Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
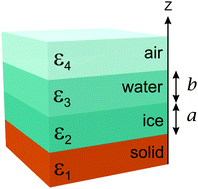
Premelting of ice adsorbed on a rock surface
Esteso, V; Palacios, SC; MacDowell, LG; Fiedler, J; Parsons, DF; Spallek, F; Miguez, H; Persson, C; Buhmann, SY; Brevik, I; Bostrom, MPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 22 (2020) 11362-11373 DOI: 10.1039/c9cp06836h
Abstract
Considering ice-premelting on a quartz rock surface (i.e. silica) we calculate the Lifshitz excess pressures in a four layer system with rock-ice-water-air. Our calculations give excess pressures across (1) ice layer, (2) water layer, and (3) ice-water interface for different ice and water layer thicknesses. We analyse equilibrium conditions where the different excess pressures take zero value, stabilized in part by repulsive Lifshitz interactions. In contrast to previous investigations which considered varying thickness of only one layer (ice or water), here we present theory allowing for simultaneous variation of both layer thicknesses. For a given total thickness of ice and water, this allows multiple alternative equilibrium solutions. Consequently the final state of a system will depend on initial conditions and may explain variation in experimental measurements of the thicknesses of water and ice layers.
May, 2020 · DOI: 10.1039/c9cp06836h
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Time-resolved operando DRIFTS-MS study of the moisture tolerance of small-pore SAPO-34 molecular sieves during CH4/CO2 separation
Romero, M; Navarro, JC; Bobadilla, LF; Dominguez, MI; Ivanova, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 298 (2020) 110071 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110071
Abstract
This study pretends to evaluate and understand the effect of moisture presence during CO2/CH4 separation on small-pore SAPO-34 molecular sieves. Two SAPO-34 samples with different physicochemical properties (composition, crystal size and texture) were prepared by hydrothermal synthesis using either one or a mixture of two templates. Transient operando DRIFTS-MS measurements revealed that the sample's hydrophobic character is associated to the presence of Si islands, which enhanced sample's moisture tolerance during repetitive adsorption/desorption cycles. This knowledge is fundamental to achieve the rational design of efficient SAPO-34 membranes under realistic conditions.
May, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110071
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
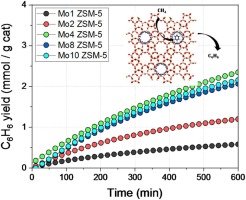
Structural and surface considerations on Mo/ZSM-5 systems for methane dehydroaromatization reaction
Lopez-Martin, A; Caballero, A; Colon, GMolecular Catalysis, 486 (2020) 110787 DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2020.110787
Abstract
We have prepared a series of Mo/ZSM-5 systems by impregnation method with different metal loading. The optimum performance has been attained for 4% metal loading, yielding to ca. 2 mmol(benzene)/g(ca)(t) at the end of the reaction. The obtained catalysts were widely structural and surface characterized. As Mo content increases, the surface feature of the support is affected specially its mesoporosity. It has been stated the enormous complexity of Mo species present in the studied system. In situ characterization by XPS reveals different reduction and carburization behaviour depending on the Mo content.
May, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2020.110787
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
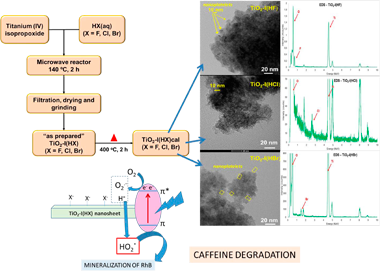
Microwave-assisted sol-gel synthesis of TiO2 in the presence of halogenhydric acids. Characterization and photocatalytic activity
Puga,F.;Navío,J.A.;Jaramillo-Páez,C.;Sánchez-Cid,P.;Hidalgo,M.C.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 394 (2020) 112457 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112457
Abstract
The synthesis of mesoporous TiO2 nanosheets is reported using Ti(IV) Isopropoxide as Ti(IV) precursor. A sol-gel process combined with microwave activation is used. Three different halogenhydric acids (HX), were used to peptise the sol: HF(ac), HCl (ac) and HBr (ac). The three obtained TiO2-I(HX) samples were characterized by XRD, XRF, N2-adsorption, SEM, TEM, DRS and XPS. The three synthesized samples have high values of specific surfaces (between 100 m2/g and 200 m2/g) and similar band gap values (3.2–3.3 eV). The analysis of the surface composition by XPS confirms the presence of the halogenated species (F, Cl or Br) on the surface of each ones of the samples. The nanometric size (ca 5 nm) of the particles for each of the three samples was confirmed by XRD and by TEM. On the other hand, the nature of the halogenated acid used plays a role in the composition of the phases. While the TiO2-I (HF) sample was 100 % anatase, the other samples turned out to be biphasic, showing anatase/rutile in the TiO2-I(HCl) sample and anatase/brookite in the TiO2-I(HBr) sample. The samples were tested under two illumination conditions (UV and visible light) using rhodamine B and caffeine. The indirect role of the halide agent on the photocatalytic activities thereof is discussed.
May, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112457
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Dibenzo-tetraphenyl diindeno perylene as hole transport layer for high-bandgap perovskite solar cells
Pegu, M; Caliò, L; Ahmadpour, M; Rubahn, HG; Kazim, S; Madsen, M; Ahmad, SEmergent Materials, 3 (2020) 109-116 DOI: 10.1007/s42247-020-00098-x
Abstract
Semi-transparent perovskite solar cells have the competitive edge of being employed for building integrated photovoltaics due to their esthetic benefits as light harvesting windows/facades. Perovskites have received considerable attention in recent years as a thin film photovoltaic alternative, that can also be tweaked for its transparency, evolving from potentially high bandgaps that are suited for semi-transparent solar cell fabrication. Due to the existing trade of between the efficiency and transparency of a perovskite solar cell, tuning the band gap can address this by making a bridge between the aforementioned parameters. We report our findings on the use of a wide-bandgap perovskite MAPbBr3, with a rational energetic level hole transport materials based on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon molecules that can be a promising alternative class of p-type material. In the present work, DBP (Dibenzo{[f,f′]-4,4′,7,7′-tetraphenyl}diindeno[1,2,3-cd :1′,2′,3′-lm]perylene was evaluated with high bandgap as well as with mixed (FAPbI3)0.85(MAPbBr3)0.15 perovskites for the fabrication of solar cell. DBP-based solar cells yielded competitive power conversion efficiencies as compared with classical HTMs.
May, 2020 · DOI: 10.1007/s42247-020-00098-x
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optical properties of molybdenum in the ultraviolet and extreme ultraviolet by reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy
Pauly, N; Yubero, F; Tougaard, SApplied Optics, 59 (2020) 4527-4532 DOI: 10.1364/AO.391014
Abstract
Optical properties of polycrystalline molybdenum are determined from ultraviolet up to extreme ultraviolet by reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy (REELS). Calculations are performed within the dielectric response theory by means of the quantitative analysis of electron energy losses at surfaces QUEELS-epsilon (k, omega)-REELS software [Surf. Interface Anal. 36, 824 (2004)] that allows the simulation of inelastic scattering cross sections, using a parametric energy loss function describing the optical response of the material. From this energy loss function, the real and imaginary parts of the dielectric function, the refractive index, and the extinction coefficient are deduced and compared with previously published results.
