Artículos SCI
2024
2024
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Impact of the biogas impurities on the quality of the precipitated calcium carbonate in the regenaration stage of a chemical absorption biogas upgrading unit
Salinero, J; Fernández, LMG; Portillo, E; González-Arias, J; Baena-Moreno, FM; Navarrete, B; Vilches, LFJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 12 (2024) 113868 DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2024.113868
Abstract
Combining Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) with producing competitive secondary raw materials is key to decarbonizing industry and reducing resource extraction. Biogas upgrading to biomethane stand out as an alternative, but a significant gap remains in integrating this process within a circular economy framework. This issue has been recently addressed by a process that integrates biogas upgrading via caustic absorption with the production of Precipitated Calcium Carbonate (PCC) and the recovery of sodium hydroxide from waste brine solution using membrane technologies. The profitability of this approach depends on the quality of the PCC, a critical factor that this work addresses. By characterizing PCC is determined whether trace compounds in biogas contaminate the PCC and potentially affect its commercial value. It also examines the CO2 absorption process and analyzes the aqueous samples from the filtration phase of the PCC slurry. Results confirm the high purity of PCC obtained from biogas treatment using Raman spectroscopy, X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). The analyses show that the PCC is pure calcium carbonate, mainly in the stable calcite form, with a typical tetrahedral morphology and no detectable impurities. Characterization of aqueous solutions revealed organic trace compounds from biogas, with TOC concentrations of 9.7 (+/- 6.4) and 16.0 (+/- 8) mg C/l. Silicon measurements showed similar concentrations in the absorbent solution and filtrated PCC slurry. Additionally, ammonia escapes as gas, and hydrogen sulfide in the biogas likely contributed to sulfate salt formation. Analysis of the COQ absorption shows a first-order reaction with OH-, where the amount of COQ absorbed (46.3-50.0 g) closely matches the theoretical value of 48 g. The study reveals that most of the biogas impurities dissolve into the aqueous solution, being crucial for future studies and downstream membrane treatments, and the PCC is unaffected by these impurities with a purity suitable for commercial applications.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2024.113868
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Strong Grain Boundary Passivation Effect of Coevaporated Dopants Enhances the Photoemission of Lead Halide Perovskites
Justin, IAK; Tiede, DO; Piot, M; Forzatti, M; Roldán-Carmona, C; Galisteo-López, FJ; Míguez, H; Bolink, HJACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 16 (2024) 61305-61313 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c13434
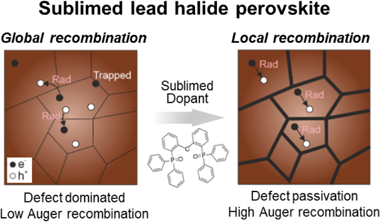
Abstract
Herein, we demonstrate that coevaporated dopants provide a means to passivate buried interfacial defects occurring at perovskite grain boundaries in evaporated perovskite thin films, thus giving rise to an enhanced photoluminescence. By means of an extensive photophysical characterization, we provide experimental evidence that indicate that the codopant acts mainly at the grain boundaries. They passivate interfacial traps and prevent the formation of photoinduced deep traps. On the other hand, the presence of an excessive amount of organic dopant can lead to a barrier for carrier diffusion. Hence, the passivation process demands a proper balance between the two effects. Our analysis on the role of the dopant, performed under different excitation regimes, permits evaluation of the performance of the material under conditions more adapted to photovoltaic or light emitting applications. In this context, the approach taken herein provides a screening method to evaluate the suitability of a passivating strategy prior to its incorporation into a device.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c13434
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Application of novel Zn-MIL53(Fe) for removal of micropollutants using an activated peroxymonosulphate system
Terrón, D; Holgado, JP; Giráldez, A; Rosales, E; Sanromán, MA; Pazos, MJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 12 DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2024.113403
Abstract
Novel zinc-doped Metal-Organic Framework based on MIL53(Fe) (Zn-MIL53(Fe)) has been successfully synthesised in one-step, exhibiting dual applications as adsorbent and catalyst. Initially, the adsorption capacity of MIL53(Fe) and Zn-MIL53(Fe) for removing Rhodamine B was assessed through kinetic and isotherm studies. The bimetallic variant exhibited superior performance, showcasing enhanced adsorption capabilities, particularly in the context of its physical interaction under natural pH. After that, the catalytic activity of both synthesised materials was evaluated to generate sulphate radicals by activating PeroxyMonoSulphate (PMS). It was also demonstrated that Zn-MIL53(Fe) exhibited the best catalytic activity being optimised using response surface methodology for Rhodamine B degradation (0.11 mM PMS and 43.2 mg Zn-MIL53(Fe)). Under optimal conditions, favourable outcomes were attained, facilitating the degradation of Rhodamine B, Fluoxetine, and Sulfamethoxazole by 93, 99, and 75 %, respectively. Furthermore, the operational stability of the Zn-MIL53(Fe) was verified, as it remains structurally and catalytically intact after different cycles.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2024.113403
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Analysis of the impact of remote oxygen plasma treatment on the surface chemistry and electrochemical properties of graphite felt electrodes for redox flow batteries
Murillo-Herrera, LM; Mingoes, CJ; Obrero-Pérez, J; Sánchez-Valencia, JR; Thielke, MW; Barranco, A; Jorge Sobrido, ABEnergy Advances, 3 (2024) 2503-2511 DOI: 10.1039/d4ya00383g
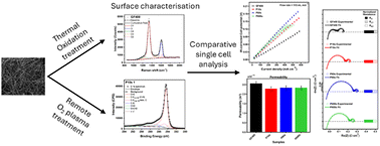
Abstract
The effects of a remote oxygen plasma (ROP) treatment on the surface of commercial graphite felts were investigated and compared against a conventional thermal treatment. In contrast to methodologies where the sample is directly exposed to the plasma, ROP allows for a high control of sample-plasma interaction, thereby avoiding extensive etching processes on the fibre surface. To assess the impact of ROP treatment time, the electrodes were subjected to three different periods (10, 60, and 600 seconds). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy showed that the ROP treatment introduced nearly three times more surface oxygen functionalities than the thermal treatment. Raman spectroscopy measurements revealed a significant increase in amorphous carbon domains for the ROP samples. The thermal treatment favoured increases in graphitic defects and resulted in an order of magnitude larger ECSA compared to the ROP treated materials despite having lower content in oxygen functionalities. The electrochemical analysis showed enhanced charge-transfer overpotentials for GF400. The ROP samples exhibited a lower mass-transport overpotential than the thermally treated material and had similar permeabilities, which overall translated to the thermal treatment offering better performance at fast flow rates. However, at slow flow rates (similar to 10 mL min-1), the ROP treatment for the shortest period offered comparable performance to conventional thermal treatment.
Remote oxygen plasma is compared to conventional thermal activation of electrodes for flow batteries and their impact on the mass transport and charge transfer properties of the resulting carbons.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1039/d4ya00383g
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
A Circular Economy Perspective: Recycling Wastes through the CO2 Capture Process in Gypsum Products. Fire Resistance, Mechanical Properties, and Life Cycle Analysis
Ruiz-Martinez, JD; Moreno, V; González-Arias, J; Capilla, BP; Baena-Moreno, FM; Leiva, CFire-Switzerland, 7 (2024) 365 DOI: 10.3390/fire7100365
Abstract
In recent years, the implementation of CO2 capture systems has increased. To reduce the costs and the footprint of the processes, different industrial wastes are successfully proposed for CO2 capture, such as gypsum from desulfurization units. This gypsum undergoes an aqueous carbonation process for CO2 capture, producing an added-value solid material that can be valorized. In this work, panels have been manufactured with a replacement of (5 and 20%) commercial gypsum and all the compositions kept the water/solid ratio constant (0.45). The density, surface hardness, resistance to compression, bending, and fire resistance of 2 cm thick panels have been determined. The addition of the waste after the CO2 capture diminishes the density and mechanical strength. However, it fulfills the requirements of the different European regulations and diminishes 56% of the thermal conductivity when 20%wt of waste is used. Although the CO2 waste is decomposed endothermically at 650 degrees C, the fire resistance decreases by 18% when 20%wt. is added, which allows us to establish that these wastes can be used in fire-resistant panels. An environmental life cycle assessment was conducted by analyzing a recycling case in Spain. The results indicate that the material with CO2 capture waste offers no environmental advantage over gypsum unless the production plant is located within 200 km of the waste source, with transportation being the key factor.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.3390/fire7100365
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Triboelectric pixels as building blocks for microscale and large-area integration of drop energy harvesters
Ghaffarinejad, A; García-Casas, X; Núñez-Gálvez, F; Budagosky, J; Godinho, V; López-Santos, C; Sánchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Borrás, ADevice, 3 (2024) 100566. DOI: 10.1016/j.device.2024.100566
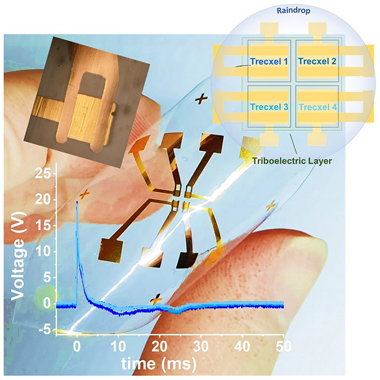
Abstract
Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) are the most promising technology for harvesting energy from low-frequency liquid flows and impacts such as rain droplets. However, current drop energy harvester technologies suffer from low output power due to limitations in triboelectric materials, suboptimal device designs, and the inability to fully capture the kinetic energy of falling drops. This article introduces a microscale TENG capable of efficiently converting drop impact energy into electrical power in a single, rapid step. The device features a capacitive structure that enhances energy conversion through instantaneous capacitance changes when the drops contact the submillimetric top electrodes. This compact design establishes a path toward the development of dense arrays and rain panels and is adaptable to various liquids, scales, triboelectric surfaces, and thin-film configurations, including flexible and transparent materials.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.device.2024.100566
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Advances in life cycle assessment of chemical absorption-based carbon capture technologies
Wang, P; Liu, Z; Pan, Z; González-Arias, J; Shang, L; Wang, Y; Zhang, ZSeparation and Purification Technology, 346 (2024) 127252 DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2024.127252
Abstract
With the rapid advancement of industry and the continuous growth of population, there has been a noteworthy surge in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, thereby exacerbating the impact of climate change. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is widely recognized as a pivotal technology in addressing global climate change. This is attributed to its alignment with existing energy infrastructure and its substantial potential for significant reduction in CO2 emissions. Among the alternatives for carbon capture, chemical absorption stands out due to its robust processing capacity, adaptability, and high reliability, making it the most mature technology for capturing CO2 in contemporary power plants. Life cycle assessment (LCA) can assist decision-makers in determining whether the use of the technology to mitigate GHG emissions will result in elevated environmental impacts. This work offers an overview of the problems and present status associated with different chemical solvents in CO2 capture and emphasizes the merits and drawbacks in the use of different solvents within the absorption process. Although the integration of chemical absorption systems in power plants leads to a substantial reduction in direct CO2 emissions, there are varying degrees of impacts on other environmental impact categories (e.g., acidification, eutrophication, ecological and human toxicity, etc.) in addition to global warming. This paper analyzes the potential environmental impacts associated with carbon capture using different solvents and suggests directions for improvement. Finally, it is reviewed in the aspects of combination with new technology and interdisciplinary evaluation. This work aims to deepen our comprehension of the environmental impacts linked to diverse post-combustion CO2 capture systems relying on chemical absorption, facilitating decision-makers in developing optimal solutions that provide both economic and environmental benefits.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2024.127252
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones - Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Controlling copper location on exchanged MOR-type aluminosilicate zeolites for methanol carbonylation: In situ/operando IR spectroscopic studies
Luque-Alvarez, LA; Torres-Sempere, G; Romero-Sarria, F; Bobadilla, LF; Ramírez-Reina, T; Odriozola, JAMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 378 (2024) DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2024.113258
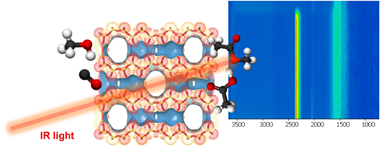
Abstract
