Artículos SCI
2021
2021
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Pb2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ removal by designed functionalized swelling high-charged micas
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDScience of The Total Environment, 764 (2021) 142811
Show abstract ▽
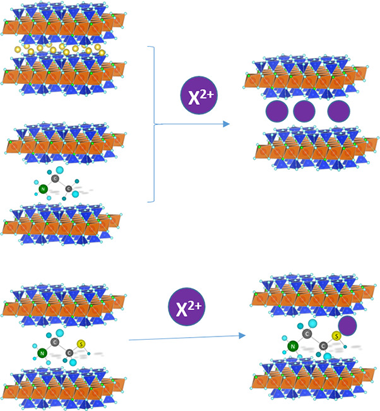
The increasing accumulation of toxic heavy metals in the environment has generated the need of efficient removal systems, being the adsorption method the most popular one applied in aqueous solutions. Of particular concern is the case of Pb2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ due to their high potential hazard. In this paper, we describe the feasibility of a new family of nanomaterials, swelling high charge micas, in the removal of these cations from aqueous solutions. Batch adsorption experiments were carried out in the as-made micas, NaMn, and after functionalization with ethylammonium, EA-Mn, and mercaptoethylammonium, MEA-Mn. The results have demonstrated that all of them are efficient heavy metal adsorbents, being Na-M2 the best adsorbent for Pb2+ and Cd2+, and, MEA-M2 for Hg2+.
Abril, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142811
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
LED-driven controlled deposition of Ni onto TiO2 for visible-light expanded conversion of carbon dioxide into C-1-C-2 alkanes
Sanz-Marco, A; Hueso, JL; Sebastian, V; Nielsen, D; Mossin, S; Holgado, JP; Bueno-Alejo, CJ; Balas, F; Santamaria, JNanoscale Advances
Show abstract ▽
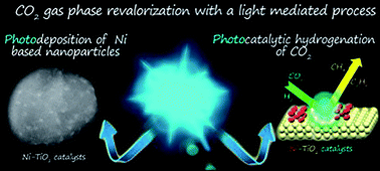
Photocatalytic gas-phase hydrogenation of CO2 into alkanes was achieved over TiO2-supported Ni nanoparticles under LED irradiation at 365 nm, 460 nm and white light. The photocatalysts were prepared using photo-assisted deposition of Ni salts under LED irradiation at 365 nm onto TiO2 P25 nanoparticles in methanol as a hole scavenger. This procedure yielded 2 nm Ni particles decorating the surface of TiO2 with a nickel mass content of about 2%. Before the photocatalytic runs, Ni/TiO2 was submitted to thermal reduction at 400 °C in a 10% H2 atmosphere which induced O-defective TiO2−x substrates. The formation of oxygen vacancies, Ti3+ centers and metallic Ni sites upon photocatalytic CO2 hydrogenation was confirmed by operando EPR analysis. In situ XPS under reaction conditions suggested a strong metal–support interaction and the co-existence of zero and divalent Ni states. These photoactive species enhanced the photo-assisted reduction of CO2 below 300 °C to yield CO, CH4 and C2H6 as final products.
Abril, 2021 | DOI: 10.1039/d1na00021g
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Electrochromic response and porous structure of WO3 cathode layers
Louloudakis, D; Mouratis, K; Gil-Rostra, J; Koudoumas, E; Alvarez, R; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARElectrochimica Acta, 376 (2021) 138049
Show abstract ▽
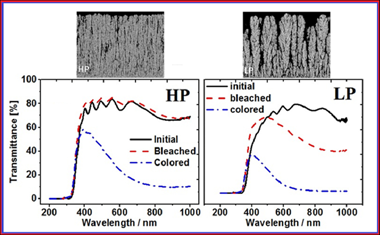
Maximizing the electrochromic response of tungsten oxide-based systems demands highly porous electrode layers that facilitate the incorporation of electrolyte cations during the reduction process. In this work, amorphous and porous WO3 thin films were grown on indium tin dioxide glass substrates by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles at two different plasma gas pressures. Remarkably, the film that showed higher porosity presented a worse electrochromic response in terms of durability, time response and charge density capacity. This result is analyzed and explained on the basis of the features of the porous structure of the films: While the typical nanostructure developed at low pressures possesses large and connected pore voids with few ramifications, the nanostructure generated at a higher pressure presents a rather sponge-like porous structure with numerous and small well-connected voids. A general discussion on the role of the porous structure and, particularly, on the accessible pore volume and area is carried out. It is concluded that not only the accessible pore volume, defining the volume of electrolyte that stays inside the layer, but also the accessible pore area, which defines the efficiency of the incorporation/release of Li+ cations within the electrode material, determine the efficiency and reversibility of the electrochromic response.
