Artículos SCI
2021
2021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical synthesis of ternary chalcogenide chalcostibite CuSbS2 and its characterization
Dutkova, E; Sayagues, MJ; Fabian, M; Kovac, J; Kovat, J; Balaz, M; Stahorsky, MJournal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics (2021)
Show abstract ▽
In this work, the very rapid one-step mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline ternary chalcogenide chalcostibite CuSbS2 prepared from copper, antimony, and sulfur precursors by high-energy milling for only 30 min in a planetary mill is reported. XRD confirmed the orthorhombic crystal structure of CuSbS2. The crystallite size of CuSbS2 calculated by LeBail refinement of the X-ray powder diffraction data was 25 nm. The nanocrystalline chalcostibite CuSbS2 was also confirmed by transmission electron microscopy. The purity of CuSbS2 was verified by Raman spectroscopy. The synthesized chalcostibite exhibits the specific surface area value of 2.4 m(2)g(-1). UV-Vis spectroscopy showed the optical bandgap of CuSbS2 as 1.54 eV with wide range of absorption in visible region. Photoresponse of CuSbS2 was confirmed by I-V measurements under dark and light illumination. The proposed mechanochemical synthesis provides an alternative approach to prepare also other ternary semiconductor nanomaterials. CuSbS2 semiconductor nanocrystals have the potential to be used as light absorbers in photovoltaics.
Agosto, 2021 | DOI: 10.1007/s10854-021-06767-9
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
One-reactor vacuum and plasma synthesis of transparent conducting oxide nanotubes and nanotrees: from single wire conductivity to ultra-broadband perfect absorbers in the NIR
Castillo-Seoane, J; Gil-Rostra, J; Lopez-Flores, V; Lozano, G; Ferrer, FJ; Espinos, JP; Ostrikov, K; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Borras, ANanoscale, 13 (2021) 13882-13895
Show abstract ▽
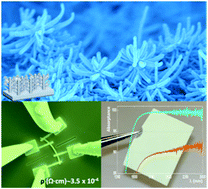
The eventual exploitation of one-dimensional nanomaterials needs the development of scalable, high yield, homogeneous and environmentally friendly methods capable of meeting the requirements for fabrication of functional nanomaterials with properties on demand. In this article, we demonstrate a vacuum and plasma one-reactor approach for the synthesis of fundamental common elements in solar energy and optoelectronics, i.e. the transparent conducting electrode but in the form of nanotube and nanotree architectures. Although the process is generic and can be used for a variety of TCOs and wide-bandgap semiconductors, we focus herein on indium doped tin oxide (ITO) as the most previously researched in previous applications. This protocol combines widely applied deposition techniques such as thermal evaporation for the formation of organic nanowires serving as 1D and 3D soft templates, deposition of polycrystalline layers by magnetron sputtering, and removal of the templates by simply annealing under mild vacuum conditions. The process variables are tuned to control the stoichiometry, morphology, and alignment of the ITO nanotubes and nanotrees. Four-probe characterization reveals the improved lateral connectivity of the ITO nanotrees and applied on individual nanotubes shows resistivities as low as 3.5 +/- 0.9 x 10(-4) omega cm, a value comparable to that of single-crystalline counterparts. The assessment of diffuse reflectance and transmittance in the UV-Vis range confirms the viability of the supported ITO nanotubes as random optical media working as strong scattering layers. Their further ability to form ITO nanotrees opens a path for practical applications as ultra-broadband absorbers in the NIR. The demonstrated low resistivity and optical properties of these ITO nanostructures open a way for their use in LEDs, IR shields, energy harvesting, nanosensors, and photoelectrochemical applications.