Replacing homogeneous catalytic processes by heterogeneous routes based on the utilization of solid catalysts is of great interest from an environmental point of view. Owing to their genuine pore structure, zeolites such as mordenites (MOR) have emerged as game-changing materials to enable the heterogenization of catalytic processes including methanol carbonylation. Cu-exchange zeolites take the edge over pristine zeolites, leading to enhanced catalytic performance in terms of greater activity, selectivity, and stability. Herein, the overall catalytic activity and stability can be modulated upon controlling the environment and location of copper active sites in zeolites. In this study, Cu-exchanged mordenites were strategically synthesized to investigate the role of Cu location inside of MOR cavities under working conditions by means of in situ/operando infrared (IR) spectroscopic studies. The results obtained revealed that a major proportion of Cu in the MR-8 cavities notably enhances the activity and stability of the catalyst. This study provides crucial insights for fine-tuning zeolite catalysts to achieve the heterogenization of homogeneous carbonylation processes.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2024.113258
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Navigating the Legislative Interventions, Challenges, and Opportunities in Revolutionizing Textile Upcycling/Recycling Processes for a Circular Economy
Saif, M; Blay-Roger, R; Zeeshan, M; Bobadilla, LF; Ramíres Reina, T; Asif Nawaz, M; Odriozola, JAACS Sustainable Resource Management, 1 (2024) 2338-2349. DOI: 10.1021/acssusresmgt.4c00242

Abstract
Embracing a circular economy in the textile industry represents a crucial step toward sustainability, where fashion and textile sectors contribute significantly to CO2 emissions. However, transitioning from a linear “take-make-waste” model to circularity, poses multifaceted challenges, that highlight the staggering volume of annual textile waste surpassing industry predictions, thus emphasizing the urgent need for comprehensive strategies. Despite advancements in recycling technologies, challenges persist in collecting and sorting textile waste, where fragmentation in waste management and recycling processes hinders effective management of post-consumer waste. Addressing these challenges demands elevated efforts in collection, sorting, and pre-processing, alongside regulatory interventions to drive enhanced waste collection and circular business models. Efforts are underway to promote sustainable textile recycling, with initiatives like the EU’s Sustainable and Circular Textiles Strategy aiming to reduce reliance on virgin resources. However, achieving a circular textile market in the near future requires collaborative action and innovative solutions. Though challenges in scaling and technological limitations still remain, recent breakthroughs in textile-recycling technologies offer promise, signaling a shift toward scalable and sustainable alternatives to virgin fibers, where bio-based chemical processes, and thermochemical recycling processes present transformative opportunities. Where, bold scaling targets, collaborative efforts, and short-term funding support narrated in this perspective article are imperative to accelerate the transition to a circular textile economy, thus delving into the pivotal role of textile recycling, tracing the evolution of recycling technologies, and addressing critical challenges hindering widespread adoption.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acssusresmgt.4c00242
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Revisiting plant cuticle biophysics
Heredia, A; Benitez, JJ; Moreno, AG; Domínguez, ENew Phytologist, 244 (2024) 65-73 DOI: 10.1111/nph.20009
Abstract
The plant cuticle is located at the interface of the plant with the environment, thus acting as a protective barrier against biotic and abiotic external stress factors, and regulating water loss. Additionally, it modulates mechanical stresses derived from internal tissues and also from the environment. Recent advances in the understanding of the hydric, mechanical, thermal, and, to a lower extent, optical and electric properties of the cuticle, as well as their phenomenological connections and relationships are reviewed. An equilibrium based on the interaction among the different biophysical properties is essential to ensure plant growth and development. The notable variability reported in cuticle geometry, surface topography, and microchemistry affects the analysis of some biophysical properties of the cuticle. This review aimed to provide an updated view of the plant cuticle, understood as a modification of the cell wall, in order to establish the state-of-the-art biophysics of the plant cuticle, and to serve as an inspiration for future research in the field.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1111/nph.20009
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of calcination temperature on the synthesis of Ni-based cerium zirconate for dry reforming of methane
Martín-Espejo, JL; Merkouri, LP; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TR; Pastor-Pérez, LCeramics International, 50 (2024) 38406-38414 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.07.205
Abstract
Dry reforming of methane (DRM) represents an alluring approach to the direct conversion of CO2 and CH4, gases with the highest global warming potential, into syngas, a value-added intermediate used in chemical industry. In this study, mixed oxide structures of cerium and zirconium doped with 10 wt% Ni were used due to the high thermal stability. This study showcased the importance of choosing suitable conditions and explored the impact of calcination temperature on Ce-Zr mixed oxides with Ni. XRD analysis confirmed the existence of different crystalline phases according to the calcination temperature. Redox characterisation showed a trade-off among calcination temperature, the dispersion of Ni clusters and its interaction with the support structure. Calcined catalysts at 900 and 1000 degrees C underwent harsh, long-term DRM conditions. Despite the low surface area of the designed catalysts, the stability experiments proved a relation between dispersion of Ni active phase and catalytic performance, showing an optimum calcination temperature of 1000 degrees C.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.07.205
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
A sustainable lecithin-based ligand for the bio-functionalization of iron and hybrid metal organic frameworks (MOFs) nanoparticles with the sugar mannose
Cova, CM; Ramos, V; Escudero, A; Holgado, JP; Khiar, N; Zuliani, AGreen Chemistry, 26 (2024) 11563-11575 DOI: 10.1039/D4GC03743J
Abstract
The functionalization of nanoparticles with specific ligands, such as antibodies, peptides, and small molecules, plays a critical role in achieving targeted delivery, enhancing biocompatibility, and controlling drug release. However, to date, practically no attention has been paid to the design of green ligands. Herein, an innovative approach to develop a sustainable ligand for nanoparticle functionalization is reported. Its synthesis involved a photochemical thio-ene "click" reaction between the natural compounds phosphatidylcoline, the main component of lecithin, and cysteine, followed by a reductive amination with mannose, a sugar of growing interest for biomedical targeting, in a continuous flow hydrogenation reactor. Comprehensive characterization techniques, including nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), mass spectrometry (MS), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and elemental analysis, confirmed the structure and properties of the novel ligand. The environmental sustainability of the ligand was evaluated determining some green metrics using the EATOS software. The obtained E-factor was compared with a conventional PEG-based ligand. The newly developed lecithin-derived ligand was successfully used to functionalize diverse NP platforms, including the MOFs MIL-101(Fe), PCN-222, UiO-66, and iron nanoparticles (in the form of akaganeite), demonstrating its potential in nanomedicine applications.
A sustainable lecithin-based ligand was developed using a photochemical thio-ene "click" reaction with cysteine and reductive amination with d-Mannose. The ligand functionalized various nanoparticles, showing potential for biomedical applications.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1039/D4GC03743J
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
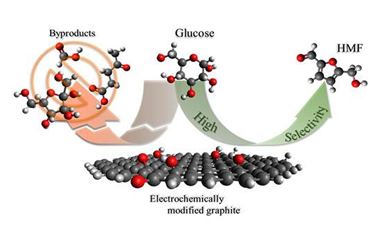
Electrochemical tailoring of graphite properties for tunable catalytic selectivity of glucose conversion to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural
Delgado, G; Bounoukta, CE; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Villar-Rodil, S; Paredes, JI; Cazaña, F; Monzón, A; García-Dalí, SApplied Surface Science, 671 (2024) 160677 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.160677
Abstract
This study presents a novel approach for boosting the selectivity of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) production from glucose through electrochemical modification of graphite materials. Three distinct graphitic substrates were subjected to controlled electrochemical treatments utilizing sodium sulfate or phosphoric acid as electrolytes. The process expanded the graphite particles/pieces and introduced oxygenated functional groups to the exposed surfaces while preserving the structural integrity of the bulk material. The resulting modifications influenced the type and quantity of Lewis and Brønsted acidic sites, providing exhaustive control over reaction pathways leading to HMF. This electrochemically modified graphite demonstrated superior tunability compared to traditional metal-based catalysts, enabling dynamic optimization of reaction conditions for enhanced HMF yield. The controlled introduction of functional groups facilitated the tailoring of active sites, significantly impacting the kinetics of glucose conversion and achieving HMF selectivity up to 95%. This level of precision in controlling catalytic properties is essential for maximizing HMF yield while minimizing undesired by-product formation, addressing a critical challenge in HMF production.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.160677
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Redefining the Symphony of Light Aromatic Synthesis Beyond Fossil Fuels: A Journey Navigating through a Fe-Based/HZSM-5 Tandem Route for Syngas Conversion
Nawaz, MA; Blay-Roger, R; Saif, M; Meng, FH; Bobadilla, LF; Reina, TR; Odriozola, JAACS Catalysis, 14 (2024) 15150-15196 DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.4c03941

Abstract
The escalating concerns about traditional reliance on fossil fuels and environmental issues associated with their exploitation have spurred efforts to explore eco-friendly alternative processes. Since then, in an era where the imperative for renewable practices is paramount, the aromatic synthesis industry has embarked on a journey to diversify its feedstock portfolio, offering a transformative pathway toward carbon neutrality stewardship. This Review delves into the dynamic landscape of aromatic synthesis, elucidating the pivotal role of renewable resources through syngas/CO2 utilization in reshaping the industry's net-zero carbon narrative. Through a meticulous examination of recent advancements, the current Review navigates the trajectory toward admissible aromatics production, highlighting the emergence of Fischer-Tropsch tandem catalysis as a game-changing approach. Scrutinizing the meliorated interplay of Fe-based catalysts and HZSM-5 molecular sieves would uncover the revolutionary potential of rationale design and optimization of integrated catalytic systems in driving the conversion of syngas/CO2 into aromatic hydrocarbons (especially BTX). In essence, the current Review would illuminate the path toward cutting-edge research through in-depth analysis of the transformative power of tandem catalysis and its capacity to propel carbon neutrality goals by unraveling the complexities of renewable aromatic synthesis and paving the way for a carbon-neutral and resilient tomorrow.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.4c03941
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
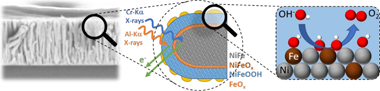
Hard X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Probing Fe Segregation during the Oxygen Evolution Reaction
Longo, F; Loreda-Jurado, PJ; Gil-Rostra, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Yubero, F; Thoma, SLJ; Neels, A; Borgschulte, AACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 16 (2024) 59516-59527 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c11902
Abstract
NiFe electrocatalysts are among the most active phases for water splitting with regard to the alkaline oxygen evolution reaction (OER). The interplay between Ni and Fe, both at the surface and in the subsurface of the catalyst, is crucial to understanding such outstanding properties and remains a subject of debate. Various phenomena, ranging from the formation of oxides/(oxy)hydroxides to the associated segregation of certain species, occur during the electrochemical reactions and add another dimension of complexity that hinders the rational design of electrodes for water splitting. In this work, we have developed the procedure for the quantification of chemical depth profiling by XPS/HAXPES measurements and applied it to two NiFe electrodes with different porosities. The main outcome of this study is related to the surface reconstruction of the electrodes during the OER, followed at two different depths by means of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. We find that Fe initially segregates at the surface when exposed to ambient conditions, resulting in the formation of an inactive FeOx phase. In addition, the porosity of the catalyst plays a significant role in the segregation process and thus in the performance of the electrode. In particular, the higher porosity of the nanostructured sample is responsible for a more pronounced diffusion of Fe from the subsurface to the surface with a more effective suppression of the activity of the Ni1–xFexOOH phase. These results highlight the importance of the fact that the chemical state of the surface of a multielement system is a snapshot in time, dependent on both external parameters, such as the applied potential and the adjacent electrolyte, and the underlying bulk properties accessible with HAXPES.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c11902
Materiales Coloidales
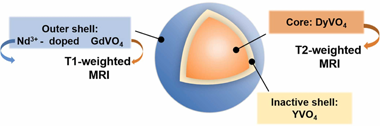
Lanthanide vanadate-based nanoparticles as multimodal T1 -T2 MRI contrast agent and NIR luminescent imaging probe
Gómez-González, E; Núñez, NO; Caro, C; García-Martín, ML; Becerro, AI; Ocaña, MJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 1003 (2024) 175647 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2024.175647
