Artículos SCI
2024
2024
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Exciton-carrier coupling in a metal halide perovskite nanocrystal assembly probed by two-dimensional coherent spectroscopy
Rojas-Gatjens, E; Tiede, DO; Koch, KA; Romero-Perez, C; Galisteo-López, JF; Calvo, ME; Míguez, H; Kandada, ARSJournal of Physics-Materials, 7 (2024) 025002
Show abstract ▽
The surface chemistry and inter-connectivity within perovskite nanocrystals play a critical role in determining the electronic interactions. They manifest in the Coulomb screening of electron-hole correlations and the carrier relaxation dynamics, among other many-body processes. Here, we characterize the coupling between the exciton and free carrier states close to the band-edge in a ligand-free formamidinium lead bromide nanocrystal assembly via two-dimensional coherent spectroscopy. The optical signatures observed in this work show: (i) a nonlinear spectral lineshape reminiscent of Fano-like interference that evidences the coupling between discrete electronic states and a continuum, (ii) symmetric excited state absorption cross-peaks that suggest the existence of a coupled exciton-carrier excited state, and (iii) ultrafast carrier thermalization and exciton formation. Our results highlight the presence of coherent coupling between exciton and free carriers, particularly in the sub-100 femtosecond timescales.
Abril, 2024 | DOI: 10.1088/2515-7639/ad229a
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth dynamics of nanocolumnar thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles
Alvarez, R; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Regodon, G; Ferrer, FJ; Rico, V; Garcia-Martin, JM; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, ANanotechnology, 35 (2024) 095705
Show abstract ▽
The morphology of numerous nanocolumnar thin films deposited by the magnetron sputtering technique at oblique geometries and at relatively low temperatures has been analyzed for materials as different as Au, Pt, Ti, Cr, TiO2, Al, HfN, Mo, V, WO3 and W. Despite similar deposition conditions, two characteristic nanostructures have been identified depending on the material: a first one defined by highly tilted and symmetric nanocolumnar structures with a relatively high film density, and a second one characterized by rather vertical and asymmetric nanocolumns, with a much lower film density. With the help of a model, the two characteristic nanostructures have been linked to different growth dynamics and, specifically, to different surface relaxation mechanisms upon the incorporation of gaseous species with kinetic energies above the surface binding energy. Moreover, in the case of Ti, a smooth structural transition between the two types of growths has been found when varying the value of the power used to maintain the plasma discharge. Based on these results, the existence of different surface relaxation mechanisms is proposed, which quantitatively explains numerous experimental results under the same conceptual framework.
Febrero, 2024 | DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/ad113d
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Renewable Carbonaceous Materials from Biomass in Catalytic Processes: A Review
Villora-Picó, JJ; González-Arias, J; Baena-Moreno, FM; Reina, TRMaterials, 17 (2024) 565
Show abstract ▽
This review paper delves into the diverse ways in which carbonaceous resources, sourced from renewable and sustainable origins, can be used in catalytic processes. Renewable carbonaceous materials that come from biomass-derived and waste feedstocks are key to developing more sustainable processes by replacing traditional carbon-based materials. By examining the potential of these renewable carbonaceous materials, this review aims to shed light on their significance in fostering environmentally conscious and sustainable practices within the realm of catalysis. The more important applications identified are biofuel production, tar removal, chemical production, photocatalytic systems, microbial fuel cell electrodes, and oxidation applications. Regarding biofuel production, biochar-supported catalysts have proved to be able to achieve biodiesel production with yields exceeding 70%. Furthermore, hydrochars and activated carbons derived from diverse biomass sources have demonstrated significant tar removal efficiency. For instance, rice husk char exhibited an increased BET surface area from 2.2 m2/g to 141 m2/g after pyrolysis at 600 °C, showcasing its effectiveness in adsorbing phenol and light aromatic hydrocarbons. Concerning chemical production and the oxidation of alcohols, the influence of biochar quantity and pre-calcination temperature on catalytic performance has been proven, achieving selectivity toward benzaldehyde exceeding 70%.
Febrero, 2024 | DOI: 10.3390/ma17030565
2023
2023
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Alkane metathesis over immobilized pincer-ligated iridium complexes: Effect of support nature
Megías-Sayago, C; Centeno-Vega, I; Bobadilla, LF; Ivanova, S; Rendon, N; Suarez, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 338 (2023) 123002
Show abstract ▽
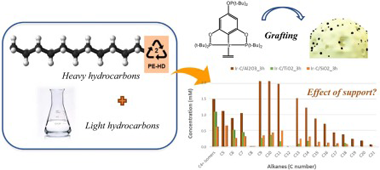
In this work, catalytic alkane metathesis has been evaluated as a suitable approach to upcycle hydrocarbons (polyolefins) at moderate temperatures. To this end, a pincer-ligated iridium complex (dehydrogenation catalyst) has been combined with a rhenium-based (metathesis) catalyst, being the effect of immobilizing the Ir complex over different supports deeply investigated. FTIR spectroscopy has been used to confirm the complex grafting and to elucidate the anchoring site to the support. Additionally, the supports have been dehydroxylated at different conditions to evaluate its possible impact in both the complex grafting and the catalytic activity. The influence of the support nature and its participation in the catalytic reaction have been clearly evidenced.
Diciembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.123002
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Scalable synthesis of 2D Ti2CTx MXene and molybdenum disulfide composites with excellent microwave absorbing performance
Miao, BJ; Cao, YE; Zhu, QS; Nawaz, MA; Ordiozola, JA; Reina, TR; Bai, ZM; Ren, JN; Wei, FCAdvanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 6 (2023) 61
Show abstract ▽
The signal crosstalk and electromagnetic interference (EMI) problems direly need to be resolved in the rapid development of modern microwave communication technology for a better working frequency and transmission power of electronic systems. Where the new absorbing materials such as molybdenum disulfide (MoS2)/titania (TiO2)/Ti2CTx and MoS2/Ti2CTx composites could meet the requirement of "thin, strong, light weight, and wide band" for excellent absorbing performance. In this work, a lighter Ti2CTx material was selected as the matrix, and MoS2 was in-situ grown on Ti2CTx matrix by traditional hydrothermal method and microwave solvothermal method. The fabricated composite exhibited synergic effect of two-dimensional heterostructural interface and double dielectric elements, where a small amount of TiO2 and a certain proportion of MoS2 jointly improve the impedance matching of the composite material. In here, the extreme reflection loss (RLmin) can reach - 54.70 dB (with a frequency of 7.59 GHz, 3.39 mm thickness), and the maximum effective absorption bandwidth (EAB(max)) can reach 4 GHz. Polyethylene glycol 200 was used as the solvent instead of water to make Ti2CTx less oxidized during the composite process, where the microwave heating would attain fast speed, short time, high efficiency, and uniform product. Since, the MoS2/Ti2CTx composite without oxidizing possessed a wider effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) at a thinner thickness, thus resulting in the excellent microwave absorption performance and confirming the validity and rationality of new microwave absorption materials.
Abril, 2023 | DOI: 10.1007/s42114-023-00643-2
- ‹ anterior
- 6 of 410
- siguiente ›
icms











