Artículos SCI
2020
2020
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Recent progress on the enhancement of photocatalytic properties of BiPO4 using π–conjugated materials
Naciri, Y., Hsini, A., Ajmal, Z., Navio, J.A., Bakiz, B., Albourine, A., Ezahri, M., Benlhachemi, A.Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 280 (2020) 102160
Show abstract ▽
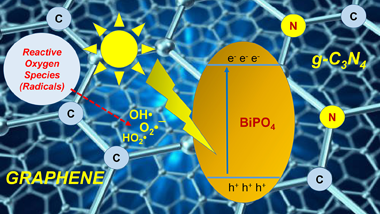
Semiconductor photocatalysis is regarded as most privileged solution for energy conversion and environmental application. Recently, photocatalysis methods using bismuth-based photocatalysts, such as BiPO4, have been extensively investigated owing to their superior efficacy regarding organic pollutant degradation and their further mineralization into CO2 and H2O. It is well known that BiPO4 monoclinic phase exhibited better photocatalytic performance compared to Degussa (Evonik) P25 TiO2 in term of ultraviolet light driven organic pollutants degradation. However, its wide band gap, poor adsorptive performance and large size make BiPO4 less active under visible light irradiation. However, extensive research works have been conducted in the past with the aim of improving visible light driven BiPO4 activity by constructing a series of heterostructures, mainly coupled with π-conjugated architecture (e.g., conductive polymer, dye sensitization and carbonaceous materials). However, a critical review of modified BiPO4 systems using π-conjugated materials has not been published to date. Therefore, this current review article was designed with the aim of presenting a brief current state-of-the-art towards synthesis methods of BiPO4 in the first section, with an especial focuses onto its crystal-microstructure, optical and photocatalytic properties. Moreover, the most relevant strategies that have been employed to improve its photocatalytic activities are then addressed as the main part of this review. Finally, the last section presents ongoing challenges and perspectives for modified BiPO4 systems using π–conjugated materials
Junio, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cis.2020.102160
Reactividad de Sólidos
Role of particle size on the multicycle calcium looping activity of limestone for thermochemical energy storage
Duran-Martin, JD; Jimenez, PES; Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; Arcenegui-Troya, J; Trinanes, PG; Maqueda, LAPJournal of Advanced Research, 22 (2020) 67-76
Show abstract ▽
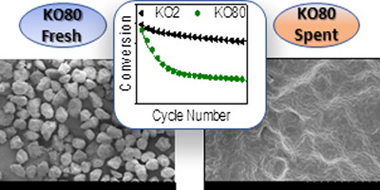
The calcium looping process, based on the reversible reaction between CaCO3 and CaO, is recently attracting a great deal of interest as a promising thermochemical energy storage system to be integrated in Concentrated Solar Power plants (CaL-CSP). The main drawbacks of the system are the incomplete conversion of CaO and its sintering-induced deactivation. In this work, the influence of particle size in these deactivation mechanisms has been assessed by performing experimental multicycle tests using standard limestone particles of well-defined and narrow particle size distributions. The results indicate that CaO multicycle conversion benefits from the use of small particles mainly when the calcination is carried out in helium at low temperature. Yet, the enhancement is only significant for particles below 15 μm. On the other hand, the strong sintering induced by calcining in CO2 at high temperatures makes particle size much less relevant for the multicycle performance. Finally, SEM imaging reveals that the mechanism responsible for the loss of activity is mainly pore-plugging when calcination is performed in helium, whereas extensive loss of surface area due to sintering is responsible for the deactivation when calcination is carried out in CO2 at high temperature.