Abstract
We report the development of a multimodal lanthanide vanadate system suitable as dual T1-T2 MRI contrast agent as well as a luminescent imaging probe in the near-infrared region, using Dy3+ and Gd3+ as T2 and T1 components, respectively, and Nd3+ as the luminescent center. The vanadate matrix was chosen to avoid the undesired solubility associated to previously reported fluoride-based contrast agents. With such aim, we first optimized the design of the MRI system by comparatively evaluating the magnetic relaxivities of two different architectures consisting of i) uniform NPs incorporating both paramagnetic cations in solid solution (single-phase NPs), and ii) core-shell NPs consisting of a DyVO4 core coated with a homogeneous GdVO4 shell (DyVO4@GdVO4). We found that, although both samples presented magnetic relaxivity properties that make them adequate for their use as dual T1-T2 contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging, the core-shell architecture would be more suitable because of their higher magnetic relaxivity values. Secondly, to prepare the multimodal system, the GdVO4 layer of such optimal dual T1-T2 MRI probe was doped with Nd3+ cations. An inert YVO4 intermediate shell was also introduced between the cores and the outer layer aiming to avoid energy transfer from Nd3+ to Dy3+, which would cause luminescence quenching. These core-shell-shell nanoparticles showed magnetic relaxivity values similar to those of the core-shell system and an intense luminescence in the near-infrared region. Moreover, they were dispersible and chemically stable under conditions that mimic the physiological media, and they were nontoxic for cells. Therefore, such multimodal nanoparticles meet the main requirements for their use as a dual T1-T2 contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging and as a probe for luminescent imaging in the near-infrared region.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2024.175647
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
CuOx supported LaCoO3 perovskite for the photoassisted reverse water gas shift reaction at low temperature
Escamilla, M; Caballero, A; Colon, GJournal of CO2 Utilization, 88 (2024) 102925 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2024.102925
Abstract
CuOx/LaCoO3 systems have been studied for the rWGS reaction under thermal assisted photocatalytic conditions within low temperature range of 180-330 degrees C. CuOx species deposited from chemical reduction method over LaCoO3 homogeneously covered the perovskite surface. The reduction pretreatment before reaction leads to the partial Co reduction and the complete reduction of Cu. A significant improvement on CO production has been attained upon Cu incorporation. In addition, upon UV-vis irradiation the CO production is also enhanced. Best results have been obtained for 5 wt% Cu. The highest synergistic effect was observed for the lowest temperature, for which catalytic contribution is negligible. Thus, a good compromise is attained at 300 degrees C for which a CO production of 5.45 mmol/h center dot g and 92 % selectivity, showing a good synergistic effect between thermo and thermo-photocatalytic activity.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2024.102925
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
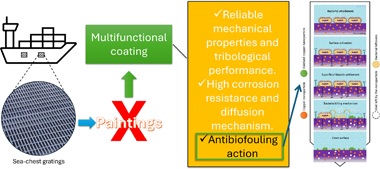
Unleashing the antibiofouling potential of nano-structured ZrN-Cu coating through electricity
Castro, JD; Carvalho, I; Sánchez-López, JC; Rojas, TC; Escobar-Galindo, R; Carvalho, SSurface & Coatings Technology, 494 (2024) 131503 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2024.131503
Abstract
The world needs more environmentally friendly materials every time, especially when the application demands constant interaction with fragile habitats. The naval industry is a crucial player in a globalised economy, and the ambient impact of ships on the seas is well-known. Biofouling is one of the significant issues in this industry, and paints with biocides are used as the principal coating solution. However, those are mechanically poor, releasing heavy pollutants into the oceans. Multifunctional coatings obtained by PVD technology could help overcome this situation. The present study proposes a solution to create an advanced coating composed of zirconium nitride and copper in a specific nano-architecture. The developed coating was obtained in a hybrid magnetron co-sputtering system, employing high-power impulse and direct current power sources in a reactive atmosphere. SEM and TEM expose the morphology and the structure of the coatings. EDX, RBS, and XPS were used to assess the chemical insights of the coating. Halo and biofilm tests (with Cobetia marina) were employed to evaluate the antibiofouling action of the coating. The results showed that the activation of the coating, regardless of the used method, provoked the copper migration to the surface, being crucial to obtaining the antibacterial action (reduced bacteria adhesion and > 3 log reduction in CFU on the surface) without affecting the coating integrity (assessed by SEM), and not releasing heavy metals in a significant manner (< 2 log reduction CFU on supernatant). This opens the option of this kind of material, which is environmentally friendly, to be applied in real applications.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2024.131503
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Interplay between connectivity and passivating agents in perovskite quantum dot networks
Moran-Pedroso, M; Tiede, DO; Romero-Perez, C; Calvo, ME; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry C (2024). DOI: 10.1039/d4tc02362e
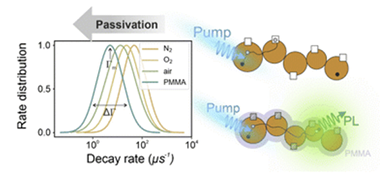
Abstract
Introducing quantum dots (QDs) as the active element of an optoelectronic device demands its incorporation in the shape of interconnected arrays that allow for some degree of electronic coupling in order to inject/extract charge carriers. In doing so, beyond reducing the degree of quantum confinement, carriers are exposed to an enhanced defect landscape as they can access adjacent QDs, which is at the origin of the strong reduction of photoluminescence observed in QD solids when compared to that of the isolated QDs. In this work we demonstrate how a proper defect passivating strategy or atmospheric treatment can greatly enhance charge diffusion in a QD film, needed for an optimal carrier injection/extraction demanded for optoelectronic applications, and also improved its stability against external radiation. From a fundamental perspective, we provide evidence showing that trap density distribution, rather than QD size distribution, is mostly responsible for the observed variations in emission decay rates present in the QD networks under analysis.
Different treatments (comprising polymeric encasement and different atmospheres) are applied to quantum dot solids in order to modify their defect landscape. The role of the latter in both, carrier recombination and stability, is unveiled.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1039/d4tc02362e
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nucleation and growth of plasma sputtered silver nanoparticles under acoustic wave activation
Reichel, H; García-Valenzuela, A; Espino-Román, JA; Gil-Rostra, J; Regodón, GF; Rico-Gavira, V; Borrás, A; Gómez-Ramírez, A; Palmero, A; González-Elipe, AR; Oliva-Ramírez, MApplied Surface Science, 669 (2024) 160566 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.160566
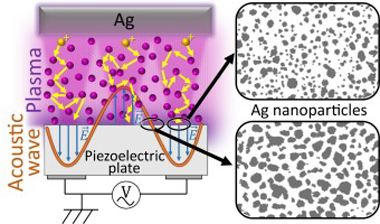
Abstract
Early results on the plasma deposition of dielectric thin films on acoustic wave (AW) activated substrates revealed a densification pattern arisen from the focusing of plasma ions and their impact on specific areas of the piezoelectric substrate. Herein, we extend this methodology to tailor the plasma deposition of metals onto AW-activated LiNbO3 piezoelectric substrates. Our investigation reveals the tracking of the initial stages of nanoparticle (NP) formation and growth during the submonolayer deposition of silver. We elucidate the specific role of AW activation in reducing particle size, enhancing particle circularity, and retarding NP agglomeration and account for the physical phenomena making these processes differ from those occurring on non-activated substrates. We provide a comparative analysis of the results obtained under two representative plasma conditions: diode DC sputtering and magnetron sputtering. In the latter case, the AW activation gives rise to a 2D pattern of domains with different amounts of silver and a distinct size and circularity for the silver NPs. This difference was attributed to the specific characteristics of the plasma sheath formed onto the substrate in each case. The possibilities of tuning the plasmon resonance absorption of silver NPs by AW activation of the sputtering deposition process are discussed.
Octubre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.160566
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Reactive Surface Explored by NAP-XPS: Why Ionic Conductors Are Promoters for Water Gas Shift Reaction
García-Moncada, N; Penkova, A; González-Castaño, M; Odriozola, JAACS Catalysis 14 (2024) 14947–14957. DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.4c04287
Abstract
Near-ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (NAP-XPS) experiments have been carried out in N-2 and N-2-H2O atmospheres on a Pt-based catalyst physically mixed with an Eu-doped ZrO2 ionic conductor as a function of temperature under realistic conditions of the water gas shift (WGS) reaction. This work aims to demonstrate the significant effect of having active H2O on the ionic conductor surface at reaction temperatures to provide it to Pt metal sites. The ionic conductor, Eu-doped zirconia matrix, presents defects (oxygen vacancies, O-v) that allows upon H2O dissociation the formation of a hydrogen-bonded molecular water layer favoring diffusion through a Grotthuss mechanism below 300 degrees C. In the presence of H2O, the O-v are occupied by hydroxyl species as observed in the Eu 4d spectra, which differentiate two types of Eu oxidation states. The Eu3+-to-Eu2+ atomic ratio increases with the occupancy of the O-v by hydroxyls. Moreover, while the Pt-based catalyst alone is unable to create Pt-OH bonds, the physical mixture of the Pt-based catalyst and the ionic conductor allows the formation of Pt-OH bonds from room temperature up to 300 degrees C. These data demonstrate that the increase in molecular water concentration on the ionic conductor surface up to 300 degrees C acts as a reservoir to provide water to the Pt surface, enhancing the catalyst performance in the WGS reaction, supporting the importance of the surface H2O concentration in the reaction kinetics.
Septiembre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.4c04287
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
In situ XRD and operando XRD-XANES study of the regeneration of LaCo0.8Cu0.2O3 perovskite for preferential oxidation of CO
Pereñiguez, RP; Ferri, DMaterials Today Sustainability, 27 (2024) 100867 DOI: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2024.100867
Abstract
Combinations of perovskite-type oxides with transition and precious metals exhibit remarkable regenerating properties that can be exploited for catalytic applications. The objective of the present work was to study the structural changes experienced by LaCo0.8Cu0.2O3 under reducing/oxidizing atmosphere (redox) and Preferential Oxidation of CO (PrOx, with high H2 concentration) conditions and their reversibility. LaCo0.8Cu0.2O3 was prepared by ultrasonic spray combustion and was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). Structural changes were followed by operando XRD and XAS. Metallic Co and Cu were segregated under both sets of reducing conditions and re-dissolved into the perovskite upon oxidation at 500 °C. Simultaneously, the perovskite-type oxide disappeared under reducing conditions and formed again upon high-temperature oxidation. The effects of this reversible reduction/dissolution of B-site metals on catalyst structure and activity were studied concerning the catalytic process of PrOx. The active phases of cobalt and copper oxides suffer a reduction during the PrOx reaction due to the high H2 concentration; thus, the application of an intermediate oxidation treatment can regenerate the catalytic system and the perovskite can be used for several cycles of reaction and regeneration. In contrast, when this intermediate oxidation treatment is not applied, the catalytic performance decreases in successive activity cycles.
Septiembre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2024.100867
Amber provenance as a Chrono-Cultural Proxy: Insights from FTIR analysis in the Iberian Peninsula
Garrido-Cordero, J.A.; Odriozola, C.P.; Sousa, A.C.; Romero-García, G.; Sánchez-Gómez, D.; Blanes, J.M.M.; Lázarich, M.; Zambrana-Vega, M.D.; Gonçalves, J.L.V.Journal of Archaeological Science Reports, 57 (2024) 104647 DOI: 10.1016/j.jasrep.2024.104647
Abstract
In recent years, significant advancements have occurred in our comprehension of amber consumption patterns in the Iberian Peninsula. This progress stems from the increasing volume of FTIR data related to both archaeological and geological amber. Consequently, a chronological model has been established, delineating amber consumption in the Iberian Peninsula from the Late Paleolithic to the Iron Age. Broadly, local amber consumption has been minimal since the Paleolithic period. Sicilian amber makes its appearance in Iberia around the 5th millennium BCE and fades away in the 2nd millennium BCE, giving way to Baltic amber, which has remained the sole source since then. The well-defined chronological model, the abundance of FTIR provenance data, and the infrequent association of amber with absolute or relative dates prompt us to explore whether provenance can serve as a chrono-cultural proxy for amber beads. This study introduces new amber finds, presents fresh FTIR data on archaeological amber ornaments, and incorporates minor updates and bug fixes to the general catalog. It is the outcome of a thorough bibliographic review and on-site analysis and examination of the beads. The results obtained in this study enable the reconstruction of amber consumption throughout Iberian prehistory, drawing on 29 newly FTIR-analyzed ambers from 9 sites. Our findings expand the empirical foundation, facilitating the confirmation of diachronic changes in amber consumption. Importantly, they affirm that amber provenance can indeed be employed as a viable chrono-cultural proxy.