May, 2020 · DOI: 10.1364/AO.391014
Reactividad de Sólidos
Development of a high-pressure thermobalance working under constant rate thermal analysis
Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Thermal Analysis ande Calorimetry, 142 (2020) 1329-1334 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-020-09644-5
Abstract
A thermogravimetric instrument that works at high pressure of different gases has been designed and assembled. The instrument has been devised to work in a temperature range from room temperature to 1000 degrees C in various controlled pressures of selected gas up to 15 bar, and under conventional rising temperature and constant rate thermal analysis (CRTA) modes. CRTA method allows an intelligent control of the reaction temperature using a feedback system that monitors the mass gain or mass loss of the sample in such a way that the reaction rate is maintained constant all over the process at a preselected value. CRTA method provides a significant advantage for studying processes under high pressure as it reduces heat and mass transfer phenomena that are very relevant under these high-pressure experimental conditions. The thermal oxidation of Ni at 8 bar of pure oxygen has been used for testing the performance of the instrument under both linear heating rate and CRTA conditions.
April, 2020 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-020-09644-5
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
In Vitro and In Vivo Study of Titanium Grade IV and Titanium Grade V Implants with Different Surface Treatments
Diaz-Sanchez, RM; de-Paz-Carrion, A; Serrera-Figallo, MA; Torres-Lagares, D; Barranco, A; Leon-Ramos, JR; Gutierrez-Perez, JLMetals, 10 (2020) 449 DOI: 10.3390/met10040449
Abstract
The aim of our study is to evaluate different implant surface treatments using TiIV and TiV in in vitro and in vivo studies. An in vitro study was established comprising four study groups with treated and untreated TiIV titanium discs (TiIVT and TiIVNT) and treated and untreated TiV titanium discs (TiVT and TiVNT). The surface treatment consisted in a grit blasting treatment with alumina and double acid passivation to modify surface roughness. The surface chemical composition and the surface microstructure of the samples were analyzed. The titanium discs were subjected to cell cultures to determine cell adhesion and proliferation of osteoblasts on them. The in vivo study was carried out on the tibia of three New Zealand rabbits in which 18 implants divided into three experimental groups were placed (TiIVT, TiIVNT, and TiVT). Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) was performed to determine bone density around the implants. The results showed that cell culture had minor adhesion and cell proliferation in TiIVT and TiVT within the first 6 and 24 h. However, no differences were found after 48 h. No statistically significant differences were found in the in vivo micro-CT and histological study; however, there was a positive trend in bone formation in the groups with a treated surface. Conclusions: All groups showed a similar response to in vitro cell proliferation cultures after 48 h. No statistically significant differences were found in the in vivo micro-CT and histological study
April, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/met10040449
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
A 4-view imaging to reveal microstructural differences in obliquely sputter-deposited tungsten films
El Beainou, R; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Raschetti, M; Cote, JM; Alvarez, R; Palmero, A; Potin, V; Martin, NMaterials Letters, 264 (2020) 127381 DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.127381
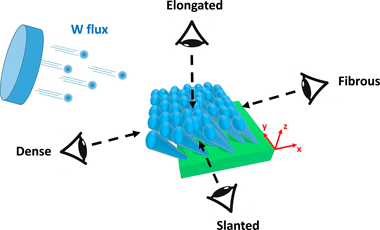
Abstract
We report on the morphological disparity of the columnar growth in W thin films sputter-deposited by oblique angle deposition. Oriented tungsten thin films (400 +/- 50 nm thick) are prepared using a tilt angle alpha of 80 degrees and a sputtering pressure of 0.25 Pa. Inclined columns (beta = 38 +/- 2 degrees) are produced and the microstructure is observed by scanning electron microscopy. A 4-view imaging is performed in order to show inhomogeneous growing evolutions in the columns. Morphological features vs. viewing direction are also investigated from a growth simulation of these tilted W columns. Experimental and theoretical approaches are successfully compared and allow understanding how the direction of the W particle flux leads to dense or fibrous morphologies, as the column apexes are in front of the flux or in the shadowing zone.
April, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.127381
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Monitoring, Modeling, and Optimization of Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystal Growth within Porous Matrices
Tiede, DO; Rubino, A; Calvo, ME; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2020) 8041-8046 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c01750
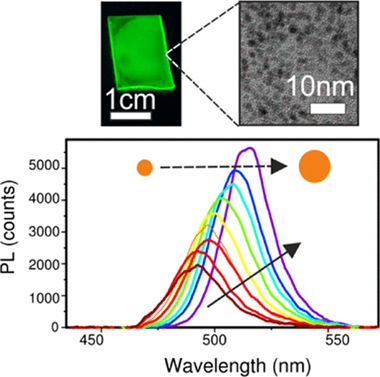
Abstract
The growth of lead halide perovskites within metal-oxide nanoporous films has been recently considered as a means to obtain chemically and photostable ligand-free high-quality nanocrystals (NCs). The growth process, governed by the reactions taking place in nanoreactors dictated by the matrix pore size, has not been explored so far. In this work, we use photoluminescence as a tool to monitor the growth of perovskite NCs within the void network of an optically transparent matrix. We consider the effect of different external factors, such as temperature, light illumination, or precursor concentration, on the growth dynamics, and discuss a possible formation mechanism of the confined perovskite NCs. Based on this analysis, guidelines that could serve to improve the fabrication and optoelectronic quality of this type of NCs are also proposed.
April, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c01750
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Advanced Strategies in Thin Films Engineering by Magnetron Sputtering
Palmero, A; Martin, NCoatings, 10 (2020) 419 DOI: 10.3390/coatings10040419
Abstract
This Special Issue contains a series of reviews and papers representing some recent results and some exciting perspectives focused on advanced strategies in thin films growth, thin films engineering by magnetron sputtering and related techniques. Innovative fundamental and applied research studies are then reported, emphasizing correlations between structuration process parameters, new ideas and approaches for thin films engineering and resulting properties of as-deposited coatings.
April, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/coatings10040419
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Bio-Based Coatings for Food Metal Packaging Inspired in Biopolyester Plant Cutin
Benitez, JJ; Osbild, S; Guzman-Puyol, S; Heredia, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAPolymers, 12 (2020) 942 DOI: 10.3390/polym12040942
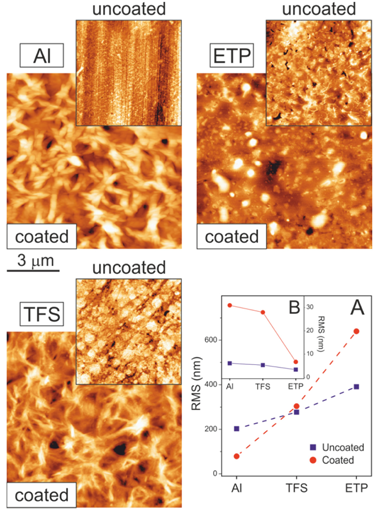
Abstract
Metals used for food canning such as aluminum (Al), chromium-coated tin-free steel (TFS) and electrochemically tin-plated steel (ETP) were coated with a 2-3-mu m-thick layer of polyaleuritate, the polyester resulting from the self-esterification of naturally-occurring 9,10,16-trihydroxyhexadecanoic (aleuritic) acid. The kinetic of the esterification was studied by FTIR spectroscopy; additionally, the catalytic activity of the surface layer of chromium oxide on TFS and, in particular, of tin oxide on ETP, was established. The texture, gloss and wettability of coatings were characterized by AFM, UV-Vis total reflectance and static water contact angle (WCA) measurements. The resistance of the coatings to solvents was also determined and related to the fraction of unreacted polyhydroxyacid. The occurrence of an oxidative diol cleavage reaction upon preparation in air induced a structural modification of the polyaleuritate layer and conferred upon it thermal stability and resistance to solvents. The promoting effect of the tin oxide layer in such an oxidative cleavage process fosters the potential of this methodology for the design of effective long-chain polyhydroxyester coatings on ETP.
April, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/polym12040942
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Study of the influence of the precursors on the sensing properties of ZnO:Cu system
Ramos, A; Urbieta, A; Escalante, G; Hidalgo, P; Espinos, JP; Fernandez, PCeramics International, 46 (2020) 8358-8367 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.12.068
Abstract
The properties of ZnO based materials for ethanol detection have been studied. Cu doped samples obtained from different precursors have been investigated. ZnO and ZnS have been used as host and Cu and CuO as dopant sources.
The sensing measurements have been mostly performed at room temperature. To monitor the effect of the presence of gas, resistivity and photoluminescence experiments with and without sensing gas have been carried out. The sensing behaviour is affected by the nature of the precursors used. For ZnO:Cu and ZnO:CuO series, a higher sensitivity is obtained at the lower gas concentrations, the better response is obtained for the sample ZnO:Cu with wt.1% of metallic copper. Strong segregation effects observed in these samples could be deleterious for the sensing properties. In the series ZnS:CuO, no segregation is observed, however the sensing behaviour is erratic and attributed to the reduction of Cu ions to the metallic state.
April, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.12.068
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Vegetable hierarchical structures as template for bone regeneration: New bio‐ceramization process for the development of a bone scaffold applied to an experimental sheep model
Filardo, G; Roffi, A; Fey, T; Fini, M; Giavaresi, G; Marcacci, M; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Martini, L; Ramirez-Rico, J; Salamanna, F; Sandri, M; Sprio, S; Tampieri, A; Kon, EJournal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B-Applied Materials, 108 (2020) 600-611 DOI: 10.1002/jbm.b.34414
Abstract
Long bone defects still represent a major clinical challenge in orthopedics, with the inherent loss of function considerably impairing the quality of life of the affected patients. Thus, the purpose of this study was to assess the safety and potential of bone regeneration offered by a load‐bearing scaffold characterized by unique hierarchical architecture and high strength, with active surface facilitating new bone penetration and osseointegration in critical size bone defects. The results of this study showed the potential of bio‐ceramization processes applied to vegetable hierarchical structures for the production of new wood‐derived bone scaffolds, further improved by surface functionalization, with good biological and mechanical properties leading to successful treatment of critical size bone defects in the sheep model. Future studies are needed to evaluate if these scaffolds prototypes, as either biomaterial alone or in combination with augmentation strategies, may represent an optimal solution to enhance bone regeneration in humans.
April, 2020 · DOI: 10.1002/jbm.b.34414
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
A Microstructure Insight of MTA Repair HP of Rapid Setting Capacity and Bioactive Response
Jimenez-Sanchez, MC; Segura-Egea, JJ; Diaz-Cuenca, AMaterials, 13 (2020) 1641 DOI: 10.3390/ma13071641
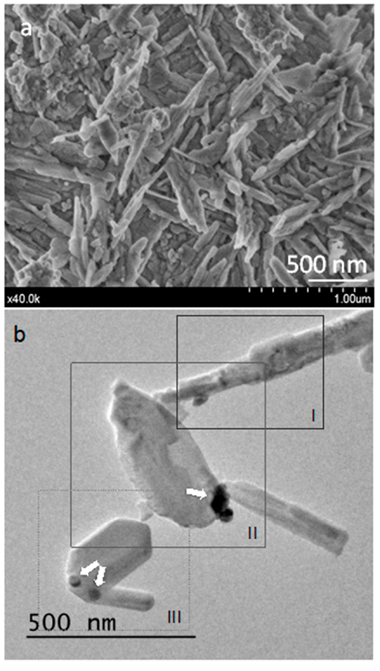
Abstract
Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) is considered a bioactive endodontic material, which promotes natural mineralization at the material-tooth tissue interface. MTA Repair HP stands out because of the short setting time and the quick and effective bioactive response in vitro. The bioactivity, depens on material composition and microstructure. This work is devoted to analyze MTA Repair HP microstructural features, of both the powder precursor and set material, to get insights into the material physicochemical parameters-functionality performance relationships. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM) coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) analyses were performed. X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements were carried out at different times to investigate setting process. Bioactivity evaluation in vitro was carried out by soaking the processed cement disk in simulated body fluid (SBF). The presented results point out those MTA Repair HP precursor material characteristics of tricalcium silicate particles of nanometric size and high aspect ratio, which provide an elevated surface area and maximized components dispersion of calcium silicate and very reactive calcium aluminate. The MTA Repair HP precursor powder nanostructure and formulation, allows a hydration process comprising silicate hydrate structures, which are very effective to achieve both fast setting and efficient bioactive response.
April, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/ma13071641
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Positron annihilation analysis of nanopores and growth mechanism of oblique angle evaporated TiO2 and SiO2 thin films and multilayers
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Butterling, M; Liedke, MO; Hirschmann, E; Trinh, TT; Attallah, AG; Wagner, A; Alvarez, R; Gil-Rostra, J; Rico, V; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 295 (2020) 109968 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109968
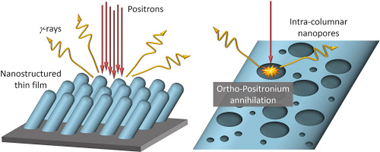
Abstract
The nano-porosity embedded into the tilted and separated nanocolumns characteristic of the microstructure of evaporated thin films at oblique angles has been critically assessed by various variants of the positron annihilation spectroscopy. This technique represents a powerful tool for the analysis of porosity, defects and internal interfaces of materials, and has been applied to different as-deposited SiO2 and TiO2 thin films as well as SiO2/TiO2 multilayers prepared by electron beam evaporation at 70 and 85 zenithal angles. It is shown that, under same deposition conditions, the concentration of internal nano-pores in SiO2 is higher than in TiO2 nanocolumns, while the situation is closer to this latter in TiO2/SiO2 multilayers. These features have been compared with the predictions of a Monte Carlo simulation of the film growth and explained by considering the influence of the chemical composition on the growth mechanism and, ultimately, on the structure of the films.
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109968
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Optical Responses of Localized and Extended Modes in a Mesoporous Layer on Plasmonic Array to Isopropanol Vapor
Murai, S; Cabello-Olmo, E; Kamakura, R; Calvo, ME; Lozano, G; Atsumi, T; Miguez, H; Tanaka, KJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2020) 5772-5779 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b10999
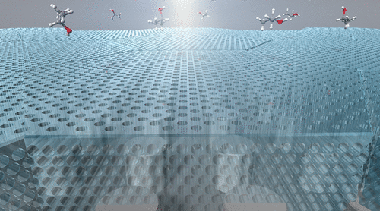
Abstract
Mesoporous silica features open and accessible pores that can intake substances from the outside. The combination of mesoporous silica with plasmonic nanostructures represents an interesting platform for an optical sensor based on the dependence of plasmonic modes on the refractive index of the medium in which metallic nanoparticles are embedded. However, so far only a limited number of plasmonic nanostructures are combined with mesoporous silica, including random dispersion of metallic nanoparticles and flat metallic thin films. In this study, we make a mesoporous silica layer on an aluminum nanocylinder array. Such plasmonic arrangements support both localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPRs) and extended modes which are the result of the hybridization of LSPRs and photonic modes extending into the mesoporous layer. We investigate in situ optical reflectance of this system under controlled pressure of isopropanol vapor. Upon exposure, the capillary condensation in the mesopores results in a gradual spectral shift of the reflectance. Our analysis demonstrates that such shifts depend largely on the nature of the modes; that is, the extended modes show larger shifts compared to localized ones. Our materials represent a useful platform for the field of environmental sensing.
