
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Subnanometric Pt clusters dispersed over Cs-doped TiO2 for CO2 upgrading via low-temperature RWGS: operando mechanistic insights to guide an optimal catalyst design
Torres-Sempere, G; Blay-Roger, R; Luque-Alvarez, LA; Santos, JL; Bobadilla, LF; Pastor-Pérez, L; Centeno, MA; Hernández, WY; Yousef, I; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TRJournal of Matertials Chemistry A, 12 (2024) 1779-1792 DOI: 10.1039/D3TA05482A
Abstract
The RWGS reaction is gathering momentum as an effective route for CO2 valorisation and given its endothermic nature the challenge lies in the design of active low-temperature catalysts. Herein we have designed two catalysts based on subnanometric Pt clusters providing effective CO2 conversion and, more importantly, high CO selectivity in the low-temperature range. The impact of Cs as a dopant in the catalyst's formulation is crucial leading to full selectivity at 300 °C. The reaction mechanisms for the studied systems namely Pt/TiO2 and PtCs/TiO2 are significantly different due to the presence of the alkali promoter. The presence of Cs neutralises the hydroxide groups of the TiO2 surface, changing the reaction pathway. The Pt/TiO2 catalyst follows a redox mechanism where CO2 dissociates to CO in the oxygen vacancies, and then these vacancies are recovered by the migration of H2 by spill over phenomena. On the other hand, the Cs doped catalyst has two possible mechanism pathways: the (ii) formyl/acyl pathway, where –CHO species are formed and, depending on the reaction conditions, evolve to CO gas or oxygenated compounds, and (ii) frustrated Lewis pair (FLP) assisted CO2 reduction route, in which the FLP induces the heterolytic dissociation of H2 and the subsequent hydrogenation of CO2 to CO. The latter route enabled by Cs-doping combined with the subnanometric Pt domains seems to be responsible for the excellent catalytic behaviour leading to fully selective low-temperature RWGS systems and thus unlocking new possibilities for less energy demanding CO2 valorisation units based on RWGS.
Enero, 2024 · DOI: 10.1039/D3TA05482A
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Scattering Spheres Boost Afterglow: A Mie Glass Approach to Go Beyond the Limits Set by Persistent Phosphor Composition
Castaing, V; Romero, M; Torres, J; Lozano, G; Míguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, 12 (2024) 2301565 DOI: 10.1002/adom.202301565
Abstract
Persistent luminescence phosphor nanoparticles (PersLNPs) offer exciting opportunities for anticounterfeiting, data storage, imaging displays, or AC-driven lighting applications owing to the possibility to process them as shapable thin coatings. However, despite unique delayed and long-lasting luminescence, the relatively low storage capacity of persistent phosphor nanoparticles combined with the difficulty of harvesting photons from transparent thin layers drastically hinder the perceived afterglow. In order to enhance persistent luminescence (PersL) of thin coatings, herein a novel approach is proposed based on resonant optical nanostructures. In particular, it is demonstrated that the integration of TiO2 scattering spheres in films (with thickness comprised between 1 and 10 mu m) made of ZnGa2O4:Cr3+ PersLNPs enables a significant increase in afterglow intensity due to the combination of effective charging and enhanced outcoupling. As a result, a approximate to 3.5-fold enhancement of the PersL is observed in 2 mu m-thick films stuffed with scattering centers using low-light illumination conditions. Furthermore, inclusion of scattering centers leads to an unprecedented acceleration of the PersL charging speed. These results constitute the first example of photonic engineering applied to enhance the properties of PersL materials coatings.
Enero, 2024 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.202301565
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Mechanistic insights into methanol carbonylation to methyl acetate over an efficient organic template-free Cu-exchanged mordenite
Luque-Alvarez, LA; Gonzalez-Arias, J; Romero-Sarria, F; Reina, TR; Bobadilla, LF; Odriozola, JACatalysis Science & Technology, 14 (2024) 128-136 DOI: 10.1039/d3cy01271a
Abstract
Currently, acetic acid is produced via the carbonylation reaction of methanol with the main route entailing the use of homogeneous noble metal-based catalysts, which has certain limitations, including the use of polluting alkyl halide promoters and difficulty in catalyst recovery. To overcome these challenges, the exploration of alternative methods utilizing heterogeneous catalysts, particularly zeolites with copper as a redox center, has gained attention. Nonetheless, the conversion and selectivity obtained are sought after to compete against the homogeneous route. Therefore, a deeper understanding of the reaction and mechanism is needed to determine the weak points and overcome them. In this study, we propose the use of time-resolved operando DRIFTS-MS to study the methanol carbonylation reaction over a Cu–H-MOR catalyst. The study aimed to propose a reaction mechanism through an investigation of the behavior of the catalyst, including potential identification of the location of the copper redox center in the zeolite. The catalytic performance of the Cu–H-MOR catalyst was also evaluated, demonstrating its activity and stability in the methanol carbonylation reaction. The operando DRIFTS-MS results provide insights into the reaction mechanism and the involvement of the acid and redox centers in the process. Based on the findings, we propose a reaction mechanism for methanol carbonylation on Cu–H-MOR zeolite: (i) methanol dehydration, (ii) CO insertion into methoxide groups, (iii) reaction between dimethyl ether and acetyl groups, and (iv) hydrolysis of methyl acetate. Overall, we believe that this work contributes to a deeper understanding of the heterogeneous route for acetic acid production and offers potential avenues for optimizing the process.
Enero, 2024 · DOI: 10.1039/d3cy01271a
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones - Reactividad de Sólidos
Investigating the room- and cryo-milling impact in lignocellulosic biomass and its consequence over pyrolysis and oxidative treatments
Pérez, CR; González, MDA; Sarria, FR; López, MDH; Gallego, JMCJournal of Cleaner Production, 437 (2024) 140761 DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.140761
Abstract
The lignocellulosic biomass recalcitrance is the uppermost factor for the utilization of this renewable resource. The development of new pre -treatments, addressed to enhance performance in lignocellulosic biomass conversion into biofuels, fine chemicals, and as potential sources of building blocks for materials, must be focus in two main areas: effectiveness (cost-effective and chemical effective) and green chemistry. In this research, a set of different biomass sources (farmer, harvested wild trees and secondary products) were studied to evaluate the high efficiency of the non -liquid nitrogen (LN) and LN-treated biomass samples' planetary ball milling performance. The samples have been characterized by particle size distribution, thermogravimetric, FT-IR, statistical chemometric and chemical oxidation analysis. The results have shown a high level on the rupture of the crystallinity and depolymerization degrees of the cellulose and the lignin, for both, non-LN and LN-treated samples. The thermogravimetric analysis showed a clear diminishing in temperature degradation, and a larger amount of biomass degraded at lower temperature, as well as, a high chemical oxidation degree than not milled samples. Finally, the LN-treated samples even exhibited a lower degradation temperature, a larger amount of biomass degraded at lower temperature and a higher oxidation degree, than those non-LN milled.
Enero, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.140761
- ‹ anterior
- 3 of 37
- siguiente ›














