Artículos SCI
2021
2021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis and Characterization of a Nearly Single Bulk Ti2AlN MAX Phase Obtained from Ti/AlN Powder Mixture through Spark Plasma Sintering
Salvo, C; Chicardi, E; Poyato, R; Garcia-Garrido, C; Jimenez, JA; Lopez-Pernia, C; Tobosque, P; Mangalaraja, RVMaterials, 14 (2021) 2217
Show abstract ▽
MAX phases are an advanced class of ceramics based on ternary carbides or nitrides that combine some of the ceramic and metallic properties, which make them potential candidate materials for many engineering applications under severe conditions. The present work reports the successful synthesis of nearly single bulk Ti2AlN MAX phase (>98% purity) through solid-state reaction and from a Ti and AlN powder mixture in a molar ratio of 2:1 as starting materials. The mixture of Ti and AlN powders was subjected to reactive spark plasma sintering (SPS) under 30 MPa at 1200 degrees C and 1300 degrees C for 10 min in a vacuum atmosphere. It was found that the massive formation of Al2O3 particles at the grain boundaries during sintering inhibits the development of the Ti2AlN MAX phase in the outer zone of the samples. The effect of sintering temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the Ti2AlN MAX phase was investigated and discussed.
Mayo, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/ma14092217
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of the sulphonating agent on the catalytic behavior of activated carbons in the dehydration reaction of fructose in DMSO
Bounoukta, CE; Megias-Sayago, C; Ivanova, S; Penkova, A; Ammari, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis A-General, 617 (2021) 118108
Show abstract ▽
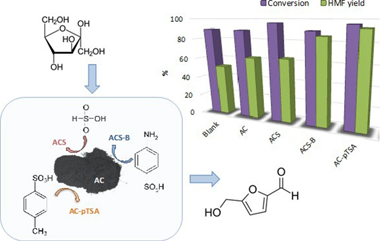
A series of -SO3R functionalized activated carbons (R=H, O, aryl) were prepared and applied in fructose dehydration reaction to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Different sulphonating methods introduce groups on catalyst surface with distinct donor-acceptor and hydrophilic properties. Their nature influences significantly not only activated carbon?s textural and chemical properties but also the product yields and selectivity in fructose dehydration reaction. The viability of the solvent free reaction was also investigated and compared to the performance of the catalyst series in presence of DMSO, where the best catalytic results were obtained.
Mayo, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2021.118108
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Nanofibrous Matrix of Defined Composition Sustains Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Culture
Borrego-Gonzalez, S; de la Cerda, B; Diaz-Corrales, FJ; Diaz-Cuenca, AACS Applied Bio Materials, 4 (2021) 3035-3040
Show abstract ▽
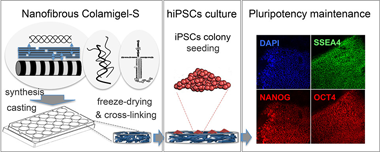
Human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) represent the most promising biological material for regenerative medicine applications. In this work, a 3D solid nanofibrous matrix of defined composition (Colamigel-S) consisting of 97 wt % gelatin, 2.6 wt % atelocollagen, and 0.4 wt % laminin has been reproducibly processed and characterized and exhibits a homogeneous nanofibrillar network of high surface area, interconnected microcavities, and typical D-periodic collagen fibril nanostructural features. The purpose of the study was to test the performance of Colamigel-S as substrate for in vitro hiPSCs culture, finding that these cells efficiently attach and grow keeping their characteristic stem morphology and undifferentiated state.
Abril, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acsabm.0c00425
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Fructose dehydration reaction over functionalized nanographitic catalysts in MIBK/H2O biphasic system
Martin, GD; Bounoukta, CE; Ammari, F; Dominguez, MI; Monzon, A; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MACatalysis Today, 366 (2021) 68-76
Show abstract ▽
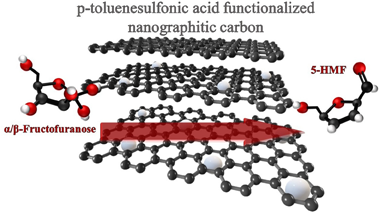
A series of functionalized nanographitic carbons is prepared, characterized and tested in fructose dehydration reaction to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. The functionalization treatment was selected to introduce various Bro?nsted acid sites and to modify the textural and catalytic properties of the initial carbon material. Within the series, the sulfonated carbons present the most interesting catalytic behavior resulting in important selectivity to the desired product once the reaction variables were properly adjusted.
Abril, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.03.016
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Biogas Conversion to Syngas Using Advanced Ni-Promoted Pyrochlore Catalysts: Effect of the CH4/CO2 Ratio
le Sache, E; Moreno, AA; Reina, TRFrontiers in Chemistry, 9 (2021) 672419
Show abstract ▽
Biogas is defined as the mixture of CH4 and CO2 produced by the anaerobic digestion of biomass. This particular mixture can be transformed in high valuable intermediates such as syngas through a process known as dry reforming (DRM). The reaction involved is highly endothermic, and catalysts capable to endure carbon deposition and metal particle sintering are required. Ni-pyrochlore catalysts have shown outstanding results in the DRM. However, most reported data deals with CH4/CO2 stoichiometric ratios resulting is a very narrow picture of the overall biogas upgrading via DRM. Therefore, this study explores the performance of an optimized Ni-doped pyrochlore, and Ni-impregnated pyrochlore catalysts in the dry reforming of methane, under different CH4/CO2 ratios, in order to simulate various representatives waste biomass feedstocks. Long-term stability tests showed that the ratio CH4/CO2 in the feed gas stream has an important influence in the catalysts' deactivation. Ni doped pyrochlore catalyst, presents less deactivation than the Ni-impregnated pyrochlore. However, biogas mixtures with a CH4 content higher than 60%, lead to a stronger deactivation in both Ni-catalysts. These results were in agreement with the thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of the post reacted samples that showed a very limited carbon formation when using biogas mixtures with CH4 content <60%, but CH4/CO2 ratios higher than 1.25 lead to an evident carbon deposition. TGA analysis of the post reacted Ni impregnated pyrochlore, showed the highest amount of carbon deposited, even with lower stoichiometric CH4/CO2 ratios. The later result indicates that stabilization of Ni in the pyrochlore structure is vital, in order to enhance the coke resistance of this type of catalysts.
Abril, 2021 | DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.672419
- ‹ anterior
- 78 of 410
- siguiente ›