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b10999
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Binder-free supercapacitor electrodes: Optimization of monolithic graphitized carbons by reflux acid treatment
Gomez-Martin, A; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Ramirez-Rico, JFuel Processing Technology, 199 (2020) 106279 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.106279

Abstract
The rational design of electrodes mimicking the cellular structure of natural bio-resources has been a matter of increasing interest for applications in energy storage. Due to their anisotropic and hierarchical porosity, monolithic carbon materials from natural wood precursors are appealing as electrodes for supercapacitor applications due to their interconnected channels, relatively low cost and environmentally friendly synthesis process. In this work, a liquid-phase oxidative treatment with refluxing nitric acid at 100 degrees C for 8 h was performed to enhance the surface properties of beech-derived graphitized carbons treated with an iron catalyst. Microstructural, textural and surface investigations revealed that this strategy was successful in removing amorphous carbon and in functionalizing their surfaces. The crystallinity, accessible surface area, micropore volume and surface functionality of beech-derived carbons were increased upon the reflux treatment. The resulting porous carbon materials were evaluated as binderless monolithic electrodes for supercapacitors applications in aqueous KOH electrolyte. A maximum specific capacitance of 179 F.g(-1) and a volumetric capacitance of 89 Fcm(-3) in galvanostatic charge/discharge experiments were reached. Monolithic electrodes exhibited good cycling stability, with a capacitance retention over 95% after 10,000 cycles.
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.106279
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Optical interference effects on the Casimir-Lifshitz force in multilayer structures
Esteso, V; Carretero-Palacios, S; Miguez, HPhysical Review A, 101 (2020) 033815 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.101.033815
Abstract
The Casimir-Lifshitz force F(C-L) between planar objects when one of them is stratified at the nanoscale is herein investigated. Layering results in optical interference effects that give rise to a modification of the optical losses, which, as stated by the fluctuation-dissipation theorem, should affect the Casimir-Lifshitz interaction. On these grounds, we demonstrate that, by nanostructuring the same volume of dielectric materials in diverse multilayer configurations, it is possible to access F(C-L) of attractive or repulsive nature, even getting canceled, at specific separation distances.
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.101.033815
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Potentialization of bentonite properties as support in acid catalysts
Amaya, J; Bobadilla, L; Azancot, L; Centeno, M; Moreno, S; Molina, RMaterials Research Bulletin, 123 (2020) 110728 DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.110728
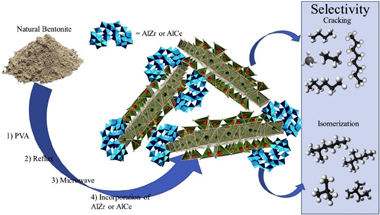
Abstract
Enhancement of the main physicochemical properties of a natural bentonite was carried out by means of modifications using surfactant, reflux, microwave treatment and, subsequently, the incorporation of AlZr and AlCe species. The evolution of the main changes in each modification stage was evaluated by means of X-ray diffraction, N-2 sortometry, scanning microscopy (SEM), NH3-TPD, NH3-DRIFTS and CO adsorption at low temperature. For the evaluation of the catalytic behavior, the dehydration-dehydrogenation reactions of 2-propanol and hydro-conversion of decane were used; both of which generate, in addition, information regarding the acidic properties of the materials. The correlation of the number, type and acid strength with the catalytic behavior, allowed establishing the effect produced by both the delamination method and the nature of the incorporated cation. This generated tools that allow controlling the physicochemical properties, and more specifically, the enhancement of the acidity of new supports based on this type of natural clay mineral.
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.110728
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of the Test Configuration and Temperature on the Mechanical Behaviour of WC-Co
Gonzalez, LM; Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJ; Bermejo, R; Llanes, L; Torres, YMetals, 10 (2020) 322 DOI: 10.3390/met10030322

Abstract
In this work, the effect of the test configuration and temperature on the mechanical behaviour of cemented carbides (WC-Co) with different carbide grain sizes (d(WC)) and cobalt volume fractions (V-Co), implying different binder mean free paths (lambda (Co)), was studied. The mechanical strength was measured at 600 degrees C with bar-shaped specimens subjected to uniaxial four-point bending (4PB) tests and with disc specimens subjected to biaxial ball-on-three-balls (B3B) tests. The results were analysed within the frame of the Weibull theory and compared with strength measurements performed at room temperature under the same loading conditions. A mechanical degradation greater than 30% was observed when the samples were tested at 600 degrees C due to oxidation phenomena, but higher Weibull moduli were obtained as a result of narrower defect size distributions. A fractographic analysis was conducted with broken specimens from each test configuration. The number of fragments (N-f) and the macroscopic fracture surface were related to the flexural strength and fracture toughness of WC-Co. For a given number of fragments, higher mechanical strength values were always obtained for WC-Co grades with higher K-Ic. The observed differences were discussed based on a linear elastic fracture mechanics (LEFM) model, taking into account the effect of the temperature and microstructure of the cemented carbides on the mechanical strength.
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/met10030322
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction as effective photocatalyst for the degradation of diclofenac and ketoprofen
Sacco, O.l; Murcia, J.J.; Lara, A.E.; Hernández-Laverde, M.; Rojas, H.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Vaiano, V.Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 107 (2020) 104839 DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104839
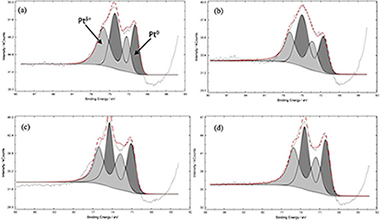
Abstract
Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction was synthetized and studied for the photocatalytic removal of diclofenac (DCF) and ketoprofen (KTF) under UV light irradiation. The physical-chemical properties of the prepared catalysts were analysed by different characterization techniques revealing that the lowest platinum nanoparticle size and the better metal distribution was observed in Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 sample. The Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction possessed the best photocatalytic activity toward both the photodegradation and mineralization of the two selected pollutants. The optimal photocatalyst showed a DCF and KTF mineralization rate of 0.0555 and 0.0746 min−1, respectively, which were higher than those of Pt–TiO2 (0.0321 min−1 for DCF and 0.0597 min−1 for KTF). The experiments driven to analyse the effects of free radical capture showed that ·OH, ·O2− and h+ have a primary role in reactive during the photocatalytic reaction. The improved photocatalytic performances of the Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction could be argue by a direct Z-scheme mechanism in which the Pt0 nanoparticles could act as a bridge between TiO2 and Nb2O5, improving the electron-hole separation and, ultimately, enhancing the photocatalytic removal rate of both DCF and KTF.
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104839
Reactividad de Sólidos
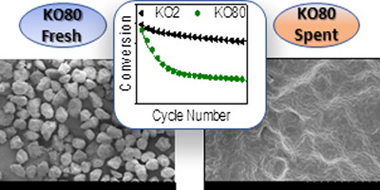
Role of particle size on the multicycle calcium looping activity of limestone for thermochemical energy storage
Duran-Martin, JD; Jimenez, PES; Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; Arcenegui-Troya, J; Trinanes, PG; Maqueda, LAPJournal of Advanced Research, 22 (2020) 67-76 DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2019.10.008
Abstract
The calcium looping process, based on the reversible reaction between CaCO3 and CaO, is recently attracting a great deal of interest as a promising thermochemical energy storage system to be integrated in Concentrated Solar Power plants (CaL-CSP). The main drawbacks of the system are the incomplete conversion of CaO and its sintering-induced deactivation. In this work, the influence of particle size in these deactivation mechanisms has been assessed by performing experimental multicycle tests using standard limestone particles of well-defined and narrow particle size distributions. The results indicate that CaO multicycle conversion benefits from the use of small particles mainly when the calcination is carried out in helium at low temperature. Yet, the enhancement is only significant for particles below 15 μm. On the other hand, the strong sintering induced by calcining in CO2 at high temperatures makes particle size much less relevant for the multicycle performance. Finally, SEM imaging reveals that the mechanism responsible for the loss of activity is mainly pore-plugging when calcination is performed in helium, whereas extensive loss of surface area due to sintering is responsible for the deactivation when calcination is carried out in CO2 at high temperature.
