Artículos SCI
2021
2021
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Designed organomicaceous materials for efficient adsorption of iodine
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9 (2021) 106577
Show abstract ▽
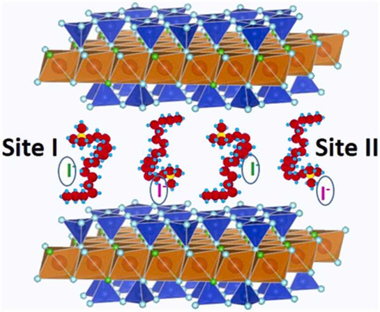
The anionic iodine I-129 has a significant contribution to overall long-term dose resulting from the nuclear waste storage and its immobilization by clay barrier is crucial. Organoclays have been tested as ideal adsorption materials, being the clay layer charge and the length and type of organic molecules the most relevant parameters affecting the adsorption. In this work, a family of designed organomicas are explored in term of iodine adsorption capacity. Their adsorption capacities were always higher than that of the traditional clays and organoclays. C-18-M4 shows a maximum monolayer adsorption capacity one order of magnitude higher than natural organoclays, with a free energy typical of physical adsorption and adsorption sites of high affinity. However, its surface is not homogeneous in terms of stability constant according to the Scatchard adsorption parameters. Hence, this study can provide a guidance for the design and construction of ultrahigh-capacity iodine adsorbents.
Diciembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.106577
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
LaFeO3 Modified with Ni for Hydrogen Evolution Via Photocatalytic Glucose Reforming in Liquid Phase
G. Iervolino; V. Vaiano; D. Sannino; F. Puga; J.A. Navío; M.C. HidalgoCatalysts, 11 (2021) 1558
Show abstract ▽
In this work, the optimization of Ni amount on LaFeO3 photocatalyst was studied in the photocatalytic molecular hydrogen production from glucose aqueous solution under UV light irradiation. LaFeO3 was synthesized via solution combustion synthesis and different amount of Ni were dispersed on LaFeO3 surface through deposition method in aqueous solution and using NaBH4 as reducing agent. The prepared samples were characterized with different techniques: Raman spectroscopy, UltraViolet-Visible Diffuse Reflectance Spettroscopy (UV–Vis-DRS), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), Transmission Electron microscopy (TEM), and Scanning Electron microscopy (SEM) analyses. For all the investigated photocatalysts, the presence of Ni on perovskite surface resulted in a better activity compared to pure LaFeO3. In particular, it is possible to identify an optimal amount of Ni for which it is possible to obtain the best hydrogen production. Specifically, the results showed that the optimal Ni amount was equal to nominal 0.12 wt% (0.12Ni/LaFeO3), for which the photocatalytic H2 production was equal to 2574 μmol/L after 4 h of UV irradiation. The influence of different of photocatalyst dosage and initial glucose concentration was also evaluated. The results of the optimization of operating parameters indicated that the highest molecular hydrogen production was achieved on 0.12Ni/LaFeO3 sample with 1.5 g/L of catalyst dosage and 1000 ppm initial glucose concentration. To determine the reactive species that play the most significant role in the photocatalytic hydrogen production, photocatalytic tests in the presence of different radical scavengers were performed. The results showed that •OH radical plays a significant role in the photocatalytic conversion of glucose in H2. Moreover, photocatalytic tests carried out with D2O instead of H2O evidenced the role of water molecules in the photocatalytic production of molecular hydrogen in glucose aqueous solution.
Diciembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/catal11121558
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Nanophotonics for current and future white light-emitting devices
Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Lozano, GJournal of Applied Physics, 130 (2021) 200901
Show abstract ▽
Photonic nanostructures have proven useful to enhance the performance of a wide variety of materials and devices for sensing, catalysis, light harvesting, or light conversion. Herein, we discuss the role of nanophotonics in current and next-generation designs of white light-emitting diodes (LEDs). We discuss recent developments on luminescent materials designed as alternatives to rare earth-doped inorganic microcrystals, i.e., phosphors, for color conversion in LEDs, which has opened the door to the integration of resonant photonic architectures. Nanophotonics enables the devised light-matter interaction with luminescent materials in the nanoscale, which allows providing emitting devices with both enhanced performance and novel functionalities to tackle technological challenges
Noviembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1063/5.0065825
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Zinc Polyaleuritate Ionomer Coatings as a Sustainable, Alternative Technology for Bisphenol A-Free Metal Packaging
Morselli, D; Cataldi, P; Paul, UC; Ceseracciu, L; Benitez, JJ; Scarpellini, A; Guzman-Puyol, S; Heredia, A; Valentini, P; Pompa, PP; Marrero-López, D; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, AACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 9 (2021) 15484-15495
Show abstract ▽
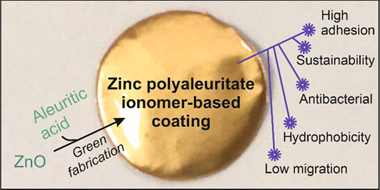
Sustainable coatings for metal food packaging were prepared from ZnO nanoparticles (obtained by the thermal decomposition of zinc acetate) and a naturally occurring polyhydroxylated fatty acid named aleuritic (or 9,10,16-trihydroxy-hexadecanoic) acid. Both components reacted, originating under specific conditions zinc polyaleuritate ionomers. The polymerization of aleuritic acid into polyaleuritate by a solvent-free, melt polycondensation reaction was investigated at different times (15, 30, 45, and 60 min), temperatures (140, 160, 180, and 200 degrees C), and proportions of zinc oxide and aleuritic acid (0:100, 5:95, 10:90, and 50:50, w/w). Kinetic rate constants calculated by infrared spectroscopy decreased with the amount of Zn due to the consumption of reactive carboxyl groups, while the activation energy of the polymerization decreased as a consequence of the catalyst effect of the metal. The adhesion and hardness of coatings were determined from scratch tests, obtaining values similar to robust polymers with high adherence. Water contact angles were typical of hydrophobic materials with values >= 94 degrees. Both mechanical properties and wettability were better than those of bisphenol A (BPA)-based resins and most likely are related to the low migration values determined using a hydrophilic food simulant. The presence of zinc provided a certain degree of antibacterial properties. The performance of the coatings against corrosion was studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy at different immersion times in an aqueous solution of NaCl. Considering the features of these biobased lacquers, they can be potential materials for bisphenol A-free metal packaging.
Noviembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c04815
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Recent Advances in Alkaline Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis and Electrode Manufacturing
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Sacedon, CG; Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; De Lucas-Consuegra, AMolecules, 26 (2021) 6326
Show abstract ▽
Water electrolysis to obtain hydrogen in combination with intermittent renewable energy resources is an emerging sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Among the available electrolyzer technologies, anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE) has been paid much attention because of its advantageous behavior compared to other more traditional approaches such as solid oxide electrolyzer cells, and alkaline or proton exchange membrane water electrolyzers. Recently, very promising results have been obtained in the AEMWE technology. This review paper is focused on recent advances in membrane electrode assembly components, paying particular attention to the preparation methods for catalyst coated on gas diffusion layers, which has not been previously reported in the literature for this type of electrolyzers. The most successful methodologies utilized for the preparation of catalysts, including co-precipitation, electrodeposition, sol-gel, hydrothermal, chemical vapor deposition, atomic layer deposition, ion beam sputtering, and magnetron sputtering deposition techniques, have been detailed. Besides a description of these procedures, in this review, we also present a critical appraisal of the efficiency of the water electrolysis carried out with cells fitted with electrodes prepared with these procedures. Based on this analysis, a critical comparison of cell performance is carried out, and future prospects and expected developments of the AEMWE are discussed.
Noviembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/molecules26216326
- ‹ anterior
- 63 of 410
- siguiente ›














