Artículos SCI
2021
2021
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Long-term low friction maintenance and wear reduction on the ventral scales in snakes
Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Schaber, CF; Gorb, SNMaterials Letters, 285 (2021) 129011
Show abstract ▽
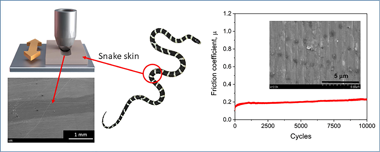
Snake skins evolved to withstand permanent friction and wear during sliding. Here, the microstructure of ventral scales of the snake Lampropeltis getula californiae was analyzed using scanning electron microscopy, and the long-term dynamic friction behavior was investigated by reciprocating sliding friction tests. A smooth epoxy resin with similar elasticity modulus and hardness was used for comparison purposes. Strong differences in frictional and wear mechanisms between the two materials were revealed in spite of similar mechanical properties. Snake skin showed a considerably lower frictional coefficient that kept stable over several thousands of sliding cycles. A reduction of the stick-slip behavior was also denoted by analyzing the variation of the friction coefficient in the forward and reverse motion influencing the wear mechanism. This frictional behavior can be explained by three different but complementary mechanisms: fibrous layered composite material of the skin with a gradient of material properties, surface microstructure, and the presence of ordered layers of lipid molecules at the skin surface.
Febrero, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.129011
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
ZnO/Ag3PO4 and ZnO–Malachite as Effective Photocatalysts for the Removal of Enteropathogenic Bacteria, Dyestuffs, and Heavy Metals from Municipal and Industrial Wastewater
Murcia, JJ; Hernández Miño, JS; Rojas, H; Brijaldo, MH; Martin-Gómez, AN; Sánchez-Cid, P; Navío, JA; Hidalgo, MC; Jaramillo-Pérez, CWater, 13 (2021) 2264
Show abstract ▽
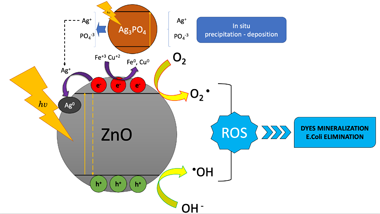
Different composites based on ZnO/Ag3PO4 and ZnO–malachite (Cu2(OH)2CO3) were synthesized in order to determine their effectiveness in the treatment of municipal and industrial wastewaters (mainly polluted by enteropathogenic bacteria, dyes, and heavy metals). The addition of Ag3PO4 and malachite did not significantly modify the physicochemical properties of ZnO; however, the optical properties of this oxide were modified as a result of its coupling with the modifiers. The modification of ZnO led to an improvement in its effectiveness in the treatment of municipal and industrial wastewater. In general, the amount of malachite or silver phosphate and the effluent to be treated were the determining factors in the effectiveness of the wastewater treatment. The highest degree of elimination of bacteria from municipal wastewater and discoloration of textile staining wastewater were achieved by using ZnO/Ag3PO4 (5%), but an increase in the phosphate content had a detrimental effect on the treatment. Likewise, the highest Fe and Cu photoreduction from coal mining wastewater was observed by using ZnO–malachite (2.5%) and ZnO/Ag3PO4 (10%), respectively. Some of the results of this work were presented at the fourth Congreso Colombiano de Procesos Avanzados de Oxidación (4CCPAOx).