Marzo, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2019.10.008
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Robust anti-icing superhydrophobic aluminum alloy surfaces by grafting fluorocarbon molecular chains
Rico, V; Mora, J; Garcia, P; Aguero, A; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Lopez-Santos, CApplied Materials Today, 21 (2020) 100815
Show abstract ▽
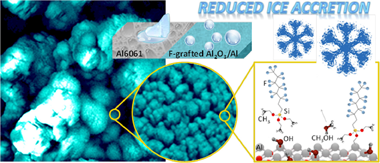
Infusion of low surface tension liquids in nanostructured surfaces is currently used to promote an anti icing response, although the long term stability of these systems is often jeopardized by losses of the infused liquid. In this work, we propose an alternative to the infusion procedure to induce a more effective and long lasting anti-icing capacity. The method consists of a combination of surface nanostructuration with the chemical grafting of fluorocarbon molecules. Al6061 substrates have been subjected to laser roughening and further modified with a nanostructured Al2O3 thin film to achieve a dual roughness and porous surface state. These surfaces have been subjected to a grafting treatment with perfluorooctyltriethoxysilane (PFOTES) vapor or, for comparative purposes, infused with a low surface tension liquid. A comparative analysis of the wetting, water condensation and anti-icing properties of these two systems showed an outstandingly better performance for the grafted surfaces with respect to the infused ones. Grafted surfaces were markedly superhydrophobic and required higher water vapor pressures to induce condensation. When looking for their anti-icing capacity, they presented quite long freezing delay times for supercooled water droplets (i.e. almost four hours) and exhibited a notably low ice accretion in a wind tunnel test. The high aging resistance and durability of these grafted surfaces and the reproducibility of the results obtained when subjected to successive ice accretion cycles show that molecular grafting is an efficient anti-icing methodology that, in aggressive media, may outperform the classical infusion procedures. The role of the fluorocarbon chains anchored on the surface in inducing an anti-icing functionality is discussed.
Diciembre, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100815
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Mesoporous Matrices as Hosts for Metal Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals
Rubino, A; Calio, L; Garcia-Bennett, A; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, (2020) 201901868
Show abstract ▽
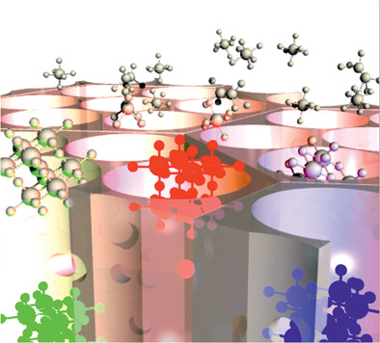
Several works have recently demonstrated that perovskite nanocrystals can be controllably formed within a variety of porous matrices employing diverse synthetic strategies. By means of the fine tuning of the pore size distribution, the thickness and composition of the walls, the geometry of the void network and its topology, strict control over the structural and morphological parameters of the hosted semiconductor can be achieved, determining its optical absorption and emission properties. Furthermore, porous hosts provide the guest semiconductor with enhanced stability and versatility in terms of processing, which favors its integration in devices. This article provides a comprehensive review of the different approaches proposed, as well as a discussion on the relevance they may have for the development of nanostructured perovskite-based optoelectronics. A critical assessment of the optical quality of the hybrid perovskite nanomaterials so obtained is presented, as well as an analysis of the fundamental and applied aspects of the nanocrystal-matrix interaction and a projected prospect of their impact in the fields of artificial lighting and renewable energy.
Febrero, 2020 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.201901868
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
An electrochemical evaluation of nitrogen-doped carbons as anodes for lithium ion batteries
Gomez-Martin, A; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Ruttert, M; Winter, M; Placke, T; Ramirez-Rico, JCarbon, 164 (2020) 261-271
Show abstract ▽
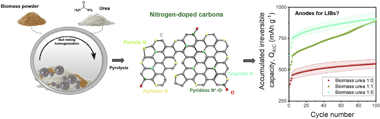
New anode materials beyond graphite are needed to improve the performance of lithium ion batteries (LIBs). Chemical doping with nitrogen has emerged as a simple strategy for enhancing lithium storage in carbon-based anodes. While specific capacity and rate capability are improved by doping, little is known about other key electrochemical properties relevant to practical applications. This work presents a systematic evaluation of electrochemical characteristics of nitrogen-doped carbons derived from a biomass source and urea powder as anodes in LIB half- and full-cells. Results show that doped carbons suffer from a continuous loss in capacity upon cycling that is more severe for higher nitrogen contents. Nitrogen negatively impacts the voltage and energy efficiencies at low charge/discharge current densities. However, as the charge/discharge rate increases, the voltage and energy efficiencies of the doped carbons outperform the non-doped ones. We provide insights towards a fundamental understanding of the requirements needed for practical applications and reveal drawbacks to be overcome by novel doped carbon-based anode materials in LIB applications. With this work, we also want to encourage other researchers to evaluate electrochemical characteristics besides capacity and cycling stability which are mandatory to assess the practicality of novel materials.
Agosto, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.04.003
- ‹ anterior
- 90 of 410
- siguiente ›
icms