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2019.10.008
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
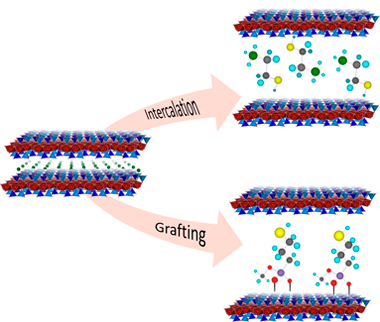
An insight on the design of mercapto functionalized swelling brittle micas
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 561 (2020) 533-541 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.028
Abstract
Surface modification of natural clay minerals with reagents containing metal chelating groups has great environmental value. The functionalization by adsorption or grafting guarantees a durable immobilization of the reactive organic groups, preventing their leaching when they are used in liquid media. The aim of this research was the designed mercapto functionalization of swelling brittle micas, Na-Mn, thorough both chemical and physical mechanisms. Na-Mn were functionalized with 2-mercaptoethylammonium (MEA), 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanol (BAL) and (3-mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane (MPTMS). The thiol concentration on swelling brittle micas is higher than the observed value for others adsorbents. The cation exchange reaction with MEA and one-step grafting with MPTMS in acid medium are the most efficient mercapto functionalization mechanism.
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.028
Reactividad de Sólidos
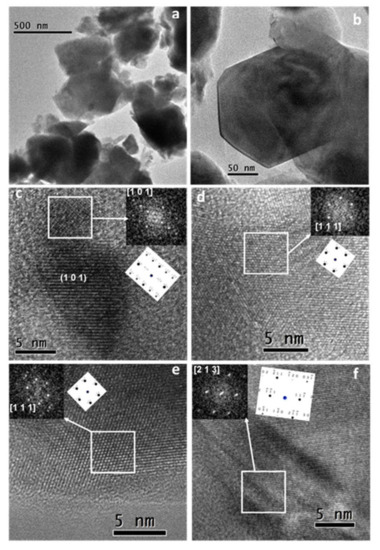
Development by Mechanochemistry of La0.8Sr0.2Ga0.8Mg0.2O2.8 Electrolyte for SOFCs
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Tang, YQ; Gotor, FJ; Sayagues, MJMaterials, 13 (2020) DOI: 10.3390/ma13061366
Abstract
In this work, a mechanochemical process using high-energy milling conditions was employed to synthesize La0.8Sr0.2Ga0.8Mg0.2O3-δ (LSGM) powders from the corresponding stoichiometric amounts of La2O3, SrO, Ga2O3, and MgO in a short time. After 60 min of milling, the desired final product was obtained without the need for any subsequent annealing treatment. A half solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) was then developed using LSGM as an electrolyte and La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 (LSM) as an electrode, both obtained by mechanochemistry. The characterization by X-ray diffraction of as-prepared powders showed that LSGM and LSM present a perovskite structure and pseudo-cubic symmetry. The thermal and chemical stability between the electrolyte (LSGM) and the electrode (LSM) were analyzed by dynamic X-ray diffraction as a function of temperature. The electrolyte (LSGM) is thermally stable up to 800 and from 900 °C, where the secondary phases of LaSrGa3O7 and LaSrGaO4 appear. The best sintering temperature for the electrolyte is 1400 °C, since at this temperature, LaSrGaO4 disappears and the percentage of LaSrGa3O7 is minimized. The electrolyte is chemically compatible with the electrode up to 800 °C. The powder sample of the electrolyte (LSGM) at 1400 °C observed by HRTEM indicates that the cubic symmetry Pm-3m is preserved. The SOFC was constructed using the brush-painting technique; the electrode–electrolyte interface characterized by SEM presented good adhesion at 800 °C. The electrical properties of the electrolyte and the half-cell were analyzed by complex impedance spectroscopy. It was found that LSGM is a good candidate to be used as an electrolyte in SOFC, with an Ea value of 0.9 eV, and the LSM sample is a good candidate to be used as cathode
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/ma13061366
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
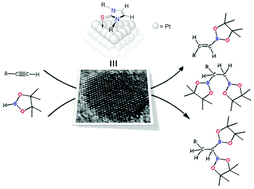
Platinum nanoparticles stabilized by N-heterocyclic thiones. Synthesis and catalytic activity in mono- and di-hydroboration of alkynes
Moraes, LCC; Figueiredo, RCC; Espinos, JPP; Vattier, F; Franconetti, A; Jaime, C; Lacroix, B; Rojo, J; Lara, P; Conejero, SNanoscale, 12 (2020) 6821-6831 DOI: 10.1039/d0nr00251h
Abstract
N-Heterocyclic Thiones (NHT) proved to be efficient ligands for the stabilization of small platinum nanoparticles (1.3-1.7 nm), synthesized by decomposition of [Pt(dba)(2)], under a H-2 atmosphere, in the presence of variable sub-stoichiometric amounts of the NHT. Full characterization by means of TEM, HR-TEM, NMR, ICP, TGA and XPS have been carried out, providing information about the nature of the metal nanoparticles and the interaction of the NHT ligands to the metal surface. Importantly, DFT calculations indicate that some NHT ligands interact with the metal through the C & xe001;C double bond of the imidazole fragment in addition to the sulfur atom, thus providing additional stabilization to the nanoparticles. According to XPS, TGA and ICP techniques, the surface coverage by the ligand increases by decreasing the size of the substituents on the nitrogen atom. The platinum nanoparticles have been used as catalyst in the hydroboration of alkynes. The most active system is that with a less covered surface area lacking an interaction of the ligand by means of the C & xe001;C double bond. This catalyst hydroborates alkynes with excellent selectivities towards the monoborylated anti-Markovnikov product (vinyl-boronate) when one equiv. of borane is used. Very interestingly, aliphatic alkynes undergo a second hydroborylation process leading to the corresponding 1,1- and 1,2-diboroylated species with good selectivities towards the former.
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.1039/d0nr00251h
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optofluidic liquid sensing on electromicrofluidic devices
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Wang, SL; Rico-Gavira, V; Lopez-Santos, C; Fan, SK; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARMaterials Research Express, 7 (2020) 036407 DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab7fdf
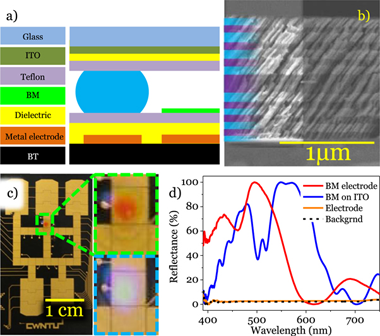
Abstract
Electromicrofluidic (EMF) devices are used to handle and move tiny amounts of liquids by electrical actuation, including electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD) and dielectrophoresis (DEP). Monitoring the liquid characteristics in one of these devices requires suitable sensing transducers incorporated within the microfluidic structure. In the present work, we describe the incorporation of an optofluidic photonic transducer in an EMF device to monitor the refractive index of a liquid during its manipulation. The incorporated transducer consists of a responsive porous Bragg Microcavity (BM) deposited via physical vapor oblique angle deposition. Besides reporting the manufacturing procedure of the sensing-EMF device combining liquid handling and monitoring, the performance of the BM is verified by infiltrating several liquids dripped on its surface and comparing the responses with those of liquid droplets electrically moved from the delivery part of the chip to the BM location. This study proved that modified EMF devices can incorporate photonic structures to analyze very low liquid volumes (similar to 0.2 mu L) during its handling.