Septiembre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jasrep.2024.104647
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
A critical view about use of scavengers for reactive species in heterogeneous photocatalysis
Puga, F; Navío, JA; Hidalgo, MCApplied Catalysis A, General, 685 (2024) 119879 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2024.119879
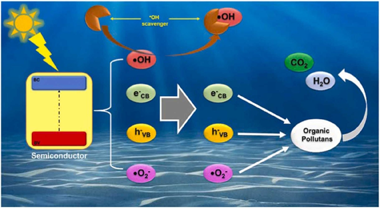
Abstract
In heterogeneous photocatalysis, different reactive species generated from the excitation of the semiconductor are responsible for the degradation of different contaminants in aqueous solution. In order to evaluate the influence of each of these reactive species on the photocatalysis process, it is common to perform an analysis using different chemical compounds, which (in theory) react selectively with only one reactive species, preventing this species from participating in the process. Questioning this analysis is the aim of this work and the reasons that lead us to this will be described and discussed. For this, different investigations were selected where this analysis was carried out on two model substrates, Rhodamine B and Phenol. With this, it was possible to determine which compounds are most used as scavengers for the different reactive species, and how these compounds influence the photodegradation process. It was possible to shown that none of the commonly used scavengers react selectively with only one reactive species, since it can also influence other reactions, either by reacting with other reactive species, with the surface of the catalyst, or with the substrate under study, among others. In our opinion, the conclusions obtained by using scavenger analysis should be carefully considered, and the compounds used should be renamed as interfering species of the photocatalytic process.
Septiembre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2024.119879
Materiales Coloidales
Sodium lanthanide tungstate-based nanoparticles as bimodal contrast agents for in vivo high-field MRI and CT imaging
Gómez-González, E; Caro, C; Núñez, NO; González-Mancebo, D; Urbano-Gámez, JD; García-Martín, ML; Ocaña, MJournal of Materials Chemistry B (2024). DOI: 10.1039/d4tb01157k
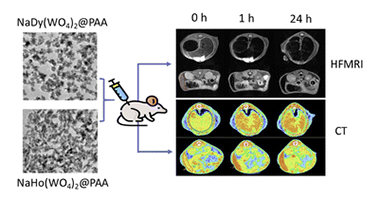
Abstract
Research on high-field magnetic resonance imaging (HF-MRI) has been increased in recent years, aiming to improve diagnosis accuracy by increasing the signal-to-noise ratio and hence image quality. Conventional contrast agents (CAs) have important limitations for HF-MRI, with the consequent need for the development of new CAs. Among them, the most promising alternatives are those based on Dy3+ or Ho3+ compounds. Notably, the high atomic number of lanthanide cations would bestow a high capability for X-ray attenuation to such Dy or Ho-based compounds, which would also allow them to be employed as CAs for X-ray computed tomography (CT). In this work, we have prepared uniform NaDy(WO4)(2) and NaHo(WO4)(2) nanoparticles (NPs), which were dispersible under conditions that mimic the physiological media and were nontoxic for cells, meeting the main requirements for their use in vivo. Both NPs exhibited satisfactory magnetic relaxivities at 9.4 T, thus making them a promising alternative to clinical CAs for HF-MRI. Furthermore, after their intravenous administration in tumor-bearing mice, both NPs exhibited significant accumulation inside the tumor at 24 h, attributable to passive targeting by the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. Therefore, our NPs are suitable for the detection of tumors through HF-MRI. Finally, NaDy(WO4)(2) NPs showed a superior X-ray attenuation capability than iohexol (commercial CT CA), which, along with their high r(2) value, makes them suitable as the dual-probe for both HF-MRI and CT imaging, as demonstrated by in vivo experiments conducted using healthy mice.
Septiembre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1039/d4tb01157k
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Oxygen vacancy-dependent low-temperature performance of Ni/CeO2 in CO2 methanation
Liao, LL; Wang, KL; Liao, GF; Nawaz, MA; Liu, KCatalysis Science & Technology, (2024). DOI: 10.1039/d4cy00679h
Abstract
The transformative power of CO2 methanation can efficiently transform greenhouse gases into high-value products, aligning with the carbon neutrality goals. However, achieving this target at low temperature requires cumbersome efforts in designing catalysts that possess high reactivity and selectivity. Focusing on understanding the pivotal role of alkaline (such as Ca) sites in catalyzing these reactions at lower temperature could be a way of strategically creating oxygen vacancies with varying activity gradients. Designing CaCe-SG via a sol-gel method in the current study to integrate Ca into the CeO2 lattice marked the highly active moderate-strength alkaline centers which resulted in the intrinsic activity soaring by an impressive 400% compared to the conventional Ni/CeO2 catalysts. Supported by H-2-TPD, Raman, and XPS analyses, a crucial revelation was unveiled where Ca modification induced a surge in the dispersion of active Ni species on Ni/CaCe-SG catalysts, thereby enhancing the abundant surface oxygen vacancies. In situ infrared spectroscopy further confirmed that the modified catalyst diligently followed the reaction pathway of CO3H* -> HCOO* -> CH4, culminating in the CO2 methanation activity with a low-temperature catalyst via the meticulous optimization of synthesis methods that propelled the process forward to the anticipated oxygen vacancy-induced moderate-strength alkaline centers.
Septiembre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1039/d4cy00679h
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Role of Inter-Particle Connectivity in the Photo-Carrier Cooling Dynamics in Perovskite Quantum Dot Solids
Tiede, DO; Koch, KA; Romero-Pérez, C; Ucer, KB; Calvo, ME; Galisteo-López, JF; Míguez, H; Kandada, ARSAdvanced Optical Materials, (2024) 2401483 DOI: 10.1002/adom.202401483
Abstract
Intraband carrier relaxation in quantum dots (QDs) has been a subject of extensive spectroscopic investigation for several decades, and have been used to optimize the efficiency of opto-electronic processes. In the past few years, metal halide perovskites-based QDs have been shown to exhibit slow hot-carrier cooling characteristics that are desirable for photo-energy harvesting technologies. While several mechanisms are proposed to rationalize the retardation of the cooling dynamics, including hot-phonon bottleneck and polaronic effects, the role of inter-particle connectivity in these dynamics is largely ignored. Here, an in-depth study of photo-excitation dynamics and carrier cooling on perovskite QD solids with varying degrees of inter-dot coupling is presented. It is observed that inter-particle connectivity has deterministic effects on the many-body interactions that are relevant for carrier cooling. These include carrier-carrier interactions that result in Auger-reheating of the carriers, and lattice characteristics that subsequently affect the phonon-assisted cooling dynamics. This spectroscopic study of ultrafast carrier dynamics in perovskite QD solids establishes inter-dot separation as a critical material design parameter for the optimization of photo-generated carrier temperature, which fundamentally determines the luminescence characteristics and thus the opto-electronic quality of the material.
The photo-excitation dynamics and carrier cooling in metal halide perovskite quantum dot solids are investigated here. Evidence for the deterministic role of inter-particle connectivity on the many-body interactions relevant to carrier cooling is discussed. These include carrier-carrier interactions that result in Auger-reheating of the carriers, and lattice coupling that subsequently affects the phonon-assisted cooling dynamics. image
Septiembre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.202401483
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Tailoring of Self-Healable Polydimethylsiloxane Films for Mechanical Energy Harvesting
Ghosh, K; Morgan, A; García-Casas, X; Kar-Narayan, SACS Applied Energy Materials, 7 (2024) 8185-8195 DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.4c01275
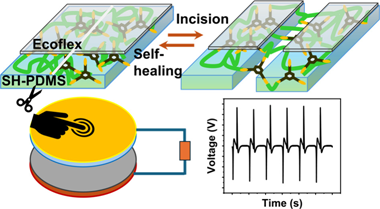
Abstract
Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) have emerged as potential energy sources, as they are capable of harvesting energy from low-frequency mechanical actions such as biological movements, moving parts of machines, mild wind, rain droplets, and others. However, periodic mechanical motion can have a detrimental effect on the triboelectric materials that constitute a TENG device. This study introduces a self-healable triboelectric layer consisting of an Ecoflex-coated self-healable polydimethylsiloxane (SH-PDMS) polymer that can autonomously repair mechanical injury at room temperature and regain its functionality. Different compositions of bis(3-aminopropyl)-terminated PDMS and 1,3,5-triformylbenzene were used to synthesize SH-PDMS films to determine the optimum healing time. The SH-PDMS films contain reversible imine bonds that break when the material is damaged and are subsequently restored by an autonomous healing process. However, the inherent stickiness of the SH-PDMS surface itself renders the material unsuitable for application in TENGs despite its attractive self-healing capability. We show that spin-coating a thin layer (approximate to 32 mu m) of Ecoflex on top of the SH-PDMS eliminates the stickiness issue while retaining the functionality of a triboelectric material. TENGs based on Ecoflex/SH-PDMS and nylon 6 films show excellent output and fatigue performance. Even after incisions were introduced at several locations in the Ecoflex/SH-PDMS film, the TENG spontaneously attained its original output performance after a period of 24 h of healing. This study presents a viable approach to enhancing the longevity of TENGs to harvest energy from continuous mechanical actions, paving the way for durable, self-healable mechanical energy harvesters.
Septiembre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.4c01275
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Elucidating the Mechanism of Iron-Catalyzed Graphitization: The First Observation of Homogeneous Solid-State Catalysis
Hunter, RD; Takeguchi, M; Hashimoto, A; Ridings, KM; Hendy, SC; Zakharov, D; Warnken, N; Isaacs, J; Fernández-Muñoz, S; Ramirez-Rico, J; Schnepp, ZAdvanced Materials, 36 (2024) 2404170 DOI: 10.1002/adma.202404170
Abstract
Carbon is a critical material for existing and emerging energy applications and there is considerable global effort in generating sustainable carbons. A particularly promising area is iron-catalyzed graphitization, which is the conversion of organic matter to graphitic carbon nanostructures by an iron catalyst. In this paper, it is reported that iron-catalyzed graphitization occurs via a new type of mechanism that is called homogeneous solid-state catalysis. Dark field in situ transmission electron microscopy is used to demonstrate that crystalline iron nanoparticles “burrow” through amorphous carbon to generate multiwalled graphitic nanotubes. The process is remarkably fast, particularly given the solid phase of the catalyst, and in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction is used to demonstrate that graphitization is complete within a few minutes.
