Artículos SCI
2021
2021
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Fluorinated and platinized Titania for Glycerol oxidation
Murcia, J.J.; Bautista, E; Ávila Martínez, E.G.; Rangel R.N.; Romero, R.; Cubillos Lobo, J.A.; Rojas Sarmiento, H.A.; Hernández, J.S.; Cárdenas, O.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Navío, J.A.; Baeza, R.Materials Proceedings, 4 (2021) 37
Show abstract ▽
In this research, photocatalysts based on TiO2 modified by fluorination and platinum addition were evaluated in the glycerol oxidation. These materials were characterized by different instrumental analysis techniques to determine the physicochemical properties. It was found that the surface modification lead to improve the materials absorption in the Visible region of the electromagnetic spectra and to increase the surface area of TiO2. By HPLC analysis was possible to observed that the photocatalysts 0.5% Pt-F-TiO2 showed the highest yield and selectivity towards glyceraldehyde (GAL). It was also observed that the increase in the platinum content until values of 2% had a negative effect in the effectiveness of fluorinated Titania in the glycerol photo-oxidation. The fluorination and platinum addition modify some physicochemical properties of TiO2, leading also to modify the reaction mechanism and selectivity during glycerol partial photo-oxidation and the dose of photocatalysts is an important reaction condition to obtain GAL and Dyhidroxyacetone (DHA) with yields above to 70%.
Abril, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/IOCN2020-07792
Materiales Coloidales
Holmium phosphate nanoparticles as negative contrast agents for high-field magnetic resonance imaging: Synthesis, magnetic relaxivity study and in vivo evaluation
Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Caro, C; Martinez-Gutierrez, D; Garcia-Martin, ML; Ocana, M; Becerro, AIJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 587 (2021) 131-140
Show abstract ▽

The increasing use of high magnetic fields in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners demands new contrast agents, since those used in low field instruments are not effective at high fields. In this paper, we report the synthesis of a negative MRI contrast agent consisting of HoPO4 nanoparticles (NPs). Three different sizes (27 nm, 48 nm and 80 nm) of cube-shaped NPs were obtained by homogeneous precipitation in polyol medium and then coated with poly(acrylic) acid (PAA) to obtain stable colloidal suspensions of HoPO4@PAA NPs in physiological medium (PBS). The transverse relaxivity (r2) of aqueous suspensions of the resulting NPs was evaluated at both 1.44 T and 9.4 T. A positive correlation between r2 values and field strength as well as between r2 values and particle size at both magnetic field strengths was found although this correlation failed for the biggest NPs at 9.4 T, likely due to certain particles aggregation inside the magnet. The highest r2 value (489.91 mM-1s−1) was found for the 48 nm NPs at 9.4 T. Toxicity studies demonstrated that the latter NPs exhibited low toxicity to living systems. Finally, in vivo studies demonstrated that HoPO4@PAA NPs could be a great platform for next-generation T2-weighted MRI contrast agents at high magnetic field.
Abril, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.11.119
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Pb2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ removal by designed functionalized swelling high-charged micas
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDScience of The Total Environment, 764 (2021) 142811
Show abstract ▽
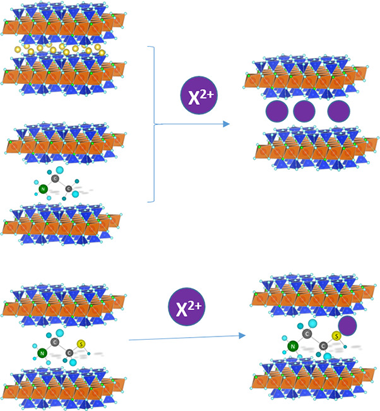
The increasing accumulation of toxic heavy metals in the environment has generated the need of efficient removal systems, being the adsorption method the most popular one applied in aqueous solutions. Of particular concern is the case of Pb2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ due to their high potential hazard. In this paper, we describe the feasibility of a new family of nanomaterials, swelling high charge micas, in the removal of these cations from aqueous solutions. Batch adsorption experiments were carried out in the as-made micas, NaMn, and after functionalization with ethylammonium, EA-Mn, and mercaptoethylammonium, MEA-Mn. The results have demonstrated that all of them are efficient heavy metal adsorbents, being Na-M2 the best adsorbent for Pb2+ and Cd2+, and, MEA-M2 for Hg2+.
Abril, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142811
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Elucidating the nature of Mo species on ZSM-5 and its role in the methane aromatization reaction
Lopez-Martin, A.; Platero, F; Colon, G.; Caballero, A.Reaction Chemistry & Engineering
Show abstract ▽
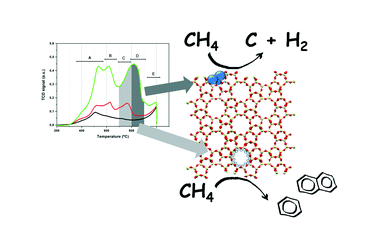
The valorization of methane is one of the most important goals during the transition period to the general use of renewable energies. Its transformation into a valuable chemical like benzene by direct aromatization of methane (DAM) reaction has been extensively studied in the past years, mainly using Mo/ZSM-5 catalytic systems. Although viable, this DAM reaction poses a number of issues mainly derived from poor conversion and deactivation processes. Therefore, a deeper knowledge of these systems is needed. Herein, by combining chemical (TPR), spectroscopic (XPS), HAADF and other techniques, we have identified the different Mo precursors stabilized in the calcined ZSM-5 support, their nature (monomers, dimers and bulk Mo oxides), location in the zeolite framework (external surface or micropores), and the partial segregation of aluminum during the preparation of catalysts. The role of each Mo phase promoting or hindering the transformation of methane in aromatics has been also clarified.
Abril, 2021 | DOI: 10.1039/d1re00044f
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
LED-driven controlled deposition of Ni onto TiO2 for visible-light expanded conversion of carbon dioxide into C-1-C-2 alkanes
Sanz-Marco, A; Hueso, JL; Sebastian, V; Nielsen, D; Mossin, S; Holgado, JP; Bueno-Alejo, CJ; Balas, F; Santamaria, JNanoscale Advances
Show abstract ▽
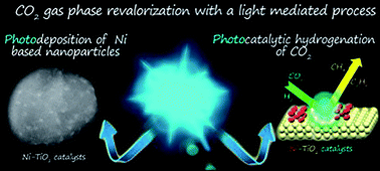
Photocatalytic gas-phase hydrogenation of CO2 into alkanes was achieved over TiO2-supported Ni nanoparticles under LED irradiation at 365 nm, 460 nm and white light. The photocatalysts were prepared using photo-assisted deposition of Ni salts under LED irradiation at 365 nm onto TiO2 P25 nanoparticles in methanol as a hole scavenger. This procedure yielded 2 nm Ni particles decorating the surface of TiO2 with a nickel mass content of about 2%. Before the photocatalytic runs, Ni/TiO2 was submitted to thermal reduction at 400 °C in a 10% H2 atmosphere which induced O-defective TiO2−x substrates. The formation of oxygen vacancies, Ti3+ centers and metallic Ni sites upon photocatalytic CO2 hydrogenation was confirmed by operando EPR analysis. In situ XPS under reaction conditions suggested a strong metal–support interaction and the co-existence of zero and divalent Ni states. These photoactive species enhanced the photo-assisted reduction of CO2 below 300 °C to yield CO, CH4 and C2H6 as final products.
Abril, 2021 | DOI: 10.1039/d1na00021g
- ‹ anterior
- 80 of 410
- siguiente ›