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab7fdf
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Localized surface plasmon effects on the photophysics of perovskite thin films embedding metal nanoparticles
Bayles, A; Carretero-Palacios, S; Calio, L; Lozano, G; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 8 (2020) 916-921 DOI: 10.1039/c9tc05785d
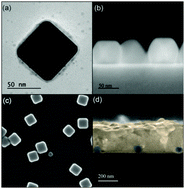
Abstract
Herein we provide direct experimental evidence that proves that the photophysical properties of thin methylammonium lead iodide perovskite films are significantly enhanced by localized surface plasmon resonances (SPRs). Observations are well supported by rigorous calculations that prove that improved light harvesting can be unequivocally attributed to plasmonic scattering and near field reinforcement effects around silver nanoparticles embedded within the semiconductor layer. Adequate design of the localized SPR allows raising the absorptance of a 300 nm thick film at well-defined spectral regions while minimizing the parasitic absorption from the metallic inclusions. Measured enhancements can be as large as 80% at specific wavelengths and 20% when integrated over the whole range at which SPR occurs, in agreement with theoretical estimations. Simultaneously, the characteristic quenching effect that the vicinity of metals has on the photoluminescence of semiconductors is largely compensated for by the combined effect of the enhanced photoexcitation and the higher local density of photon states occurring at SPR frequencies, with a two fold increase of the perovskite photoemission efficiency being measured.
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.1039/c9tc05785d
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Preparation of ZnFe2O4/ZnO composite: Effect of operational parameters for photocatalytic degradation of dyes under UV and visible illumination
Zouhier, M.; Tanji, K.; Navio, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Jaramillo-Páez, C.; Kherbeche, A.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 390 (2020) 112305 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112305
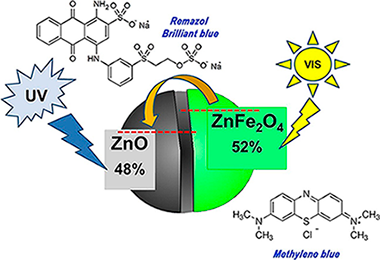
Abstract
An ZnFe2O4/ZnO composite catalyst was prepared by solution combustion method. In this study, one nominal molar percentage of iron was used in the synthesis, corresponding to 20 % molar relative to ZnO. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), Scanning Electronic Microscopy (SEM), Transmission Electronic Microscopy (TEM) and Ultraviolet-visible (UV–vis) diffuse spectroscopy (DRS). The photocatalytic activities of the catalysts were investigated based on the degradation of two dyes, methylene blue (MB) and remazol brilliant blue (RBB), in aqueous solution under both UV and visible light illumination respectively. It was found that the composite had a good photocatalytic activity at basic pH by using 1 g/L of catalyst under UV illumination for both MB and RBB. Under visible illumination, while pristine ZnO showed no activity, the composite exhibited an excellent visible efficiency, reaching up to an 80 % conversion of the initial dye concentrations in 2 h. The enhancement of the visible photocatalytic activity of Fe/ZnO sample with respect to pristine ZnO is attributed to the formation of ZnFe2O4 coupled with ZnO, having a narrow band gap value that contributes to the absorption of visible photons with an improved separation path for the photo-generated carriers.
March, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112305
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Role of Fe(III) in aqueous solution or deposited on ZnO surface in the photoassisted degradation of rhodamine B and caffeine
Tanji, Karim; Navio, J A; Martin-Gomez, A N; Hidalgo, M C; Jaramillo-Paez, C; Naja, Jamal; Hassoune, Hicham; Kherbeche, AbdelhakChemosphere, 241 (2020) 125009 DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125009
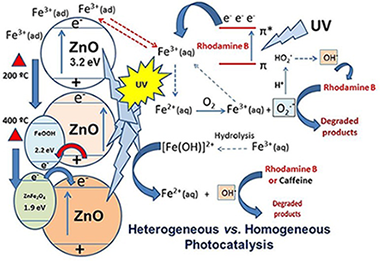
Abstract
Iron (III) was incorporated, to the surface of a synthesized ZnO, using two nominal molar percentages of Fe (III): 1% and 5% Fe relative to ZnO. Samples dried and calcined at 200 °C and 400 °C for 2 h, were characterized by XRD, XPS, XRF, N2-adsorption-BET and (UV–vis)-DRS. Photocatalytic activities of the catalysts were assessed based on the degradation of rhodamine B (RhB) and caffeine (CAF) in aqueous solution under two irradiation conditions: UV and visible light illumination. Prior to the photocatalytic tests, the interaction of each one of the substrates with either Fe(III) or Fe(II) was studied in homogeneous medium under UV-illumination and oxygenated environment. It was found that Fe (III) can play an important role in homogeneous media in the photoassisted degradation, both of rhodamine B and caffeine, while Fe (II) does not exert a relevant role in the photoassisted degradation of the referred substrates. Fe–ZnO samples display similar or poorer performance than pure ZnO in the presence of UV light for both studied substrates. The phenomenon can be attributed to the formation of either goethite or ZnFe2O4 at the ZnO surface where the coupled Fe3+/Fe2+ can act as recombination centers for the photogenerated charges. On the contrary, all Fe–ZnO samples showed enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible illumination which seems to be independent of the iron content. In this context, the mechanisms for photoassisted degradation of both the substrates in homogeneous medium and photocatalytic degradation are discussed, as well as the role of Fe in the photodegradation processes.
February, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125009
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Monolithic stirrer reactor: The selective lactose oxidation in liquid phase over Au/Al2O3 nanostructured catalysts
Regenhardt, SA; Meyer, CI; Sanz, O; Sebastian, V; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Montes, M; Marchi, AJ; Garetto, TFMolecular Catalysis, 481 (2020) 110219 DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.10.014
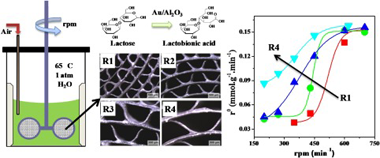
Abstract
The performance of rotating metallic monolith stirrer reactor was studied for selective lactose oxidation in liquid phase at 65 degrees C, atmospheric pressure and with air as oxidant agent. The Au/Al(2)O(3)deposition on metallic substrates was performed by wash-coating, producing catalyst coating thicknesses between 5 and 20 mu m. Monoliths with different configuration (channel size between 0.36 and 1.06 mm) were used as stirrer blades in a batch reactor. Internal and external mass transfer limitations were observed during liquid phase lactose oxidation. For stirring rates equal or higher than 600 rpm there were no important external diffusional restrictions and this was also independent of the monolith configuration. Coating with thickness higher than 15 mu m presents loss of catalyst effectiveness due to internal diffusional restrictions. Excellent stability in the catalytic tests was obtained after three regeneration-reaction cycles. Regeneration was carried out at 400 degrees C in air flow. Gold particle size distribution in the monolith washcoat, determined by TEM before and after reaction, was homogeneous with a medium size of around 5 nm. This is in agreement with the very good reproducibility and stability obtained in the catalytic tests. After calcination at 500 degrees C, some sintering and a heterogeneous distribution of metal particle size was observed, accompanied by a slight loss in catalyst activity. It is concluded that metallic monolith stirrer reactors are a promising application for selective lactose oxidation in liquid phase.
February, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.10.014
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis of Mn2+-doped ZnS by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Aviles, MA; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, FJJournal of Materials Science, 55 (2020) 1603-1613 DOI: 10.1007/s10853-019-04138-8
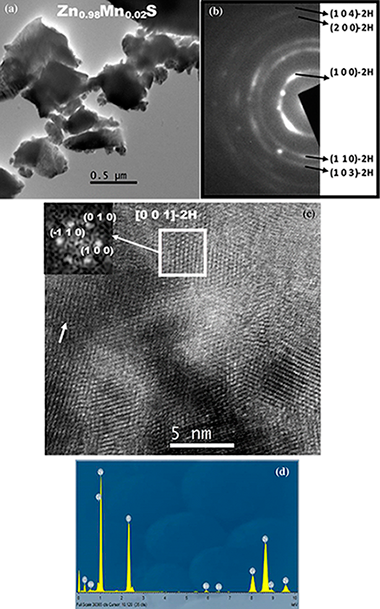
Abstract
The mechanochemical process denoted as a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction was successfully applied in obtaining Mn-doped ZnS samples with Mn content between 0 and 5 mol%. The process consists in milling Zn/Mn/S powder elemental mixtures with the appropriate stoichiometry, which promotes after approximately 80 min the induction of a combustion reaction. The doping level was properly adjusted by controlling the atomic ratio of the starting mixture. A complete characterization of samples was carried out, including X-ray diffraction, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, selected area electron diffraction, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, diffuse reflectance UV-Vis spectroscopy and emission and excitation photoluminescence measurements. A wurtzite structure, in which Mn2+ replaces Zn2+, was obtained with a nanometric character. The photoluminescence of samples showed the characteristic (Mn2+T1)-T-4-(6)A(1) emission that was highly dependent on the doping level. The maximum luminescence efficiency through the ZnS excitation was found for a doping value of 1 mol%. The photoluminescence showed virtually no contribution from the host emission, which confirmed that samples were properly doped.
February, 2020 · DOI: 10.1007/s10853-019-04138-8
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Catalytic Performance of Bulk and Al2O3-Supported Molybdenum Oxide for the Production of Biodiesel from Oil with High Free Fatty Acids Content
Navajas, A; Reyero, I; Jimenez-Barrera, E; Romero-Sarria, F; Llorca, J; Gandia, LMCatalysts, 10 (2020) 158 DOI: 10.3390/catal10020158
Abstract
Non-edible vegetable oils are characterized by high contents of free fatty acids (FFAs) that prevent from using the conventional basic catalysts for the production of biodiesel. In this work, solid acid catalysts are used for the simultaneous esterification and transesterification with methanol of the FFAs and triglycerides contained in sunflower oil acidified with oleic acid. Molybdenum oxide (MoO3), which has been seldom considered as a catalyst for the production of biodiesel, was used in bulk and alumina-supported forms. Results showed that bulk MoO3 is very active for both transesterification and esterification reactions, but it suffered from severe molybdenum leaching in the reaction medium. When supported on Al2O3, the MoO3 performance improved in terms of active phase utilization and stability though molybdenum leaching remained significant. The improvement of catalytic performance was ascribed to the establishment of MoO3-Al2O3 interactions that favored the anchorage of molybdenum to the support and the formation of new strong acidic centers, although this effect was offset by a decrease of specific surface area. It is concluded that the development of stable catalysts based on MoO3 offers an attractive route for the valorization of oils with high FFAs content.
February, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/catal10020158
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of Gold Particles Size over Au/C Catalyst Selectivity in HMF Oxidation Reaction
Megias-Sayago, C; Lolli, A; Bonincontro, D; Penkova, A; Albonetti, S; Cavani, F; Odriozola, JA; Ivanova, SChemcatchem, 12 (2020) 1177-1183 DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201901742
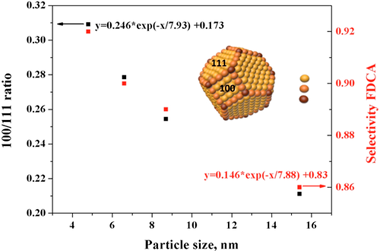
Abstract
A series of gold nanoparticles in the 4-40 nm range were prepared, immobilized on activated carbon and further tested, at low base concentration, in the catalytic oxidation of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural (HMF) to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA). Gold particles size variation has no influence on HMF conversion but significantly affects product selectivity and carbon balance. This behavior is ascribed to the thermodynamically favorable oxygen reduction reaction on Au(100) faces. As the gold particle size decreases the Au(100)/Au(111) exposure ratio, estimated by using the van Hardeveld-Hartog model, increases as well as the FDCA selectivity. The smaller the gold particle size the smaller the 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furancarboxylic acid (HMFCA) to FDCA ratio pointing to the gold size dependent behavior of the oxidation of the alcohol function of the HMF molecule.
February, 2020 · DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201901742
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Mesoporous Matrices as Hosts for Metal Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals
Rubino, A; Calio, L; Garcia-Bennett, A; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, (2020) 201901868 DOI: 10.1002/adom.201901868
Abstract
Several works have recently demonstrated that perovskite nanocrystals can be controllably formed within a variety of porous matrices employing diverse synthetic strategies. By means of the fine tuning of the pore size distribution, the thickness and composition of the walls, the geometry of the void network and its topology, strict control over the structural and morphological parameters of the hosted semiconductor can be achieved, determining its optical absorption and emission properties. Furthermore, porous hosts provide the guest semiconductor with enhanced stability and versatility in terms of processing, which favors its integration in devices. This article provides a comprehensive review of the different approaches proposed, as well as a discussion on the relevance they may have for the development of nanostructured perovskite-based optoelectronics. A critical assessment of the optical quality of the hybrid perovskite nanomaterials so obtained is presented, as well as an analysis of the fundamental and applied aspects of the nanocrystal-matrix interaction and a projected prospect of their impact in the fields of artificial lighting and renewable energy.
February, 2020 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.201901868
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Evaluation of Au–ZnO, ZnO/Ag2CO3 and Ag–TiO2 as Photocatalyst for Wastewater Treatment
Murcia, J.J.; Hernández, J.S.;Rojas, H.; Moreno-Cascante, J.; Sánchez-Cid, P.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Navío, J.A.; Jaramillo-Páez, C.Topics in Catalysis, (2020) DOI: 10.1007/s11244-020-01232-z
Abstract
In this work series of photocatalysts based on ZnO modified by Au and Ag2CO3 addition and Ag–TiO2 materials were synthesized and evaluated in the treatment of handicrafts factories wastewater and water samples taken from a highly polluted river. In general, it was found that ZnO series were more effective in the bacteria elimination than the commonly used TiO2 semiconductor. It was also observed that the metal (Au, Ag) or silver carbonate addition significantly increases the photocatalytic activity of ZnO and TiO2. It was determined that the content of the metal or carbonate added is an important factor to take into account in order to obtain suitable efficiency in the photocatalytic process, so, for example in the case of the river water samples the increase of Ag2CO3 content from 1 to 5%, had a detrimental effect over the bacteria elimination. The optimal conditions for dyes photodegradation and bacteria elimination were found by using a response surface study and the Au–ZnO (1%) photocatalyst. From this study it was determined that even after recycling this material leads to obtain a removal percentage of these pollutants over than 94%.