Septiembre, 2024 · DOI: 10.1002/adma.202404170
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Trap Depth Distribution Determines Afterglow Kinetics: A Local Model Applied to ZnGa2O4:Cr3+
Romero, M; Castaing, V; Lozano, G; Míguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c01296
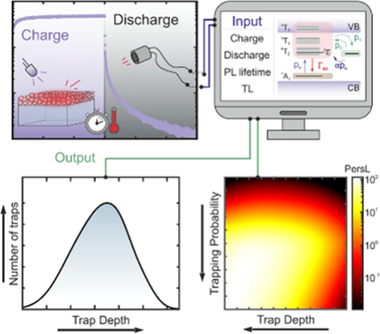
Abstract
Persistent luminescence materials have applications in diverse fields such as smart signaling, anticounterfeiting, and in vivo imaging. However, the lack of a thorough understanding of the precise mechanisms that govern persistent luminescence makes it difficult to develop ways to optimize it. Here we present an accurate model to describe the various processes that determine persistent luminescence in ZnGa2O4:Cr3+, a workhorse material in the field. A set of rate equations has been solved, and a global fit to both charge/discharge and thermoluminescence measurements has been performed. Our results establish a direct link between trap depth distribution and afterglow kinetics and shed light on the main challenges associated with persistent luminescence in ZnGa2O4:Cr3+ nanoparticles, identifying low trapping probability and optical detrapping as the main factors limiting the performance of ZnGa2O4:Cr3+, with a large margin for improvement. Our results highlight the importance of accurate modeling for the design of future afterglow materials and devices.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c01296
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Effect of the interaction between basicity and reductive character of melting atmosphere - both extreme - on the oxidation and coordination states assumed by transition metals when doped to silicate glasses
Zandona, A; Castaing, V; Shames, AI; Helsch, G; Pirri, A; Toci, G; Deubener, J; Allix, M; Goldstein, AJournal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 637 (2024) 123038 DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2024.123038
Abstract
The influence of an extremely reductive melting atmosphere on the oxidation and coordination states adopted by transition metals in an ultrabasic host was evaluated. An invert glass (46SiO(2)center dot 11Na(2)O center dot 21CaO center dot 22BaO, basicity = 0.71) was synthesized in container-less conditions, on a jet of Ar 5%H-2. Performed measurements included optical absorption, optical emission and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. The results revealed that the used atmosphere dramatically decreases the oxidation state(s) dopants assume, compared to those stable under oxidative melting in such a host. After reductive melting: (i) Ti3+ appears alongside Ti4+; (ii) V3+ is added to V5+; (iii) Mn2+ fully substitutes Mn3+ and Mn5+; (iv) Cu2+ is entirely replaced by Cu(+)and Cu-0. These results could be rationalized considering the action of additional factors like ligand-field stabilization energy, ionization energy and special filling numbers of the 3d-subshell. They modulate the interaction between basicity and atmosphere redox character, in a way specific to each transition metal.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2024.123038
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
A zirconia/tantalum biocermet: in vitro and in vivo evaluation for biomedical implant applications
Smirnov, A; Guitián, F; Ramírez-Rico, J; Bartolomé, JFJournal of Materials Chemistry B (2024) DOI: 10.1039/d4tb01158a
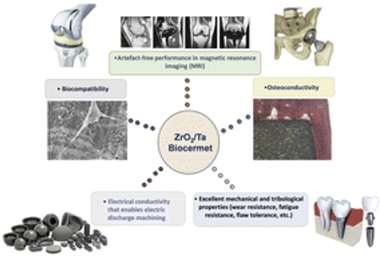
Abstract
A biocermet made of zirconia/20 vol% tantalum (3Y-TZP/Ta) is a new composite with exceptional capabilities due to a combination of properties that are rarely achieved in conventional materials (high strength and toughness, cyclic fatigue resistance and flaw tolerance, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, etc.). In this study, for the first time, the biomedical performance of a 3Y-TZP/Ta biocermet was evaluated in detail. Its in vitro biocompatibility was assessed using mesenchymal stem cell culture. The effectiveness of in vivo osteointegration of the biocermet was confirmed 6 months after implantation into the proximal tibiae of New Zealand white rabbits. In addition, the possibility of using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for medical analysis of the considered biocermet material was studied. The 3Y-TZP/Ta composite showed no injurious effect on cell morphology, extracellular matrix production or cell proliferation. Moreover, the implanted biocermet appeared to be capable of promoting bone growth without adverse reactions. On the other hand, this biocermet demonstrates artefact-free performance in MRI biomedical image analysis studies, making it more suitable for implant applications. These findings open up possibilities for a wide range of applications of these materials in orthopedics, dentistry and other areas such as replacement of hard tissues.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.1039/d4tb01158a
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Adsorptive removal of cationic dye from aqueous solutions using activated carbon prepared from Crataegus monogyna/sodium alginate/polyaniline composite beads: Experimental study and molecular dynamic simulation
Chaima, H; Eddine, BC; Faouzia, B; Rana, H; Salah, BA; Gil, A; Imene, BA; Ferhat, D; Riadth, B; Mokhtar, BJournal of Molecular Liquids, 408 (2024) 125372 DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2024.125372
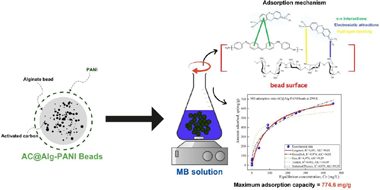
Abstract
This study presents a novel composite beads, AC@Alg-PANI, consisting of activated carbon (AC) derived from Crataegus monogyna, sodium alginate (Alg), and polyaniline (PANI), tested for the removal of methylene blue (MB). The physicochemical characteristics of the composite beads were analyzed using methods such as pHPZC, FTIR, TGA/DTA, SEM, and BET. Moreover, factors affecting the adsorption of MB, such as initial pH, dye concentration, adsorbent weight, ionic strength, and temperature, were also explored. A full factorial design was implemented to identify the optimum conditions for removal, which were found to be a pH of 6, an adsorbent amount of 100 mg, and a dye concentration of 100 mg/L. The isotherm data indicated that the adsorption of MB by AC@Alg-PANI follows the Langmuir model, with a maximum adsorption capacity of 774.6 mg/g. The adsorption kinetics followed the pseudo-first-order model, indicating that the adsorption process is physical in nature. The thermodynamic results suggest that MB adsorption on AC@Alg-PANI was favorable, spontaneous, and endothermic. Additionally, after five regeneration cycles, the composite beads demonstrated excellent recyclability for MB dye removal with high efficiency. Furthermore, molecular dynamics simulations (MDS) of the adsorption energy highlighted the physically spontaneous nature of the process, involving various weak interactions, including van der Waals forces, intermolecular interactions, hydrogen bonding, and π-electron interactions.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2024.125372
Materiales Coloidales
Mixed oxide ion-proton conductivity and the ionic migration mechanism in isolated tetrahedral LaVO4 by acceptor doping
Geng, XY; Hang, GQ; Fernadez-Carrion, AJ; Ming, X; Deng, SH; He, LH; Kuang, XJ; Yang, XYInorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 11 (2024) DOI: 10.1039/D4QI00870G
Abstract
Solid-state oxide ion and proton conductors are garnering significant attention due to their high ionic conductivity and potential applications in a range of electrochemical devices, including solid oxide fuel cells and gas sensors. In this study, we report the influence of partial substitution of La3+ in isolated tetrahedral LaVO4 ceramics with 0.01 mol of alkaline-earth metals Ca2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+ on the phase stability and electrical properties. It was found that acceptor doping effectively enhances mixed oxide ion and proton conductivities, with Sr2+ substitution yielding the highest conductivity, achieving ∼10−3 S cm−1 at 900 °C under a wet O2 atmosphere. DFT calculations and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations revealed that protons preferentially form hydrogen bonds with the lattice oxygen near the dopants and migrate through a continuous process of hopping and rotation between inter- and intra-tetrahedral VO4 groups. Additionally, the existence of oxygen vacancies facilitates the formation of V2O7 dimers through sharing corners with adjacent isolated VO4 tetrahedra, enabling ion exchange through a synergistic mechanism involving V2O7 dimer breaking and reforming. This research highlights the critical role of the deformation and rotational flexibility of isolated tetrahedral units in facilitating oxide ion and proton transport, underscoring the potential for developing mixed oxide ion and proton conductors in oxygen vacancy-deficient oxides with tetrahedral-based structures.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.1039/D4QI00870G
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Efficient tuning of the selectivity of Cu-based interface for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction by ligand modification
Yan, Y; Li, TX; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Zhao, YG; Wang, S; Chen, X; Wang, D; Schaaf, P; Wang, XY, Guo, GSMaterials Today Energy, 44 (2024) 101620 DOI: 10.1016/j.mtener.2024.101620
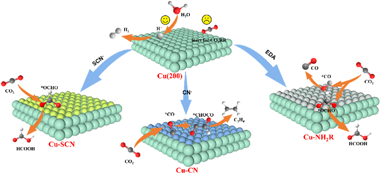
Abstract
The development of efficient strategies to tune the CO2RR selectivity of Cu-based catalytic interfaces, especially on specific domains, such as Cu (200) facets with high activity toward competitive hydrogenation evolution reaction (HER), remains a challenging task. In this work, Cu-based catalytic layers with thiocyanate (-SCN), cyanide (-CN), or ethylenediamine (-NH2R) coordination linkages are prepared on Cu nanocolumns arrays (Cu NCAs) with predominant (200) exposed facets. The coordination of these ligands induces more Cu+ species and inhibits the adsorption of H & lowast; on the Cu (200) facet, leading to enhanced CO2RR performance and substantially suppressing the competitive HER. The faradaic efficiency (FE) of Cu-SCN, Cu-CN, and Cu-NH2R NWAs for producing HCOOH, C2H4, and C1 mixture products (HCOOH and CO) reach to 66.5%, 21.1%, and 57.1%, respectively. In situ spectroscopic studies reveal Cu-SCN, Cu-CN, and Cu-NH2R exhibit more reasonable adsorption energy toward & lowast;OCHO, *CO, and *COOH intermediates, promoting the HCOOH, C2H4, and C1 mixture generation, respectively. This study might provide a new perspective for the development of high-performance Cu-based CO2RR catalytic electrodes based on the combination of various commercial free-standing Cu substrates and organic/inorganic ligands. (c) 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mtener.2024.101620
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
An efficient pressure sensor based on environmental-friendly CNTs-graphene-PDMS film
Sadiq, H; Hu, H; Huang, S; Rizwan, M; Muhammad, A; Nawaz, MA; Zeeshan, MPhysica Scripta, 99 (2024) 0859a9 DOI: 10.1088/1402-4896/ad564a
Abstract
Given the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence, there is an escalating demand for wearable sensors. An efficient graphene-based material synthesized from the mesophase pitch of waste slurry oil was integrated into a cost-effective piezoresistive pressure sensor consisting of a conductive film made of carbon nanotubes (CNTs), graphene, and Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). A simple fabrication approach has been suggested to infuse PDMS with CNTs-graphene, resulting in a pressure sensor exhibiting superior conductivity, enhanced sensitivity, and quick responsiveness to diverse pressure variations. Moreover, films containing varying percentages of graphene were compared. Scanning electron microscopy was utilized to examine the surface and structural characteristics of the CNTs-graphene-PDMS film, alongside studying the pressure sensor's sensing capabilities. Various applications were examined for both the individual sensor and the array of sensors. The findings demonstrate the successful detection of diverse human motions, Morse code recognition, and effective discernment of various pressures by the fabricated pressure sensor, indicating its potential for applications in smart devices, robotics, and wearable sensors.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.1088/1402-4896/ad564a
Materiales Coloidales
Realization of Extreme Nonstoichiometry in Gadolinium Aluminate Garnets by Glass Crystallization Synthesis
Fang, X; Castaing, V; Becerro, AI; Cao, WW; Veron, E; Zanghi, D; Dyer, MS; Genevois, C; Allix, M; Pitcher, MJChemistry of Materials, 36 (2024) 8555-8563 DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.4c02266
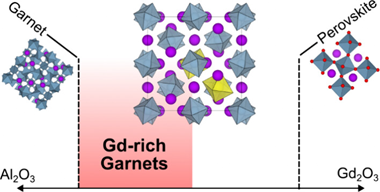
Abstract
The garnet aluminates RE3Al5O12 (RE = Gd - Lu, Y) are an important class of optical materials with a range of applications. Typically, they do not tolerate large deviations from ideal stoichiometry, and their luminescence properties are controlled by dopant selection rather than modification of the host structure. Here, we use glass crystallization as a nonequilibrium synthesis route to a new family of highly nonstoichiometric gadolinium aluminate garnets, of formula Gd3+xAl5-xO12 with x <= 0.60. Remarkably, this range is much broader than the previously reported Y3+xAl5-xO12 series (x <= 0.4), despite the vast size contrast between Al3+ and Gd3+, which are forced to share a crystallographic site in the nonstoichiometric materials: the endmember Gd3.6Al4.4O12 lies halfway between ideal garnet and perovskite stoichiometries, with 30% of its octahedral Al3+ sites substituted by Gd3+. In principle, this crystal chemistry should allow the synthesis of phosphor systems with rare-earth activators distributed over two different cation sublattices. To probe the response of luminescence properties to extreme nonstoichiometry in Gd3+xAl5-xO12, we synthesized three model phosphor systems by doping with Ce3+, Tb3+, or Tm3+/Yb3+ and found that upconversion (Tm3+/Yb3+) phosphors have the most potential to be tuned by this approach. These results demonstrate that highly nonstoichiometric garnet aluminates are not limited to small rare-earth hosts such as YAG, opening new opportunities for development of different garnet-based optical and magnetic materials.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.4c02266