Abril, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138049
Materiales Avanzados
Mining Wastes of an Albite Deposit as Raw Materials for Vitrified Mullite Ceramics
Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Garzon, E; Perez-Villarejo, L; Angelopoulos, GN; Eliche-Quesada, DMinerals, 11 (2021) 232
Show abstract ▽
In this work, an examination of mining wastes of an albite deposit in south Spain was carried out using X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), particle size analysis, thermodilatometry and Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) and Thermogravimetric (TG) analysis, followed by the determination of the main ceramic properties. The albite content in two selected samples was high (65-40 wt. %), accompanied by quartz (25-40 wt. %) and other minor minerals identified by XRD, mainly kaolinite, in agreement with the high content of silica and alumina determined by XRF. The content of Na2O was in the range 5.44-3.09 wt. %, being associated with albite. The iron content was very low (<0.75 wt. %). The kaolinite content in the waste was estimated from similar to 8 to 32 wt. %. The particle size analysis indicated values of 11-31 wt. % of particles <63 mu m. The ceramic properties of fired samples (1000-1350 degrees C) showed progressive shrinkage by the thermal effect, with water absorption and open porosity almost at zero at 1200-1250 degrees C. At 1200 ffiC, the bulk density reached a maximum value of 2.38 g/cm(3). An abrupt change in the phase evolution by XRD was found from 1150 to 1200 degrees C, with the disappearance of albite by melting in accordance with the predictions of the phase diagram SiO2-Al2O3-Na2O and the system albite-quartz. These fired materials contained as main crystalline phases quartz and mullite. Quartz was present in the raw samples and mullite was formed by decomposition of kaolinite. The observation of mullite forming needle-shape crystals was revealed by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). The formation of fully densified and vitrified mullite materials by firing treatments was demonstrated.
Marzo, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/min11030232
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Facile synthesis and characterization of a novel 1,2,4,5-benzene tetracarboxylic acid doped polyaniline@zinc phosphate nanocomposite for highly efficient removal of hazardous hexavalent chromium ions from water
Abdelghani Hsini, Yassine Naciri, Mohamed Benafqir, Zeeshan Ajmal, Nouh Aarab, Mohamed Laabd, J.A. Navío, F. Puga, Rabah Boukherroub, Bahcine Bakiz, Abdallah AlbourineJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 585 (2021) 560-573
Show abstract ▽
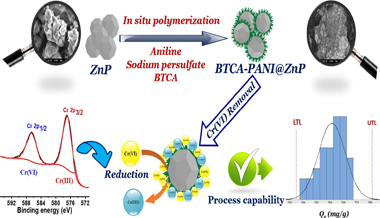
The present study describes the preparation of a novel 1,2,4,5-benzene tetracarboxylic acid doped polyaniline@zinc phosphate (BTCA-PANI@ZnP) nanocomposite via a facile two-step procedure. Thereafter, the as-prepared composite material adsorption characteristics for Cr(VI) ions removal were evaluated under batch adsorption. Kinetic approach studies for Cr(VI) removal, clearly demonstrated that the results of the adsorption process followed the pseudo second order and Langmuir models. The thermodynamic study indicated a spontaneous and endothermic process. Furthermore, higher monolayer adsorption was determined to be 933.88 mg g1 . In addition, the capability study regarding Cr(VI) ions adsorption over BTCA-PANI@ZnP nanocomposite clearly revealed that our method is suitable for large scale application. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis confirmed Cr(VI) adsorption on the BTCA-PANI@ZnP surface, followed by its subsequent reduction to Cr(III). Thus, the occurrence of external mass transfer, electrostatic attraction and reduction phenomenon were considered as main mechanistic pathways of Cr(VI) ions removal. The superior adsorption performance of the material, the multidimensional characteristics of the surface and the involvement of multiple removal mechanisms clearly demonstrated the potential applicability of the BTCA-PANI@ZnP material as an effective alternative for the removal of Cr(VI) ions from wastewater.
Marzo, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.10.036
- ‹ anterior
- 81 of 410
- siguiente ›