Agosto, 2021 | DOI: 10.1039/d1nr01937f
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Laser-induced scanning transfer deposition of silver electrodes on glass surfaces: A green and scalable technology
Molina, R; Ertugrul, M; Larrea, A; Navarro, R; Rico, V; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR: De la Fuente, GF; Angurel, LAApplied Surface Science, 556 (2021) 149673
Show abstract ▽
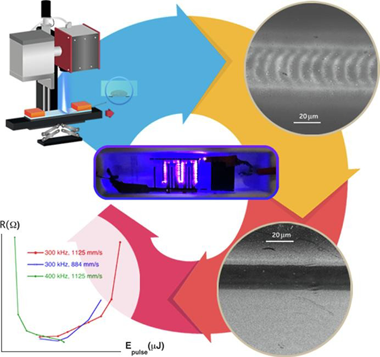
A pulsed laser ablation backwriting technique with high repetitive rates is implemented for the fabrication of silver coatings on glass surfaces. This method enables geometrical constraint-free deposition of metallic coatings. These exhibit sufficiently low electrical resistance to be used as electrodes in dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma elements. Ambient air deposition of metallic silver electrodes on standard glass slides is explored using a sub-ns UV laser source, combined with hybrid beam scanning methods. The green nature of the overall deposition process includes a preliminary irradiation scan to homogenise the target surface before the subsequent backwriting step. Metal transfer is achieved by combining two phenomena within a simple beam scanning process: LIRT (laserinduced reverse transfer) of silver from the target to the glass, with a partial and secondary LIFT (Laser-Induced Forward Transfer) of silver from the glass to the target. Appropriate selection of pulse energy and pulse repetition rates, beam scanning velocities and target motion enable the growth of sufficiently thick Ag deposits on glass with the required low electrical resistivity and nearly 2D constraint-free geometry. This method avoids the use of vacuum and liquids, resulting in a cheap, facile and green methodology for the deposition of silver electrodes onto transparent substrate surfaces.
Agosto, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149673
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Light-Harvesting Properties of a Subphthalocyanine Solar Absorber Coupled to an Optical Cavity
Esteso, V; Calio, L; Espinos, H; Lavarda, G; Torres, T; Feist, J; Garcia-Vidal, FJ; Bottari, G; Míguez, HSOLAR RRL, (2021) 2100308
Show abstract ▽
Herein, both from the experimental and theoretical point of view, the optical absorption properties of a subphthalocyanine (SubPc), an organic macrocycle commonly used as a sunlight harvester, coupled to metallic optical cavities are analyzed. How different electronic transitions characteristic of this compound and specifically those that give rise to excitonic (Q band) and charge transfer (CT band) transitions couple to optical cavity modes is investigated. It is observed that whereas the CT band couples weakly to the cavity, the Q band transitions show evidence of hybridization with the photon eigenstates of the resonator, a distinctive trait of the strong coupling regime. As a result of the different coupling regimes of the two electronic transitions, very different spectral and directional light-harvesting features are observed, which for the weakly coupled CT transitions are mainly determined by the highly dispersive cavity modes and for the strongly coupled Q band by the less angle-dependent exciton-polariton bands. Modeling also allows discriminating parasitic from productive absorption in each case, enabling the estimation of the expected losses in a solar cell acting as an optical resonator.
Julio, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/solr.202100308
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Mechanistic Considerations on the H-2 Production by Methanol Thermal-assisted Photocatalytic Reforming over Cu/TiO2 Catalyst
Platero, F; Lopez-Martin, A; Caballero, A; Colon, GCHEMCATCHEM, 13 (2021) 3878-3888
Show abstract ▽
We have studied the gas phase H-2 production by methanol thermo-photoreforming using Cu-modified TiO2. Metal co-catalyst has been deposited by means of photodeposition method. The concentration of methanol in the steam was also considered. It appears that H-2 production is notably higher as temperature increases. Moreover, the optimum H-2 yield is achieved using methanol concentration of 10 % v/v. CO and CO2 were monitored as side products of the overall reaction. It has been stated that CO evolution is significant at lower temperatures. As temperature increases, CO evolution is hindered and H-2 appeared boosted. We have demonstrated that other reactions such water-gas-shift or formate dehydration would participate in the overall process. On this basis, optimal operational condition for H-2 production is attained for thermo-photocatalytic reforming of methanol solution 10 % v/v at 200 degrees C.
Julio, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/cctc.202100680
- ‹ anterior
- 71 of 410
- siguiente ›