Crafting illusions: Human-made composite coating used to simulate amber beads in prehistoric Iberia
Odriozola, CP; Garrido-Cordero, JA; Sousa, AC; Martínez-Blanes, JM; Romero-García, G; Sánchez-Gómez, D; Benaigues, MEI; Romero-Vera, D; Simón-Vallejo, MD; Vega, MDZ; González, JLMJournal of Archaelogical Science, 168 (2024) 106011 DOI: 10.1016/j.jas.2024.106011
Abstract
The discovery of a set of beads, comprising both Sicilian amber and resin-coated beads in the Middle Bronze Age burial site of Cova del Gegant (Sitges, Barcelona, Spain), has sparked inquiries into whether the coating was intended for imitation or counterfeiting of amber. We assert that human-made materials, such as bead coatings, are intentionally conceived, designed, and crafted to fulfill specific functions. Thus, for an object to effectively fulfill its intended purpose, it must meet particular performance criteria influenced by situational factors. This paper aims to construct an empirically grounded narrative elucidating the development and function of resin-coated bead technology. Our methodology includes a comprehensive quantitative analysis of the coating and beads, an exploration of the interplay between technical choices and situational factors, and an investigation into whether the simulation of sensory performance characteristics played a pivotal role in the concept and design of resin-coated beads. Additionally, we synthesize data to unveil broader patterns related to the crafting and utilization of resin-coated and amber beads across time and space. We have documented resin-coated beads in the Iberian Peninsula from the Neolithic period (5th to 3rd millennia BCE) until at least the Middle Bronze Age (first half of the 2nd millennium BCE), where they coexisted with amber beads. Analysis employing ATR-FTIR and mu-CT imaging has revealed a composite coating comprising pine resin, beeswax, and carotene, adhered to shell beads with bone glue. This composite material represents the earliest known development in human history, unique to the Iberian Peninsula and without parallel in Prehistoric Europe. Our examination of the performance characteristics and functional roles of resin-coated beads suggests their potential as substitutes for amber beads, particularly in regions where amber was scarce or inaccessible. Despite being crafted from commonplace materials, these coated beads exhibit intentional design choices likely aimed at simulating the visual performance characteristics of amber. This deliberate effort, alongside their widespread distribution across time and space, indicates that composite-coated beads held symbolic and social significance akin to amber beads.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jas.2024.106011
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Transparent porous films with real refractive index close to unity for photonic applications
Miranda-Muñoz, JM; Viaña, JM; Calvo, ME; Lozano, G; Míguez, HMaterials Horizons (2024). DOI: 10.1039/d4mh00826j
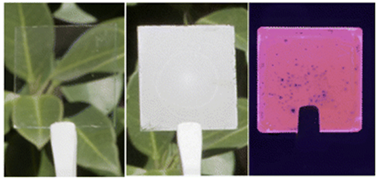
Abstract
Herein, we demonstrate mechanically stable large-area thin films with a purely real refractive index (n) close to 1 in the optical range. At specific wavelengths, it can reach values as small as n = 1.02, the lowest reported for thin solid slabs. These are made of a random network of interwoven spherical silica shells, created by chemical vapour deposition of a thin layer of silica on the surface of randomly packed monodisperse polymer nanoparticles that form a film. Thermal processing of the composites results in highly porous silica-based transparent thin films. We demonstrate the potential of this approach by making novel photonic materials such as strong optical diffusers, built by integrating scattering centers within the ultralow n transparent films, or highly efficient light-emitting slabs, in which losses by total internal reflection are practically absent as a result of the almost null optical impedance at the film-air interface.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.1039/d4mh00826j
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
FGD-Gypsum Waste to Capture CO2 and to Recycle in Building Materials: Optimal Reaction Yield and Preliminary Mechanical Properties
Moreno, V; González-Arias, J; Ruiz-Martinez, JD; Balart-Gimeno, R; Baena-Moreno, FM; Leiva, CMaterials, 17 (2024) 3774 DOI: 10.3390/ma17153774
Abstract
The use of waste to capture CO2 has been on the rise, to reduce costs and to improve the environmental footprint. Here, a flue gas desulfurization (FGD) gypsum waste is proposed, which allows us to obtain a CaCO3-based solid, which should be recycled. The CO2 capture stage has primarily been carried out via the direct carbonation method or at high temperature. However, a high energy penalty and/or long reaction times make it unattractive from an industrial perspective. To avoid this, herein an indirect method is proposed, based on first capturing the CO2 with NaOH and later using an aqueous carbonation stage. This allows us to capture CO2 at a near-ambient temperature, improving reaction times and avoiding the energy penalty. The parameters studied were Ca2+/CO32− ratio, L/S ratio and temperature. Each of them has been optimized, with 1.25, 100 mL/g and 25 °C being the optimal values, respectively, reaching an efficiency of 72.52%. Furthermore, the utilization of the produced CaCO3 as a building material has been analyzed. The density, superficial hardness and the compressive strength of a material composed of 10 wt% of CaCO3 and 90 wt% of commercial gypsum, with a water/solid ratio of 0.5, is measured. When the waste is added, the density and the mechanical properties decreased, although the compressive strength and superficial hardness are higher than the requirements for gypsum panels. Thus, this work is promising for the carbonation of FGD-gypsum, which involves its chemical transformation into calcium carbonate through reacting it with the CO2 of flue gasses and recycling the generated wastes in construction materials
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.3390/ma17153774
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Levofloxacin Degradation, Antimicrobial Activity Decrease, and Potential for Water Disinfection Using Peroxydisulfate Activation by Ag/TiO2 under Sunlight
Jojoa-Sierra, SD; Jaramillo-Pérez, C; Serna-Galvis, EA; García-Rubio, I; Hidalgo, MC; Navío, JA; Ormad, MP; Torres-Palma, RA; Mosteo, RWater, 16(17) (2024) 2434 DOI: 10.3390/w16172434
Abstract
Water quality and usability are global concerns due to microbial and chemical pollution resulting from anthropogenic activities. Therefore, strategies for eliminating contaminants are required. In this context, the removal and decrease in antibiotic activity (AA) associated with levofloxacin (LEV), using TiO2 and Ag/TiO2 catalysts, with and without sunlight and peroxydisulfate, was evaluated. Additionally, the disinfection capacity of catalytic systems was assessed. The catalysts were synthesized and characterized. Moreover, the effect of Ag doping on visible light absorption was determined. Then, the photocatalytic treatment of LEV in water was performed. The materials characterization and EPR analyses revealed that LEV degradation and AA decrease were ascribed to a combined action of solar light, sulfate radical, and photocatalytic activity of the TiO2-based materials. Also, the primary byproducts were elucidated using theoretical analyses (predictions about moieties on LEV more susceptible to being attacked by the degrading species) and experimental techniques (LC-MS), which evidenced transformations on the piperazyl ring, carboxylic acid, and cyclic ether on LEV. Moreover, the AA decrease was linked to the antibiotic transformations. In addition, the combined system (i.e., light/catalyst/peroxydisulfate) was shown to be effective for E. coli inactivation, indicating the versatility of this system for decontamination and disinfection.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.3390/w16172434
Reactividad de Sólidos - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
BN nanosheets reinforced zirconia composites: An in-depth microstructural and mechanical study
Muñoz-Ferreiro, C; Reveron, H; Rojas, TC; Reyes, DF; Cottrino, S; Moreno, P; Prada-Rodrigo, J; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Chevalier, J; Gallardo-López, A; Poyacto, RJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 44(10) (2024) 5846-5860 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2024.02.002
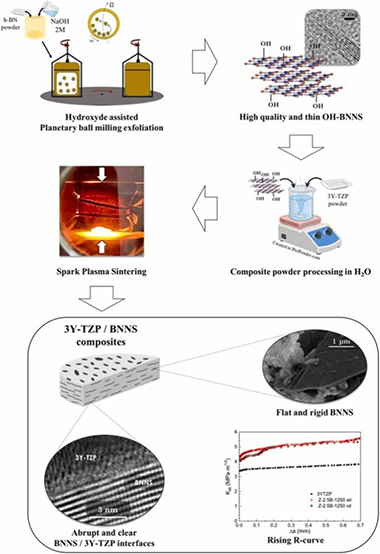
Abstract
This paper deals with the effect of hydroxylated boron nitride nanosheets (BNNS) incorporation on the microstructural and mechanical features of zirconia ceramics. Few-layered BNNS were synthesized via a simple hydroxide-assisted planetary ball milling exfoliation technique. 3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (3Y-TZP) with 2.5 vol% BNNS powders were prepared by an environmentally friendly process in water, and spark-plasma sintered at three temperatures to explore the in-situ reduction of the functionalized BNNS. An exhaustive study by (S)TEM techniques was performed to elucidate the influence of the sintering temperature on the matrix and the 3Y-TZP/BNNS interfaces, revealing that BNNS were homogeneously distributed throughout the matrix with an abrupt transition at 3Y-TZP/BNNS interfaces. BNNS effectively hindered slow crack growth, thus increasing the composite's crack growth resistance by about 30 %. A 1 MPa·m1/2 rising R-curve was also induced by crack bridging.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2024.02.002
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Integrating catalytic tandem reactions for the next of biofuels: A
Blay-Roger, R; Carrasco-Ruiz, S; Reina, TR; Bobadilla, LF; Odriozola, JA; Nawaz, MAChem Catalysis, 4 (2024) 100987 DOI: 10.1016/j.checat.2024.100987
Abstract
In this piece, we explore the transformative potential of sustainable biofuel production as a solution to the energy crisis and a pivotal element in realizing the environmental and societal ambitions of Society 5.0. Through a critical examination of "bottom-up"and "topdown"strategies for converting bio-feedstocks sourced from anthropogenic activities into renewable fuels, the work underscores the need for innovation in catalysts and process intensification. By highlighting the advances and challenges in harnessing unconventional feedstocks and integrating renewable energy, this work points to a future where biofuels stand as a cornerstone of a sustainable energy landscape. The significance of this discussion extends beyond the technical realm, offering a vision for a circular economy that reduces dependence on fossil fuels, addresses climate change, and promotes global energy security. It calls for a united front among researchers, industry leaders, and policymakers to drive the biofuel sector toward efficiency, scalability, and widespread adoption.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.checat.2024.100987
Materiales Avanzados
Design of a Trailer Adapted for Accommodation and Transport of Beehives
Garzón, E; García-Garzón, V; Pascual García, J; Sánchez-Soto, PJDesigns, 8 (2024) 82 DOI: 10.3390/designs8040082
Abstract
There is relevant interest concerning beehives, taking into account climate change and its influence on bees’ behavior. A part of the industrial engineering sector is focusing on beekeeping applications. More specifically, the present study aims to develop a trailer for the transport of beehives adapted to be placed or fixed to a tractor or a vehicle trailer, with the objective of transporting the beehives safely and stably during transhumance. The proposed novel design relates to a trailer that incorporates a device for housing a rectangular section of the beehives, which can be adapted for fixing or housing in a vehicle or in a vehicle trailer. The device comprises a lower support structure, adapted to support a plurality of rectangular sections of beehives stacked horizontally on the lower structure, an upper frame adapted to house the beehives inside, and two or more connecting elements between the lower structure and the upper frame. The connection of the trailer with the device facilitates the loading and unloading of the beehives by mechanical means. The different parts have been designed as individual pieces and then assembly is carried out to achieve the complete design. This method of implementation is because the simulation of individual components is simpler and easier, since if it is carried out through assembly, the type of joint, such as welding, and the length of the weld would have to be indicated at each point of contact between components, along with its thickness and all the necessary parameters. Therefore, in those welding points, fixed fastenings are indicated and so will simplify it. In accordance with the individual creation of each part, its own load simulation has been carried out. Static analyses are performed taking into account structural elements of this proposed design, with restrictions and loads being established. The analysis, including upper bars and supports, has been completed with several situations. Based on stress values, deformations have been determined and calculations evaluated. The trays have been manufactured using flat steel bars and angled bars for the legs and support of the hives.
