Artículos SCI
2023
2023
Reactividad de Sólidos
Partial oxycombustion-calcium looping hybridisation for CO2 capture in waste-to-energy power plants
Ortiz, C; García-Luna, S; Chacartegui, R; Valverde, JM; Pérez-Maqueda, LJournal of Cleaner Production, 403 (2023) 136776
Show abstract ▽
Integrating bioenergy and carbon capture and storage (BECCS) presents a great opportunity for power produc-tion with negative global CO2 emissions. This work explores a novel synergetic system that integrates mem-branes, partial biomass oxycombustion and the calcium looping (CaL) process. Polymeric membranes generate oxygen-enriched air (OEA) with an O2 concentration of 39%v/v, which is used for partial oxycombustion of biomass waste. The CO2-enriched flue gas evolves from the waste-to-energy plant to the CaL unit, where CO2 concentration is increased up to 90-95%v/v, ready for purification and sequestration. Compared to only oxy-combustion systems, the proposed concept presents fewer technological challenges in retrofitting boilers to waste-to-energy plants. Moreover, this new approach is highly efficient as integrating membranes to produce OEA instead of cryogenic distillation systems significantly reduces energy consumption. A novel integration concept is modelled to evaluate the whole process efficiency and the effect of key parameters on the system performance, such as the temperature of the reactors, the membrane surface area, and the partial oxy-combustion degree. The results show that the so-called mOxy-CaL system has an energy consumption associ-ated with CO2 capture below 4 MJ/kg CO2 (a 31% lower than that for a conventional CaL process), with a higher CO2 capture efficiency than oxycombustion and the CaL process separately. On the other hand, the economic analysis shows a higher CO2 capture cost for the novel configuration than for the typical CaL configuration due to the additional investment cost of the membrane system. Improvements in membrane performance by increasing its permeance and diminishing the required surface area would significantly reduce the economic cost of this novel integration. Using membranes with permeance over 400 GPU would boost the system's competitiveness.
Junio, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136776
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Plasticized, greaseproof chitin bioplastics with high transparency and biodegradability
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Benitez, JJ; Porras-Vazquez, JM; Tedeschi, G; Morales, Y; Fernandez-Ortuno, D; Athanassiou, A; Guzman-Puyol, SFood Hydrocolloids, 145 (2023) 109072
Show abstract ▽
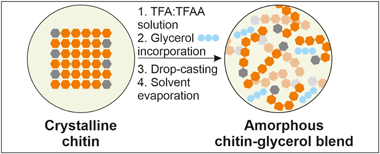
A mixture of trifluoroacetic acid:trifluoroacetic anhydride (TFA:TFAA) was used to dissolve chitin from shrimp shells. Free-standing films were prepared by blending the chitin solution and glycerol at different percentages, followed by drop-casting, and the complete evaporation of the solvents. After this process, the chitin matrix showed an amorphous molecular structure, as determined by X-ray diffraction. Optical, mechanical, thermal, and antioxidant properties were also thoroughly investigated. The incorporation of glycerol induced a plasticizing effect on the mechanical response of films and improved their transparency. In addition, hydrodynamic and barrier properties were determined by contact angle and water vapor/oxygen transmission rates, respectively, and revealed typical values of other polysaccharides. These bioplastics also presented an excellent greaseproof behavior with the highest degree of oil repellency as determined by the Kit test. Moreover, the overall migration was evaluated by using Tenax & REG; as a dry food simulant and levels were compliant with European regulations. Their antifungal properties were tested using Botrytis cinerea as a model. Biodegradability was also determined by measuring the biological oxygen demand in seawater. Degradation rates were high and similar to those of other fully-degradable materials.
Diciembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109072
Materiales Coloidales
Carboxylate functionalized NaDy(MoO4)(2) nanoparticles with tunable size and shape as high magnetic field MRI contrast agents
Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Nuñez, NO; Caro, C; Garcia-Martin, ML; Ocaña, MJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 629 (2023) 310-321
Show abstract ▽
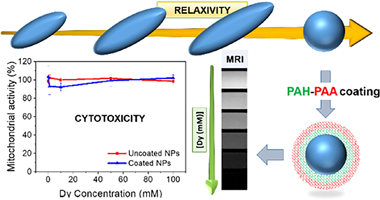
Uniform sodium-dysprosium double molybdate (NaDy(MoO4)(2)) nanoparticles having different morphologies (spheres and ellipsoids) and tunable size have been synthesized for the first time in literature. The procedure is based on a homogeneous precipitation process at moderated temperatures (<= 220 ?) from solutions containing appropriated precursors dissolved in ethylene glycol-water mixtures, in the absence (spheres) or the presence (ellipsoids) of tartrate anions. The effects of the morphological characteristics (size and shape) of the nanoparticles on the magnetic relaxivity at high field (9.4 T) have been evaluated finding that the latter magnitude was higher for the spheres than for the ellipsoids, indicating their better suitability as contrast agents for high-field magnetic resonance imaging. Such nanoparticles have been successfully coated with polymers bearing carboxylate functional groups through a layer-by -layer process, which improves the colloidal stability of the nanoparticles in physiological media. It has been also found that the coating layer had no significant effects on the nanoparticles relaxivity and that such coated nanoparticles exhibited a high biocompatibility and a high chemical stability. In summary, we have developed NaDy(MoO4)(2 )based bioprobes which meet the required criteria for their use as contrast agents for high-field magnetic resonance imaging.
Enero, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.08.130
Materiales Coloidales
Lanthanide vanadate-based trimodal probes for near-infrared luminescent bioimaging, high-field magnetic resonance imaging, and X-ray computed tomography
Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Nunez, NO; Caro, C; Garcia-Martin, ML; Becerro, AI; Ocaña, MJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 646 (2022) 721-731
Show abstract ▽
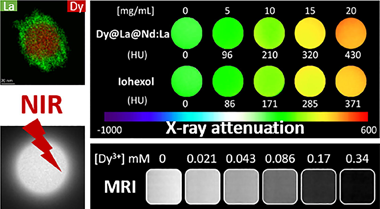
We have developed a trimodal bioimaging probe for near-infrared luminescent imaging, high-field magnetic resonance imaging, and X-ray computed tomography using Dy3+ as the paramagnetic component and Nd3+ as the luminescent cation, both of them incorporated in a vanadate matrix. Among different essayed architectures (single phase and core-shell nanoparticles) the one showing the best luminescent properties is that consisting of uniform DyVO4 nanoparticles coated with a first uniform layer of LaVO4 and a second layer of Nd3+-doped LaVO4. The magnetic relaxivity (r2) at high field (9.4 T) of these nanoparticles was among the highest values ever reported for this kind of probes and their X-ray attenuation properties, due to the presence of lanthanide cations, were also better than those of a commercial contrast agent (iohexol) commonly used for X-ray computed to-mography. In addition, they were chemically stable in a physiological medium in which they could be easily dispersed owing to their one-pot functionalization with polyacrylic acid, and, finally, they were non-toxic for human fibroblast cells. Such a probe is, therefore, an excellent multimodal contrast agent for near-infrared luminescent imaging, high-field magnetic resonance imaging, and X-ray computed tomography.
Septiembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2023.05.078
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Is the RWGS a viable route for CO2 conversion to added value products? A techno-economic study to understand the optimal RWGS conditions
Portillo, E; Gandara-Loe, J; Reina, TR; Pastor-Perez, LScience of the Total Environment, 857 (2023) 159394
Show abstract ▽
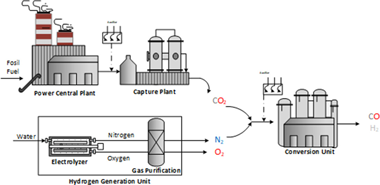
Understanding the viability of the RWGS from a thermodynamic and techno-economic angle opens new horizons within CO2 conversion technologies. Unfortunately, profitability studies of this technology are scarce in literature and mainly focused on overall conversion and selectivity trends with tangential remarks on energy demands and pro-cess costs. To address this research gap, herein we present a comprehensive techno-economic study of the RWGS reac-tion when coupling with Fischer-Tropsch synthesis is envisaged to produced fuels and chemicals using CO2 as building block. We showcase a remarkable impact of operating conditions in the final syngas product and both CAPEX and OPEX. From a capital investment perspective, optimal situations involve RWGS unit running at low temperatures and high pressures as evidenced by our results. However, from the running cost angle, operating at 4 bar is the most favorable alternative within the studied scenarios. Our findings showcase that, no matter the selected temperature the RWGS unit should be preferentially run at intermediate pressures. Ultimately, our work maps out multiple operat-ing scenarios in terms of energy demand and process cost serving as guideline to set optimal reaction conditions to un-lock the potential of the RWGS for chemical CO2 recycling.
Enero, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159394
- ‹ anterior
- 11 of 411
- siguiente ›
icms