Agosto, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/w13162264
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic Treatment of Stained Wastewater Coming from Handicraft Factories. A Case Study at the Pilot Plant Level
Murcia Mesa, JJ; Hernández Niño, JS; González, W; Rojas, H; Hidalgo, MC; Navío, JAWater, 13 (2021) 2705
Show abstract ▽
UV/H2O2 process and TiO2-based photocatalysis were studied in the present work. The effectiveness of these methods was tested in the treatment of effluents taken from handicraft factories. Microorganisms, dyes, and different organic pollutants were detected in the industrial effluents. The experimental procedure for the wastewater treatment was carried out in a patented sunlight reactor on a pilot plant scale. From this study, UV/H2O2 was found to be the best treatment for dye elimination. The optimal peroxide dosage for the degradation of dyes and the elimination of bacteria was 0.07 M. In this case, 70.80% of discoloration was achieved after 7 h of sunlight exposure, under an average sunlight intensity of 3.42 W/m2. The photocatalytic treatment based on TiO2 achieved the highest elimination of coliform bacteria and the lowest TOC value; however, the presence of this material in the reactor had a detrimental effect on the overall elimination of dyes. A combination of both UV/H2O2 and TiO2 treatments significantly improves the dyes discoloration, the elimination of bacteria, and the organic compounds degradation. Some of the results of this study were presented at the 4th Congreso Colombiano de Procesos Avanzados de Oxidación, 4CCPAOx.
Octubre, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/w13192705
Reactividad de Sólidos
A first insight into the microstructure and crack propagation in novel boron nitride nanosheet/3YTZP composites
Munoz-Ferreiro, C; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, RBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 60 (2021) 128-136
Show abstract ▽
In this work, novel 3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycristalline (3YTZP) ceramic composites with boron nitride nanosheets (BNNS) are investigated for the first time. Highly densified composites with 1 and 4 vol% BNNS were obtained by spark plasma sintering (SPS) after BNNS synthesis using a solution exfoliation method and BNNS dispersion into the ceramic powder by ultrasonication. The BNNS presented homogeneous distribution throughout the ceramic matrix and preferential alignment in the plane perpendicular to the pressing axis during SPS. The BNNS incorporation had practically no effect on the Vickers hardness of the material nor on the Young's modulus. Anisotropy in crack development was found in the composite with 4% vol BNNS, together with a mechanism of extensive microcracking. Several energy-absorbing mechanisms during crack propagation, such as crack deflection, crack bridging, crack branching, BNNS pull-out and BNNS debonding, were identified in the composites by a close observation of the indentation-induced fracture paths.
Marzo, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.bsecv.2020.02.003
Archeometric characterization (physical-chemical and microstructural) of tiles in the Mudejar Palace of the Royal Alcazar of Seville using non-invasive quantitative chemical methods
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Robador, MD; Castaing, J; de Viguerie, L; Garrote, MA; Pleguezuelo, ABoletin de la Sociedad Española de Ceramica y Vidrio, 60 (2021) 211-228
Show abstract ▽
The Palaces in the Alcazar of Seville, Spain, are famous for their ceramic decoration. The technique of tessellation was used extensively in all rooms in the Mudejar Palace, dated in the fourteenth century. These glazed ceramics have been analysed in situ using noninvasive quantitative chemical methods of X-ray fluorescence and diffraction (XRF and XRD). Micro-samples were taken to prepare cross-sections and analysed by optical and electronic microscopy. The composition of these ceramics, their manufacturing technique and the time of application in the different areas of the Palace have been characterized in this work. Five colours have been found in the glazed ceramics: green, black, molasses, white and blue. Fe, Co, Cu, Mn and Sn are the main chemical elements responsible for the colour of the glass phase of these ceramics. Wollastonite, quartz, bustamite and feldspars inclusions have been found in the glass phase. Casiterite and Malayaite have been also characterized by XRD. The ceramic paste used for manufacturing was calcic and was heated at about 900 degrees C. Thenardite, gypsum, sodium chloride and nitrogen compounds have been characterized in the ceramic and are responsible for their alteration. The information obtained in the 24 zones studied shows that there is no homogeneity in the ceramics due to the different times in which the tiles were placed and the restorations carried out over time. There are 3 main groups of ceramics: a) probably from 14th century, b), probably from 15-16th centuries and c) from 19-20th centuries and recent restorations.
Julio, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.bsecv.2020.03.001
- ‹ anterior
- 85 of 410
- siguiente ›
icms