Agosto, 2024 · DOI: 10.3390/designs8040082
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Direct laser writing of MnOx x decorated laser-induced graphene on paper for sustainable microsupercapacitor fabrication
Abreu, R; Klem, MD; Pinheiro, T; Pinto, JV; Alves, N; Martins, R; Carlos, E; Coelho, JFlatchem, 46 (2024) 100672 DOI: 10.1016/j.flatc.2024.100672
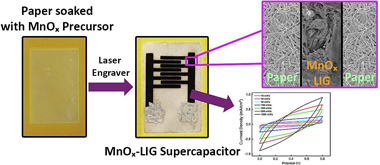
Abstract
Laser-induced graphene (LIG) on paper is a popular choice for fabricating flexible micro-supercapacitors (MSCs) as it is a simple and sustainable process. However, carbon-based MSC electrodes have limited energy densities. To address this challenge, this study presents a highly reproducible and cost-effective method for decorating manganese oxide (MnOx) x ) on interdigital LIG MSC electrodes, fabricated via a single-step direct laser writing (DLW) process on paper substrates. The paper fibers embedded with MnOx x precursors are transformed into graphene through laser processing while reducing the salt, resulting in the formation of MnOx-LIG. x-LIG. The resulting MnOx-LIG-MSC x-LIG-MSC exhibits a specific capacitance of 12.30 mF cm- 2 (0.05 mA cm- 2 ) with a 60 % retention at 1000 bending cycles (30 degrees), degrees ), due to the pseudocapacitive contribution of MnOx. x . Furthermore, the devices exhibit high electrochemical stability, retaining 190 % of the initial specific capacitance after 10,000 cycles, and a high energy density of 2.6 mu Wh cm-- 2 (at a power of 0.109 mW cm-- 2 ). The study demonstrates that manganese oxide- based LIG-MSCs have the potential to be used as energy storage devices for portable, low-cost, and flexible paper electronics.
Julio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.flatc.2024.100672
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Titania modifications with fluoride, sulfate, and platinum for photochemical reduction of chromium (VI)
Murcia, JJ; Hernández-Laverde, MS; Correa-Camargo, IA; Rojas-Sarmiento, HA; Navío, JA;Revista Facultad de Ingenieria, Universidad de Antiquia, 112 (2024) 86-97 DOI: 10.17533/udea.redin.20240304
Abstract
En este trabajo, la Titania se modificó por sulfatación o fluorización y platino en superficie, con el objetivo de mejorar la eficiencia en la reducción de Cr (VI) en comparación con el material TiO2 base sintetizado por el método sol-gel. Los materiales fueron caracterizados por DRX, SBET, UV-Vis DRS, FRX, TEM, FTIR y XPS. Las modificaciones permitieron obtener una mayor estabilidad en la fase Anatasa y en el área superficial del semiconductor. La adición de F y Pt en el TiO2 provocaron aumentos de absorción en la región visible del espectro electromagnético. Se observó una correlación entre las nuevas propiedades fisicoquímicas obtenidas tras la modificación del TiO2 y el rendimiento fotocatalítico del material. El mejor resultado en la reducción de cromo se obtuvo utilizando Pt-S-TiO2 como fotocatalizador, este material mostró una combinación adecuada de área superficial, alta absorción UV-Vis, alta hidroxilación y la existencia de nanopartículas de Pt en la superficie que favorecen un aumento de la vida media del par electrón-hueco. También se evaluaron parámetros de reacción que demostraron que el mejor desempeño fotocatalítico se obtuvo bajo atmósfera de N2, intensidad de luz de 120 W/m2 y 2 horas de tiempo total de reacción. Así mismo, se observó que aumentar el tiempo de reacción de 2 a 5 horas tuvo un efecto perjudicial sobre la eficiencia en la reducción de Cr (VI).
Julio, 2024 · DOI: 10.17533/udea.redin.20240304
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Finely Tunable Carbon Nanofiber Catalysts for the Efficient Production of HMF in Biphasic MIBK/H2O Systems
Bounoukta, CE; Megías-Sayago, C; Rendón, N; Ammari, F; Centeno, MA; Ivanova, SNanomaterials, 14 (2024) 1293 DOI: 10.3390/nano14151293
Abstract
This work proposes catalytic systems for fructose dehydration to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural using a series of functionalized carbon nanofibers. The catalysts were synthesized via finely selected covalent grafting in order to include a variety of functionalities like pure Bronsted acid, tandem Br & oslash;nsted/Lewis acid, and tandem Lewis acid/Lewis base catalysts. After the characterization and evaluation of acidity strength and the amount of acid centers, the catalyst series was screened and related to the product distribution. The best-performing catalyst was also used to optimize the reaction parameters in order to achieve 5-hydroxymethylfurfural yields rounding at 60% without significant humin formation.
Julio, 2024 · DOI: 10.3390/nano14151293
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
V2O5/TiO2 Catalyst for Catalytic Glucose Oxidation to Formic Acid in Batch Reactor: Vanadium Species Nature and Reaction Conditions Optimization
Alvarez-Hernández, D; Ivanova, S; Domínguez, MI; Blanes, JMM; Centeno, MATopics in Catalysis (2024) DOI: 10.1007/s11244-024-01982-0
Abstract
This study focused on the development of vanadium-based catalysts for formic acid production from glucose. The influence of different vanadium precursors on the catalytic activity of titania supported catalysts was contemplated and compared to the performance of commercial and synthesized unsupported V2O5. The obtained results reveal a successful deposition of multiple vanadium species on TiO2 as confirmed by XRD, Raman, and UV-Vis measurements. Catalyst screening identifies V5+ species as main player indicating its important oxidizing potential. Afterwards, the key reaction conditions, as temperature, time, pressure and catalyst loading, were optimized as well as the state of the catalyst after the reaction characterized.
Julio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1007/s11244-024-01982-0
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
New insights for valorization of polyolefins/light alkanes: catalytic dehydrogenation of n-alkanes by immobilized pincer-iridium complexes
Centeno-Vega, I; Megías-Sayago, C; Ivanova, SDalton Transactions, 53 (2024) 11216-11227 DOI: 10.1039/D4DT00847B
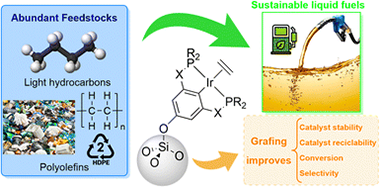
Abstract
This scientific review delves into the innovative realm of polyolefins/light alkanes valorization through their catalytic dehydrogenation employing pincer-ligated iridium organometallic complexes. These widely studied catalysts exhibit outstanding properties, although the intrinsic characteristics of homogeneous catalysis (such as challenging product–catalyst separation, poor applicability to continuous-flow processes and low recyclability) limit their activity and industrial application, as well as their thermal stability. Through the immobilization of complexes on inorganic supports, these downsides have been bypassed, harnessing the true potential of these catalysts, affording more selective and stable catalysts in addition to facilitating their implementation in industrial processes. The findings described herein contribute to the advancement in the understanding of catalytic processes in hydrocarbon transformations, offering promising avenues for sustainable and selective production of valuable chemical intermediates from readily available feedstocks.
Julio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1039/D4DT00847B
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Conformal TiO2 Aerogel-Like Films by Plasma Deposition: from Omniphobic Antireflective Coatings to Perovskite Solar Cell Photoelectrodesh
Obrero, JM; Contreras-Bernal, L; Rebollo, FJA; Rojas, TC; Ferrer, FJ; Orozco, N; Saghi, Z; Czemak, T; Pedrosa, JM; López-Santos, C; Ostrikov, KK; Borras, A; Sánchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, AACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 16 (2024) 39746-397600 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c00555
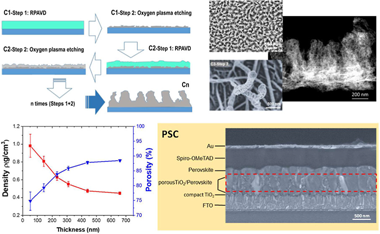
Abstract
The ability to control the porosity of thin oxide films is a key factor determining their properties. Despite the abundance of dry processes for synthesizing oxide porous layers, a high porosity range is typically achieved by spin-coating-based wet chemical methods. Besides, special techniques such as supercritical drying are required to replace the pore liquid with air while maintaining the porous network. In this study, we propose a new method for the fabrication of ultraporous titanium dioxide thin films at room or mild temperatures (T <= 120 degrees C) by a sequential process involving plasma deposition and etching. These films are conformal to the substrate topography even for high-aspect-ratio substrates and show percolated porosity values above 85% that are comparable to those of advanced aerogels. The films deposited at room temperature are amorphous. However, they become partly crystalline at slightly higher temperatures, presenting a distribution of anatase clusters embedded in the sponge-like open porous structure. Surprisingly, the porous structure remains after annealing the films at 450 degrees C in air, which increases the fraction of embedded anatase nanocrystals. The films are antireflective, omniphobic, and photoactive, becoming superhydrophilic when subjected to ultraviolet light irradiation. The supported, percolated, and nanoporous structure can be used as an electron-conducting electrode in perovskite solar cells. The properties of the cells depend on the aerogel-like film thickness, which reaches efficiencies close to those of commercial mesoporous anatase electrodes. This generic solvent-free synthesis is scalable and applicable to ultrahigh porous conformal oxides of different compositions, with potential applications in photonics, optoelectronics, energy storage, and controlled wetting.
Julio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c00555
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Embracing the sustainable horizons through bioenergy innovations: a path to a sustainable energy future
Blay-Roger, R; Saif, M; Bobadilla, LF; Ramírez-Reina, T; Nawaz, MA; Odriozola, JAFrontiers in Chemistry, 12 (2024) 1416102 DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1416102

Abstract
The urgent need for mitigating climate change necessitates a transformative shift in energy production and consumption paradigms. Amidst this challenge, bioenergy emerges as a pivotal contributor to the global energy transition, offering a diverse array of solid, liquid, and gaseous fuels derived from biomass. This mini review delves into the unique potential of bioenergy innovations, particularly renewable diesel, bio jet fuel, and ethanol, to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transform various industries. The article highlights critical technological advancements, supportive policies, and cross-sector collaboration essential for a sustainable energy transition. Specific challenges such as ensuring a consistent biomass feedstock supply, decentralizing processing units, and navigating complex regulatory frameworks are examined. Innovative solutions like decentralized biomass processing and enhanced biomass logistics are discussed as pathways to overcome these barriers. The review provides specific recommendations for near-term policies and strategies to support decentralized facilities, showcasing bioenergy's role in achieving a sustainable future.
Julio, 2024 · DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1416102
A supervised multiclass framework for mineral classification of Iberian beads
Sanchez-Gomez, D; Odriozola Lloret, CP; Sousa, AC; Garrido-Cordero, JA; Romero-García, G; Martínez-Blanes, JM; Benaiges, MEI; Villalobos-García, R; Gonçalves, VSPlos One, 19 (2024) e0302563 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302563
Abstract
Research on personal adornments depends on the reliable characterisation of materials to trace provenance and model complex social networks. However, many analytical techniques require the transfer of materials from the museum to the laboratory, involving high insurance costs and limiting the number of items that can be analysed, making the process of empirical data collection a complicated, expensive and time-consuming routine. In this study, we compiled the largest geochemical dataset of Iberian personal adornments (n = 1243 samples) by coupling X-ray fluorescence compositional data with their respective X-ray diffraction mineral labels. This allowed us to develop a machine learning-based framework for the prediction of bead-forming minerals by training and benchmarking 13 of the most widely used supervised algorithms. As a proof of concept, we developed a multiclass model and evaluated its performance on two assemblages from different Portuguese sites with current mineralogical characterisation: Cova das Lapas (n = 15 samples) and Gruta da Marmota (n = 10 samples). Our results showed that decisi & oacute;n-tres based classifiers outperformed other classification logics given the discriminative importance of some chemical elements in determining the mineral phase, which fits particularly well with the decision-making process of this type of model. The comparison of results between the different validation sets and the proof-of-concept has highlighted the risk of using synthetic data to handle imbalance and the main limitation of the framework: its restrictive class system. We conclude that the presented approach can successfully assist in the mineral classification workflow when specific analyses are not available, saving time and allowing a transparent and straightforward assessment of model predictions. Furthermore, we propose a workflow for the interpretation of predictions using the model outputs as compound responses enabling an uncertainty reduction approach currently used by our team. The Python-based framework is packaged in a public repository and includes all the necessary resources for its reusability without the need for any installation.
