Artículos SCI
2023
2023
Reactividad de Sólidos
Negative emissions power plant based on flexible calcium-looping process integrated with renewables and methane production
Ortiz, C; García-Luna, S; Carro, A; Chacartegui, R; Pérez-Maqueda, LRenewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 185 (2023) 113614
Show abstract ▽
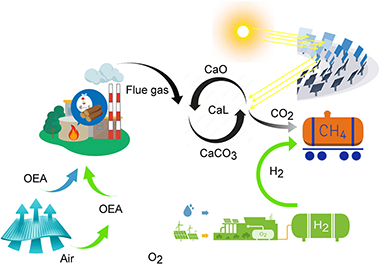
This paper provides a review of negative carbon capture technologies. Based on these technologies, here it is proposed an innovative negative emissions power plant combining the generation and storage of energy from biomass, photovoltaic, and concentrated solar power, capturing and recovering CO2 by producing H2 or CH4 as green energy carriers. The main features of the system are i) large-scale energy production system with negative CO2 emissions; ii) 100% renewable system based on biomass and solar energy with the possibility of integrating other renewables; iii) synergistic integration of processes and systems; iv) recovery of O2 generated by photovoltaic-driven electrolysis within the process of partial biomass oxycombustion and v) solar-driven limestone calcination. A detailed model of the entire plant is developed to evaluate the integration of the process. The model performance is assessed on an hourly basis throughout the whole year. The base case results show an energy consumption from 1 to 2.1 MJ/kg CO2 to capture 60–77% of CO2 emitted from the biomass plant and green methane production of more than 7500 tons/year. The negative emissions associated with the process are -612 kg CO2/MWh. It justifies the interest in the proposed negative emissions power plant.
Octubre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.113614
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Process design and utilisation strategy for CO2 capture in flue gases. Technical assessment and preliminary economic approach for steel mills
Navarro, JC; Baena-Moreno, FM; Centeno, MA; Laguna, OH; Almagro, JF; Odriozola, JARenewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 184 (2023) 113537
Show abstract ▽
The steel industry is the most relevant sector in emerging economies due to its application in numerous fields. However, steel manufacturing involves large energy investment and produces significant greenhouse gas emissions. The current world economic and environmental scenario therefore necessitates that improvements in the footprint of the steel industry be made without affecting its viability. Considering the present challenge, we report two possible processes for Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU). The first process is the competitive capture of CO2-SO2, followed by CO2 valorisation to methane. However, the CO2 capture capacity and lifetime for the adsorbent after multiple cycles could be improved through preliminary desulphurization of the gas current. The improved system demonstrates net profitability in a typical stainless steel plant. Therefore, it can be implemented in an industrial setting without profitability loss to steelmaking operations, fulfilling bot the goal of reducing CO2 emissions while protecting the mainstay of the plant.
Septiembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.113537
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Hydrogen production by catalytic aqueous-phase reforming of waste biomass: a review
González-Arias, J; Zhang, Z; Reina, TR; Odriozola, JAEnvironmental Chemistry Letters, 21 (2023) 3089-3104
Show abstract ▽
The rising adverse effects of climate change call for a rapid shift to low-carbon energy and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels. For that, biorefineries appear as promising alternatives to produce energy, chemicals, and fuels using biomass and waste as raw materials. Here, we review catalytic aqueous-phase reforming to convert biomass and organic waste carbohydrates into renewable hydrogen, with focus on reforming basics; catalyst design; reforming of model compounds, wastewater and biomass; economics and life cycle assessment. We found that platinum and palladium are technically highly effective, yet their high price may limit upscaling. Alternatively, addition of tin to nickel gives acceptable results and improves hydrogen selectivity from 35 to 90%. We observed that hydrogen production decreases from 14% for crude glycerol to 2% for pure glycerol, thus highlighting the need to do experiments with real wastewater. The rare experiments on real wastewater from brewery, juice, tuna, and cheese industries have given hydrogen production rates of up to 149.7 mg/L. Aqueous-phase reforming could be shortly competitive with prices around 3-6 USD per kg of hydrogen, which are nearing the current market prices of 2-3 USD per kg.
Agosto, 2023 | DOI: 10.1007/s10311-023-01643-w
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Catalytic conversion of syngas to light hydrocarbons via simulated intermediates CO/CO2/DME/N2/H2 over the regulated acidity of SAPO-34
Meng, FH; Wang, LA; Nawaz, MA; Wang, Q; Gong, ZY; Li, ZChemical Engineering Journal,
Show abstract ▽
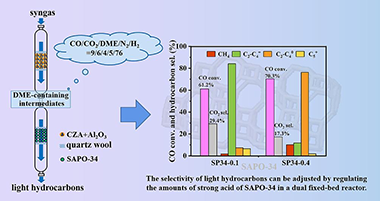
Direct conversion of syngas to light hydrocarbons has been intensively studied in recent years; however, the high selectivity of light hydrocarbons is still a challenging task to achieve a high CO conversion. Here, a bifunctional catalyst consisting of a methanol synthesis catalyst (CZA) and a methanol to dimethyl ether (DME) catalyst (Al2O3) was employed with a hydrocarbon synthesis catalyst (SAPO-34), for syngas conversion to light hydrocarbons in a dual fixed-bed reactor. The conversion of simulated intermediates CO/CO2/DME/N2/H2 with a molar ratio of 9/6/4/5/76, obtained from syngas conversion to DME over CZA and Al2O3, was studied over SAPO-34 zeolites. It was found that SP34-0.1 with Si/Al ratio of 0.1, exhibited low amount of strong acid (0.60 mmol/g) and high selectivity to light olefins (74.1%), while SP34-0.4 with Si/Al ratio of 0.4 exhibited high amount of strong acid (1.00 mmol/g) leading to high selectivity of light paraffins (88.4%). The in-situ DRIFTS analysis illustrated that DME can be rapidly adsorbed on the hydroxyl site of SAPO-34 and decomposed into the surface methyl species, where SP34-0.4 could produce more dimethylcyclopentenyl cationic species than SP340.1. It was suggested that the overall reaction route led to a high selectivity to light olefins (84.2%) with a CO conversion of 61.2% on (CZA + Al2O3) catalyst combined with SP34-0.1, while a high selectivity to light paraffins (76.3%) could be achieved by combining with SP34-0.4 at 70.3% CO conversion. Since, the current study interprets that the selectivity of hydrocarbons can be adjusted by regulating the acidity of SAPO-34 to achieve a high CO conversion in the dual fixed-bed reactor scheme.
Octubre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.145895
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Low CO2 hydrogen streams production from formic acid through control of the reaction pH
Santos, JL; Lopez, ER; Ivanova, S; Monzon, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemical Engineering Journal, 455 (2023) 140645
Show abstract ▽
There are multiple factors that influence the catalyst performance in the reaction of formic acid dehydrogena-tion: the nature of catalyst and/or support, the used solvent and reaction variables such as temperature, time, formic acid concentration, presence/absence of formates and pH of the solution. This work evaluates a series of important parameters like the influence of the pH by itself, the influence of the nature of used alkali agents and the effect of direct formate addition as reactive on hydrogen production via formic acid dehydrogenation over a commercially available catalyst. The catalytic performance appears to depend on the ionic radius of the cations of the used base which reflects consequently on the hydrogen selectivity. The best base to be used must have lower hydrated cationic radii and a starting pH around 4 to achieve important hydrogen selectivity for medium term formic acid conversion.
Febrero, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.140645
- ‹ anterior
- 8 of 410
- siguiente ›
icms











