Artículos SCI
2024
2024
Reactividad de Sólidos
Complex TiC-Ni-based composites joined to steel support by thermal explosion under load: synthesis, microstructure and tribological behavior
Lemboub, S; Boadebane, A; Boudebane, S; Bourbia, A; Mezrag, S; Gotor, FJComposites Interfaces, 31(5) (2024) 537-557
Show abstract ▽
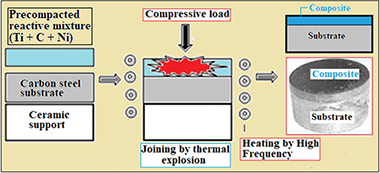
The combustion in thermal explosion mode of reactive mixtures of Ti-Ni-graphite(carbides, borides, oxides), under load, was used to produce complex composite materials, densified and joined to a C55 carbon steel support. The ignition of the exothermic reaction, carried out thanks to the rapid high-frequency heating of a green compact up to 1573 K, was followed by an isothermal holding at 1373 K for 360 s. This procedure ensured a perfect mechanical assembly between the composite material and the steel substrate. SEM analysis and concentration profiles carried out at the interface testified to the interdiffusion of iron and titanium atoms between the two materials. The maximum combustion temperature (T-max.) exceeding 2200 K induced the appearance of a liquid phase that assisted densification and joining, and in which a part of the additions was dissolved before cooling. The starting chemical composition of reactive mixtures largely determined the microstructure, hardness and tribological behavior of the composites after the process. Thereby, the maximum hardness (1235 HV0.15) and the lowest wear rate (1.824 x 10(-6) mm(3).N-1.m(-1)) were obtained in the sample containing TiC, Al2O3 and TiB2 hard phases. The manufactured samples exhibit no deterioration of the composite by spalling, regardless of the starting composition.
Mayo, 2024 | DOI: 10.1080/09276440.2023.2268968
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Green Fabrication of Stackable Laser-Induced Graphene Micro-Supercapacitors under Ambient Conditions: Toward the Design of Truly Sustainable Technological Platforms
Silvestre, SL; Morais, M; Soares, RRA; Johnson, Z; Benson, E; Ainsley, E; Pham, V; Claussen, JC; Gomes, CL; Martins, R; Fortunato, E; Pereira, L; Coelho, JAdvanced Materials Technologies, (2024) 2365709X
Show abstract ▽
Extensive research into green technologies is driven by the worldwide push for eco-friendly materials and energy solutions. The focus is on synergies that prioritize sustainability and environmental benefits. This study explores the potential of abundant, non-toxic, and sustainable resources such as paper, lignin-enriched paper, and cork for producing laser-induced graphene (LIG) supercapacitor electrodes with improved capacitance. A single-step methodology using a CO2 laser system is developed for fabricating these electrodes under ambient conditions, providing an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional carbon sources. The resulting green micro-supercapacitors (MSCs) achieve impressive areal capacitance (≈7–10 mF cm−2) and power and energy densities (≈4 μW cm-2 and ≈0.77 µWh cm−2 at 0.01 mA cm−2). Stability tests conducted over 5000 charge–discharge cycles demonstrate a capacitance retention of ≈80–85%, highlighting the device durability. These LIG-based devices offer versatility, allowing voltage output adjustment through stacked and sandwich MSCs configurations (parallel or series), suitable for various large-scale applications. This study demonstrates that it is possible to create high-quality energy storage devices based on biodegradable materials. This development can lead to progress in renewable energy and off-grid technology, as well as a reduction in electronic waste.
Mayo, 2024 | DOI: 10.1002/admt.202400261
Reactividad de Sólidos
Al2O3/Y3Al5O12 (YAG)/ZrO2 composites by single-step powder synthesis and spark plasma sintering
Vakhshouri, M; Najafzadehkhoee, A; Talimian, A; López-Pernia, C; Poyato, R; Gallardo-López, A; Gutiérrez-Mora, F; Prnova, A; Galusek, DJournal of the European Ceramic Societ (2024)
Show abstract ▽
Alumina-yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG)-zirconia composites are often produced by the melt solidification method. In the present study, we investigated the fabrication of α-Al2O3/Y3Al5O12 (YAG)/ZrO2 composite by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) of powders synthesized by Pechini’s sol-gel method. The ternary composites with homogenous microstructure and high density were produced by SPS at 1300 °C for 15 min. The addition of ZrO2 promoted the sintering of composites, resulting in a higher density and, in turn, higher hardness. A change in the indentation fracture behavior as the result of ZrO2 addition was observed.
Mayo, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2024.05.004
Reactividad de Sólidos
Ultraslow calorimetric studies of the martensitic transformation of NiFeGa alloys: detection and analysis of avalanche phenomena
Martín-Olalla, JM; Vidal-Crespo, A; Romero, FJ; Manchón-Gordón, A; Ipus, JJ; Blázquez, JS; Gallardo, MC; Conde, CFJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 149 (2024) 5165-5176
Show abstract ▽
We study the thermal properties of a bulk Ni55Fe19Ga26 Heusler alloy in a conduction calorimeter. At slow heating and cooling rates (∼1Kh-1), we compare as-cast and annealed samples. We report a smaller thermal hysteresis after the thermal treatment due to the stabilization of the 14 M modulated structure in the martensite phase. In ultraslow experiments (40mKh-1), we detect and analyze the calorimetric avalanches associated with the direct and reverse martensitic transformation from cubic to 14 M phase. This reveals a distribution of events characterized by a power law with exponential cutoff p(u)∝u-εexp(-u/ξ) where ε∼2 and damping energies ξ=370μJ (direct) and ξ=27μJ (reverse) that characterize the asymmetry of the transformation.
Mayo, 2024 | DOI: 10.1007/s10973-024-13206-4
Materiales Coloidales
B-site deficient hexagonal perovskites: Structural stability, ionic order-disorder and electrical properties
Yang, X; Fernández-Carrión, AJ; Geng, X; Kuang, XProgress in Solid State Chemistry, 74 (2024) 100459
Show abstract ▽
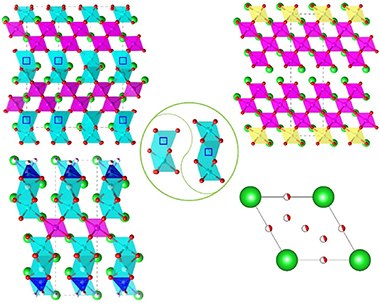
This review presents an overview on the structures and electrical properties of B-site deficient hexagonal perovskite oxides, which have been receiving increasing attention as key components as dielectric resonators in microwave telecommunications, as well as solid-state oxide ion and proton conductors in solid oxide fuel cells. The structural evolution and stability, order-disorder of cation and anions, and mechanisms underlying the dielectric and ionic conduction behaviors for the B-site deficient hexagonal perovskites are summarized and the roles of the B-site deficiency on the structural stability and option, ion order-disorder and electrical performance are highlighted. This provides useful guidance for design of new hexagonal perovskite oxide materials and structural control to enhance their electrical properties and discover new functionality as dielectric resonators and solid-state ionic conductors.
Mayo, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2024.100459
- ‹ anterior
- 6 of 419
- siguiente ›