Julio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302563
Materiales Semiconductores para la Sostenibilidad
Strong angular and spectral narrowing ofelectroluminescence in an integrated Tamm-plasmon-driven halide perovskite LED
Ying, Z; Jiménez-Solano, A; Gatkowski, K; Sun, Y; Ferrer Orri, J; Frohna, K; Salway, H; Kahmann, S; Nie, S; Vega, G; Kar, S; Novak, MP; Máckowski, S; Nyga, P; Ducati, C; Greenham, NC; Lotsch, BV; Anaya, M; Stranks, SDNature Commications, 15 (2024) 5802 DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49838-1
Abstract
Next-generation light-emitting applications such as displays and opticalcommunications require judicious control over emitted light, includingintensity and angular dispersion. To date, this remains a challenge as con-ventional methods require cumbersome optics. Here, we report highly direc-tional and enhanced electroluminescence from a solution-processed quasi-2-dimensional halide perovskite light-emitting diode by building a devicearchitecture to exploit hybrid plasmonic-photonic Tamm plasmon modes. Byexploiting the processing and bandgap tunability of the halide perovskitedevice layers, we construct the device stack to optimise both optical andcharge-injection properties, leading to narrow forward electroluminescencewith an angular full-width half-maximum of 36.6° compared with the con-ventional isotropic control device of 143.9°, and narrow electroluminescencespectral full-width half-maximum of 12.1 nm. The device design is versatile andtunable to work with emission lines covering the visible spectrum with desireddirectionality, thus providing a promising route to modular, inexpensive, anddirectional operating light-emitting devices.
Julio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49838-1
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Tandem catalytic approaches for CO2 2 enriched Fischer-Tropsch synthesis
Blay-Roger, R; Nawaz, MA; Baena-Moreno, FM; Bobadilla, LF; Reina, TR; Odriozola, JAProgress in Energy and Combustion Science, 103 (2024) 101159 DOI: 10.1016/j.pecs.2024.101159
Abstract
Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis (FTS) allows the conversion of syngas to high-density liquid fuels, playing a key role in the petrochemical and global energy sectors over the last century. However, the current Global Challenges impose the need to recycle CO2 2 and foster green fuels, opening new opportunities to adapt traditional processes like FTS to become a key player in future bioenergy scenarios. This review discusses the implementation of CO2- 2- rich streams and in tandem catalysis to produce sustainable fuels via the next generation of FTS. Departing from a brief revision of the past, present, and future of FTS, we analyse a disruptive approach coupling FTS to upstream and downstream processes to illustrate the advantages of process intensification in the context of biofuel production via FTS. We showcase a smart tandem catalyst design strategy addressing the challenges to gather mechanistic insights in sequential transformations of reagents in complex reaction schemes, the precise control of structure-activity parameters, catalysts aging-deactivation, optimization of reaction parameters, as well as reaction engineering aspects such as catalytic bed arrangements and non-conventional reactor configurations to enhance the overall performance. Our review analysis includes technoeconomic elements on synthetic aviation fuels as a case of study for FTS applications in the biofuel context discussing the challenges in market penetration and potential profitability of synthetic biofuels. This comprehensive overview provides a fresh angle of FTS and its enormous potential when combined with CO2 2 upgrading and tandem catalysis to become a front-runner technology in the transition towards a low-carbon future.
Julio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.pecs.2024.101159
Reactividad de Sólidos
On the athermal origin of flash sintering: Separating field-induced effects from Joule heating using a current ramp approach
Molina-Molina, S; Perejón, A; Pérez-Maqueda, LA; Sánchez-Jiménez, PEScripta Materialia, 247 (2024) 116086 DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2024.116086
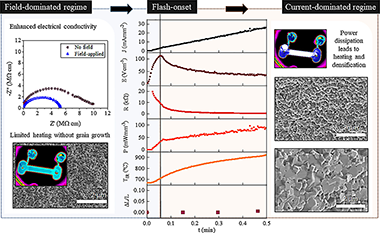
Abstract
Joule heating is generally acknowledged as the main driving force behind Flash Sintering. However, this view is challenged by the presence of athermal phenomena and the similarities between the flash process and dielectric breakdown. This work offers new insights into flash as an electrical runaway. Using current ramps to perform flash experiments on zinc oxide, two distinct stages within the process were revealed by electrical, thermal and microstructural measurements: a field-dominated regime where the flash event is triggered and a subsequent current-dominated regime associated with power dissipation. The contribution of each regime to the whole flash process was found to be determined by the initial resistivity of the sample. Furthermore, impedance spectroscopy data confirmed field-induced enhancement of conductivity at the flash-onset without significant Joule heating.
Julio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2024.116086
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
DC magnetron sputter deposition in pure helium gas: formation of porous films or gas/solid nanocomposite coatings
Ibrahim, S; Fernández, A; Brault, P; Sauldubois, A; Desgardin, P; Caillard, A; Hufschmidt, D; De Haro Jiménez, MC, Sauvage, T; Barthe, MF, Thomann, ALVacuum, 224 (2024) 113184 DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2024.113184
Abstract
Magnetron sputtering of two materials (Aluminum and Silicon) was performed in He gas and led to the formation of very different porous thin films: a fiberform nanostructure or a gas/solid nanocomposite. The composition of the thin films obtained was analyzed by means of ion beam techniques: Rutherford backscattering and proton elastic backscattering spectroscopies to measure the amount of Al(Si) deposited atoms and that of He atoms inserted inside the films. Microstructural and crystalline properties were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. Transmission electron microscopy coupled with electron energy loss spectroscopy were used to investigate the presence of empty or He filled pores or even bubbles. Correlating the Al(Si) film properties with the deposition conditions evaluated by SRIM (sputtering process at the target) and by a homemade collision code (species transport to the substrate) gave a better insight into the reason for the formation of such different films. The role of both He ions backscattered at the target and surface mobility during the growth is discussed. Comparison with low kinetic energy He + implantation experiments indicates that similar mechanisms, such as He insertion, diffusion inside the lattice, release or accumulation into pores and bubbles, are certainly taking place.
Junio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2024.113184
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of graphene-based nanostructures processing routes and aspect ratio in flexural strength and fracture mechanisms of 3Y-TZP-matrix composites
Moriche, R; Guisado-Arenas, E; Muñoz-Ferreiro, C; López-Pernía, C; Morales-Rodríguez, A; Jiménez-Piqué, E; Gallardo-López, A; Poyato, RCeramics International, 50(11) (2024) 19217-19227 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.03.021
Abstract
In this work, the influence of the aspect ratio of graphene-based nanostructures (GBNs) and content on the mechanical properties of 3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystalline 3Y-TZP matrix composites was analysed. The influence of the dispersion method and sintering parameters on the flexural strength and elastic modulus of the composites was studied, and the fracture surfaces were characterized to determine the fracture mechanisms that occur. The results showed that small amounts of exfoliated graphene nanoplatelets, with reduced lateral size, and few layer graphene, up to 1.0 and 2.5 vol%, respectively, slightly increase the 3Y-TZP flexural strength. This has been attributed to the tortuosity of the crack propagation pathways and strengthening mechanisms. Higher contents cause a decrease in flexural strength and stiffness because of overlapped GBNs, which can promote the crack propagation. The pull-out of GBN was more significant in composites with non-exfoliated graphene nanoplatelets, where no increase on the flexural or biaxial strength was measured.
Junio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.03.021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Biomass gasification, catalytic technologies and energy integration for production of circular methanol: New horizons for industry decarbonisation
Bobadilla, Luis F; Azancot, Lola; González-Castaño, Miriam; Ruíz-López, Estela; Pastor-Pérez, Laura; Durán-Olivencia, Francisco J.; Ye, Runping; Chong, Katie; Blanco-Sánchez, Paula H; Wu, Zenthao; Reina, TR; Odriozola, JAJournal of Environmental Sciences, 140 (2024) 306-318 DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.09.020

Abstract
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) recognises the pivotal role of renewable energies in the future energy system and the achievement of the zero-emission target. The implementation of renewables should provide major opportunities and enable a more secure and decentralised energy supply system. Renewable fuels provide long-term solutions for the transport sector, particularly for applications where fuels with high energy density are required. In addition, it helps reducing the carbon footprint of these sectors in the long-term. Information on biomass characteristics feedstock is essential for scaling-up gasification from the laboratory to industrial-scale. This review deals with the transformation biogenic residues into a valuable bioenergy carrier like biomethanol as the liquid sunshine based on the combination of modified mature technologies such as gasification with other innovative solutions such as membranes and microchannel reactors. Tar abatement is a critical process in product gas upgrading since tars compromise downstream processes and equipment, for this, membrane technology for upgrading syngas quality is discussed in this paper. Microchannel reactor technology with the design of state-of-the-art multifunctional catalysts provides a path to develop decentralised biomethanol synthesis from biogenic residues. Finally, the development of a process chain for the production of (i) methanol as an intermediate energy carrier, (ii) electricity and (iii) heat for decentralised applications based on biomass feedstock flexible gasification, gas upgrading and methanol synthesis is analysed.
Junio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.09.020
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Nickel-based cerium zirconate inorganic complex structures for CO2 valorisation via dry reforming of methane
Martín-Espejo, Juan Luis; Merkouri, Loukia-Pantzechroula; Gándara-Loe, Jesús; Odriozola, José AntonioJournal of Environmental Sciences, 140 (2024) 12-23 DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.01.022
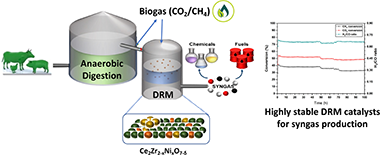
Abstract
The increasing anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases (GHG) is encouraging extensive research in CO2 utilisation. Dry reforming of methane (DRM) depicts a viable strategy to convert both CO2 and CH4 into syngas, a worthwhile chemical intermediate. Among the different active phases for DRM, the use of nickel as catalyst is economically favourable, but typically deactivates due to sintering and carbon deposition. The stabilisation of Ni at different loadings in cerium zirconate inorganic complex structures is investigated in this work as strategy to develop robust Ni-based DRM catalysts. XRD and TPR-H2 analyses confirmed the existence of different phases according to the Ni loading in these materials. Besides, superficial Ni is observed as well as the existence of a CeNiO3 perovskite structure. The catalytic activity was tested, proving that 10 wt.% Ni loading is the optimum which maximises conversion. This catalyst was also tested in long-term stability experiments at 600 and 800°C in order to study the potential deactivation issues at two different temperatures. At 600°C, carbon formation is the main cause of catalytic deactivation, whereas a robust stability is shown at 800°C, observing no sintering of the active phase evidencing the success of this strategy rendering a new family of economically appealing CO2 and biogas mixtures upgrading catalysts.
Junio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2023.01.022
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Enhanced low-temperature CO2 methanation over La-promoted NiMgAl LDH derived catalyst: Fine-tuning La loading for an optimal performance
Wang, ZL; Zhang, TY; Reina, TR; Huang, L; Xie, WF; Musyoka, NM; Oboirien, B; Wang, QFuel, 366 (2024) 131383 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2024.131383
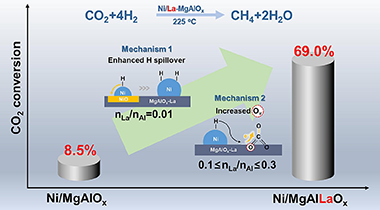
Abstract
LDH-derived Ni-based catalysts are gathering momentum due to their excellent thermal stability but their lowtemperature CO2 methanation is limited. In this study, various concentrations of La were introduced into the LDH-derived Ni-based catalysts for CO2 methanation, and the underlying mechanisms were investigated. The optimal Ni/La-0.2-MgAlOx catalyst presented a CO(2)conversion level of 69.0 % at 225 C-degrees, which is over 7 times higher than that of conventional Ni/MgAlOx. The addition of small amounts of La could significantly enhance H spillover to promote the reduction of Ni species, but the oxygen vacancy concentration became the dominant factor causing changes in low -temperature activity as the La contents continue to increase. CO2 was found to be adsorbed at the oxygen vacancies in the form of bidentate carbonates, which are more reactive under an enhanced electron -rich environment. The research offers guidance to design effective and sustainable catalysts for low -temperature CO2 methanation.
Junio, 2024 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2024.131383
- ‹ anterior
- 2 of 37
- siguiente ›














