Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Bimetallic Ni-Ru and Ni-Re Catalysts for Dry Reforming of Methane: Understanding the Synergies of the Selected Promoters
Moreno, AA; Ramirez-Reina, T; Ivanova, S; Roger, AC; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAFrontiers in Chemistry, 9 (2021) 694976
Show abstract ▽
Designing an economically viable catalyst that maintains high catalytic activity and stability is the key to unlock dry reforming of methane (DRM) as a primary strategy for biogas valorization. Ni/Al2O3 catalysts have been widely used for this purpose; however, several modifications have been reported in the last years in order to prevent coke deposition and deactivation of the samples. Modification of the acidity of the support and the addition of noble metal promoters are between the most reported strategies. Nevertheless, in the task of designing an active and stable catalyst for DRM, the selection of an appropriate noble metal promoter is turning more challenging owing to the lack of homogeneity of the different studies. Therefore, this research aims to compare Ru (0.50 and 2.0%) and Re (0.50 and 2.0%) as noble metal promoters for a Ni/MgAl2O4 catalyst under the same synthesis and reaction conditions. Catalysts were characterized by XRF, BET, XRD, TPR, hydrogen chemisorption (H2-TPD), and dry reforming reaction tests. Results show that both promoters increase Ni reducibility and dispersion. However, Ru seems a better promoter for DRM since 0.50% of Ru increases the catalytic activity in 10% and leads to less coke deposition.
July, 2021 | DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.694976
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Current scenario and prospects in manufacture strategies for glass, quartz, polymers and metallic microreactors: A comprehensive review
Dominguez, MI; Centeno, MA; Martinez, TM; Bobadilla, LF; Laguna, OH; Odriozola, JAChemical Engineering Research & Design, 171 (2021) 13-35
Show abstract ▽
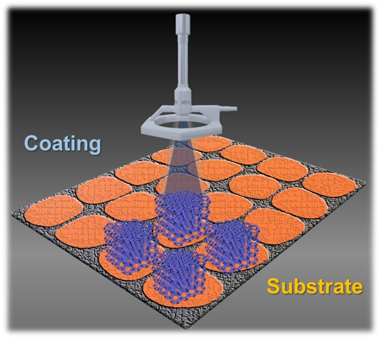
One of the most remarkable benefits of the microreactors is the achievement of more efficient processes by enhancing the heat and mass transfer phenomena, which is the key factor for processes intensification in chemical reactions, resulting in higher conversion, selectivity and yield towards desired products. Currently, the entire scenario of microreaction approach is an emergent technology and further advances are ongoing. Several strategies have been successfully applied for structuring processes that imply the fixation of the catalysts on the microreactors. However, there are features such as the physicochemical stability of the coatings under reaction conditions that must be improved, motivating the search for new protocols. This review provides a general overview of the most important methodologies applied for glass, quartz, polymers and metals microreactors manufacture and for their coating, analyzing the advantages and drawbacks of every procedure. Furthermore, an outline of the novel insights based on additive manufacturing techniques are described.
July, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cherd.2021.05.001
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Characterizing the physicochemical and mechanical properties of ZrN thin films deposited on Zr substrates by pulsed laser technique
Ghemras, I; Abdelli-Messaci, S; Alili, B; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Rico, VJ; Izerrouken, M; Khereddine, AY; Hadj-Larbi, FEuropean Physical Journal-Applied Physics, 95 (2021) 10301
Show abstract ▽
Due to their outstanding physical and mechanical features, ZrN thin films are increasingly used as coatings to protect materials intended for nuclear applications such as Zirconium. To our knowledge, there is no report of pulsed laser deposition (PLD) of ZrN thin films on a Zr substrate. In this work, we have successfully prepared ZrN thin films on Zr substrates using the PLD technique with a KrF excimer laser, in a N-2 environment at 2 Pa pressure and a fixed substrate temperature of 500 degrees C. The deposited 200 nm ZrN thin films exhibited a homogeneous surface and showed a face-centered cubic polycrystalline structure. The surface roughness was 3.69 nm. X-ray diffraction, Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy measurements confirmed the presence of ZrN. The coated sample's mean value of hardness (11.6 GP) doubled that of the uncoated sample.
July, 2021 | DOI: 10.1051/epjap/2021210064
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
How a small modification in the imidazolium-based SDA can determine the zeolite structure? MFI vs. TON
Megias-Sayago, C; Blanes, JMM; Szyja, BM; Odriozola, JA; Ivanova, SMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 322 (2021) 111160
Show abstract ▽
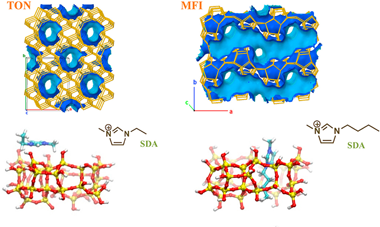
The present study proposes an important contribution to the understanding of ionic liquid role as structure directing agent for zeolite synthesis. A series of imidazolium based ionic liquids are used for this purpose. While the anionic counterpart influences the micellar organization during the synthesis, the imidazolium cation clearly directs the structure to one or another zeolite family as a function of its substituents and their interaction with the zeolite framework. The experimental observations are contrasted with molecular modeling explaining the distinct zeolite families obtained on the basis of different preferential orientation of the ionic liquids to the Si33 precursor.
July, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111160
Reactividad de Sólidos
Tuning the excitation wavelength of luminescent Mn2+-doped ZnSxSe1-x obtained by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Aviles, MA; Gotor, FJOptical Materials, 117 (2021) 111121
Show abstract ▽
Mn2+-doped ZnSxSe1-x solid solution samples (Mn:ZnSxSe1-x) were synthesized by the mechanochemical process denoted as mechanically-induced self-sustaining reaction from Mn/Zn/S/Se powder elemental mixtures. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, diffuse reflectance UV-Vis spectroscopy and emission and excitation photoluminescence measurements. The band-gap energy of samples was controlled by changing the stoichiometry, x, of the solid solution. All samples showed the characteristic Mn2+ 4T1-6A1 emission at -588 nm when exciting the host material, so it was possible to tune the excitation wavelength from 349 nm to 467 nm. However, an efficiency loss was observed with increasing Se content, probably due to the overlap between the absorption and emission spectra that induced self-absorption and emission quenching.
July, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111121
- ‹ previous
- 72 of 410
- next ›














