Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Materiales Avanzados
Geopolymers made from metakaolin sources, partially replaced by Spanish clays and biomass bottom ash
Eliche-Quesada, D; Calero-Rodriguez, A; Bonet-Martinez, E;Perez-Villarejo, L; Sanchez-Soto, PJJournal of Building Engineering, 40 (2021) 102761
Show abstract ▽
The main objective of this investigation is to study the effect of the substitution of metakaolin (MK) (from calcined industrial kaolin) by four different calcined natural Southern Spain clays traditionally used in the brick and tile sector, as well as by the biomass bottom ash residue (BBA) from the combustion of a mix of olive and pine pruning on the synthesis of geopolymer with physical, mechanical and thermal properties comparable to those of classic construction materials. As alkaline activator, a 8 M solution of sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate have been used. Raw materials, metakaolin; Spanish clays: black clay (BC), yellow clay (YC), white clay (WC), red clay (RC) and BBA were characterized by chemical analysis (XRF), mineralogical analysis (XRD), and particle size analysis. Control geopolymers containing only metakaolin, and batch of geopolymers were formulated containing equal proportions of metakaolin, BBA and each of the four types of clay. After the curing period, at 60 degrees C for 1 day geopolymers were demolded and stored 27 days at room temperature. Geopolymers were characterized using Scanning Electron Microscopy coupled with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), XRD and Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared Spec troscopy (ATR-FTIR). Their physical, mechanical and thermal properties have also been studied. The addition of BBA and different types of calcined clays to metakaolin gives rise to geopolymers with higher mechanical properties increasing the compressive strength of the control geopolymer containing only MK (24.9 MPa) by more than 50% for the GMK-BBA-WC geopolymers (38.5 MP a). The clays act as fillers and/or promote the precipitation of calcium-rich phases (Ca)-A-S-H-G gel that coexists with the (Na)-A-S-H gel type. The relevant results of physical, mechanical and thermal properties obtained in this research demonstrate the potential of Spanish clays and BBA as binders and substitutes for metakaolin.
August, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102761
Reactividad de Sólidos
Calcination under low CO2 pressure enhances the calcium Looping performance of limestone for thermochemical energy storage
Sarrion, B; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Amghar, N; Chacartegui, R; Valverde, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAChemical Engineering Journal, 417 (2021) 127922
Show abstract ▽
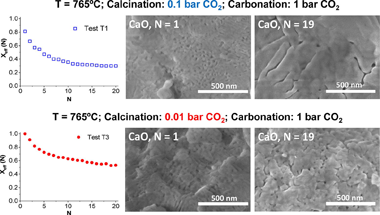
The Calcium Looping performance of limestone for thermochemical energy storage has been investigated under novel favorable conditions, which involve calcination at moderate temperatures under CO2 at low pressure (0.01 and 0.1 bar) and carbonation at high temperature under CO2 at atmospheric pressure. Calcining at low CO2 pressures allows to substantially reduce the temperature to achieve full calcination in short residence times. Moreover, it notably enhances CaO multicycle conversion. The highest values of conversion are obtained for limestone samples calcined under 0.01 bar CO2 at 765 degrees C. Under these conditions, the residual conversion is increased by a factor of 10 as compared to conditions involving calcination under CO2 at atmospheric pressure. The enhancement of CaO conversion is correlated to the microstructure of the CaO samples obtained after calcination. As seen from SEM, BET surface and XRD analysis, calcination under low CO2 pressure leads to a remarkable decrease of pore volume and CaO crystallite size. Consequently, CaO surface area available for carbonation in the fast reaction-controlled regime and therefore reactivity in short residence times is promoted.
August, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127922
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical synthesis of ternary chalcogenide chalcostibite CuSbS2 and its characterization
Dutkova, E; Sayagues, MJ; Fabian, M; Kovac, J; Kovat, J; Balaz, M; Stahorsky, MJournal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics (2021)
Show abstract ▽
In this work, the very rapid one-step mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline ternary chalcogenide chalcostibite CuSbS2 prepared from copper, antimony, and sulfur precursors by high-energy milling for only 30 min in a planetary mill is reported. XRD confirmed the orthorhombic crystal structure of CuSbS2. The crystallite size of CuSbS2 calculated by LeBail refinement of the X-ray powder diffraction data was 25 nm. The nanocrystalline chalcostibite CuSbS2 was also confirmed by transmission electron microscopy. The purity of CuSbS2 was verified by Raman spectroscopy. The synthesized chalcostibite exhibits the specific surface area value of 2.4 m(2)g(-1). UV-Vis spectroscopy showed the optical bandgap of CuSbS2 as 1.54 eV with wide range of absorption in visible region. Photoresponse of CuSbS2 was confirmed by I-V measurements under dark and light illumination. The proposed mechanochemical synthesis provides an alternative approach to prepare also other ternary semiconductor nanomaterials. CuSbS2 semiconductor nanocrystals have the potential to be used as light absorbers in photovoltaics.
August, 2021 | DOI: 10.1007/s10854-021-06767-9
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Characterizing the physicochemical and mechanical properties of ZrN thin films deposited on Zr substrates by pulsed laser technique
Ghemras, I; Abdelli-Messaci, S; Alili, B; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Rico, VJ; Izerrouken, M; Khereddine, AY; Hadj-Larbi, FEuropean Physical Journal-Applied Physics, 95 (2021) 10301
Show abstract ▽
Due to their outstanding physical and mechanical features, ZrN thin films are increasingly used as coatings to protect materials intended for nuclear applications such as Zirconium. To our knowledge, there is no report of pulsed laser deposition (PLD) of ZrN thin films on a Zr substrate. In this work, we have successfully prepared ZrN thin films on Zr substrates using the PLD technique with a KrF excimer laser, in a N-2 environment at 2 Pa pressure and a fixed substrate temperature of 500 degrees C. The deposited 200 nm ZrN thin films exhibited a homogeneous surface and showed a face-centered cubic polycrystalline structure. The surface roughness was 3.69 nm. X-ray diffraction, Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy measurements confirmed the presence of ZrN. The coated sample's mean value of hardness (11.6 GP) doubled that of the uncoated sample.
July, 2021 | DOI: 10.1051/epjap/2021210064
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
How a small modification in the imidazolium-based SDA can determine the zeolite structure? MFI vs. TON
Megias-Sayago, C; Blanes, JMM; Szyja, BM; Odriozola, JA; Ivanova, SMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 322 (2021) 111160
Show abstract ▽
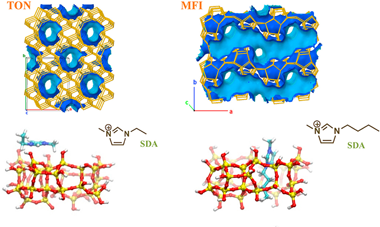
The present study proposes an important contribution to the understanding of ionic liquid role as structure directing agent for zeolite synthesis. A series of imidazolium based ionic liquids are used for this purpose. While the anionic counterpart influences the micellar organization during the synthesis, the imidazolium cation clearly directs the structure to one or another zeolite family as a function of its substituents and their interaction with the zeolite framework. The experimental observations are contrasted with molecular modeling explaining the distinct zeolite families obtained on the basis of different preferential orientation of the ionic liquids to the Si33 precursor.
July, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111160
- ‹ previous
- 71 of 410
- next ›