February, 2020 · DOI: 10.1007/s11244-020-01232-z
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Hybrid ZnO/Ag3PO4 photocatalysts, with low and high phosphate molar percentages
Martín-Gómez, A.N.;Navío, J.A.;Jaramillo-Páeza, C.;Sánchez-Cid, P.;Hidalgo, M.C.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, (2020) 112196 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112196
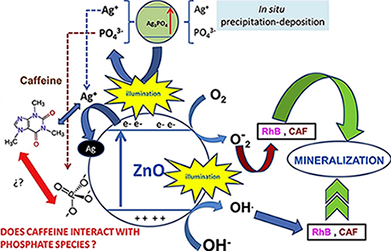
Abstract
In this work, a previously optimized synthesized ZnO photocatalyst was modified with different molar percentages of Ag3PO4 through a facile in situ precipitation–deposition method and then characterized by different techniques (XRD, XRF, BET, UV–vis DRS, SEM, TEM and XPS). The incorporation of Ag3PO4 produces important changes in the light absorption properties with a significant absorbance in the visible region observed for ZnO modified with different amounts of Ag3PO4; the optical absorption intensity in the visible region of the coupled ZnO/Ag3PO4 increases as the molar percentages of Ag3PO4 increases, evidencing a clear dependence on the content of Ag3PO4. However, this work shows that the incorporation of Ag3PO4 in almost all cases reduces the photocatalytic capacity of ZnO, except when it is used in a specific percentage of 10 % and only being more active against rhodamine B and not on the Caffeine. SEM images and elemental mapping indicate that Ag3PO4 disperses very well in the ZnO particles, exhibiting an almost homogeneous distribution, showing zones with cumulus of Ag3PO4 (rich in P-Ag) in contact with ZnO-zones (rich in Zn). All the prepared photocatalysts were tested in the photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B as a dye, and caffeine as a toxic and persistent emerging compound under UV and visible light illumination. It is reported that not only the ZnO:Ag3PO4 ratio is an important factor that influences the photocatalytic process of substrate degradation, but also the nature of the substrate has an important influence on the photocatalytic behavior of the materials under both UV and visible illumination. Thus, pristine Ag3PO4 showed high photocatalytic degradation for rhodamine B, while for caffeine negligible photocatalytic degradation was found in both the UV and visible regions. The thermal- and photo-stability of the coupled system was also studied. At least, for rhodamine B no loss of photocatalytic activity has been observed after five recycles although the mineralization degree progressively diminished along the recycles.
February, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112196
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Modulation of the acidity of a vermiculite and its potential use as a catalytic support
Amaya, J; Bobadilla, L; Azancot, L; Centeno, M; Moreno, S; Molina, RJournal of Materials Science, 55 (2020) 6482-6501 DOI: 10.1007/s10853-020-04445-5
Abstract
The modulation and characterization of the acidity of a vermiculite were carried out, which was modified by delamination by means of hydrothermal and acid treatments with the subsequent incorporation of AlZr and AlCe species to modulate the acidity. The effect of these species was evaluated regarding the structural (XRD, XPS and IR), textural (N-2 sortometry) and acidity properties (NH3-TPD, NH3-DRIFTS and CO adsorption at low temperature). The catalytic performance was studied in the dehydration-dehydrogenation reactions of 2-propanol and the hydroconversion of decane, which generate important information about the acidity properties such as the type, number and strength of acidic sites. The correlation between the number, type and acid strength with the catalytic behavior allowed to establish the important effect regarding the nature of the mineral, its method of delamination and the nature of the incorporated cation, thus generating tools for controlled processes for the potentiation of the acidity of new supports from raw vermiculite.
February, 2020 · DOI: 10.1007/s10853-020-04445-5
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Robust label-free CuxCoyOz electrochemical sensors for hexose detection during fermentation process monitoring
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez, R; Yubero, F; de Lucas-Consuegra, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSensors and Actuators B-Chemical, 304 (2020) 127360 DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.127360

Abstract
Label free electrochemical sensors of glucose are used whenever long-term operation and stable response are required. For this purpose, various metals and oxides of the first transition series have been proposed as alternative to more expensive noble metal electrochemical sensors. In this work we propose a new formulation consisting of copper-cobalt mixed oxides which, in the form of porous and nanostructured thin films with well controlled Co/Cu ratio, are prepared at room temperature in one step by a modification of the magnetron sputtering oblique angle deposition procedure. Films with various compositions were electrochemically characterized by cyclic voltammetry to determine their amperometric response to glucose as a function of voltage and NaOH electrolyte concentration. This analysis showed that films with a Co/Cu atomic ratio equal 3.4 presented a maximum sensitivity (0.710 A M−1 cm−2), a small limit of detection (0.105 μM) and a resilient behaviour upon cycling operation and long storage periods that clearly overpassed the performance of copper and cobalt single oxides. The CuxCoyO electrocatalysts also presented a good selectivity towards glucose and fructose in the presence of common interference compounds found in biological fluids (e.g., ascorbic acid, acetaminophen and uric acid), sucrose and ethanol, this latter present in many agrofood liquids. The possibilities of this sensor electrocatalyst have been tested for the analysis of a wine synthetic fermentation process. The comparison of the electrochemical results with conventional analytical methods showed a lineal amperometric response with respect hexose contents in a must at different stages of its transformation into wine.
February, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.127360
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Recent advances in selective oxidation of biomass-derived platform chemicals over gold catalysts
Megias-Sayago, C; Navarro-Jaen, S; Castillo, R; Ivanova, SCurrent Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 21 (2020) 50-55 DOI: 10.1016/j.cogsc.2019.12.001
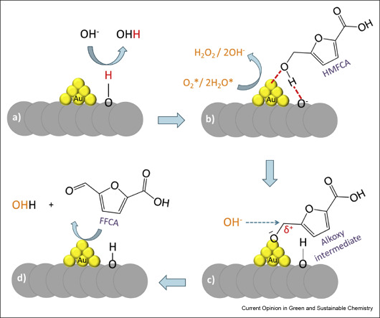
Abstract
Gold is without a doubt the best known metal for chemical oxidation. The noblest of the noble metals gained its place because of its resistance to overoxidation, low temperature of operation, especially in gas-phase oxidation, and fairly good selectivity when required. The aim for sustainable development and the need for new technologies open the possibility to introduce new raw materials and new catalyst formulation. That is why new horizons appear in the otherwise uncertain future of gold catalysis. The old glory becomes now a glorious alternative, and this mini-review gives only a small example of it.
February, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cogsc.2019.12.001
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Dipole reorientation and local density of optical states influence the emission of light-emitting electrochemical cells
Jimenez-Solano, Alberto; Martinez-Sarti, Laura; Pertegas, Antonio; Lozano, Gabriel; Bolink, Henk J; Miguez, HernanPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 22 (2020) 92-96 DOI: 10.1039/c9cp05505c
Abstract
Herein, we analyze the temporal evolution of the electroluminescence of light-emitting electrochemical cells (LECs), a thin-film light-emitting device, in order to maximize the luminous power radiated by these devices. A careful analysis of the spectral and angular distribution of the emission of LECs fabricated under the same experimental conditions allows describing the dynamics of the spatial region from which LECs emit, i.e. the generation zone, as bias is applied. This effect is mediated by dipole reorientation within such an emissive region and its optical environment, since its spatial drift yields a different interplay between the intrinsic emission of the emitters and the local density of optical states of the system. Our results demonstrate that engineering the optical environment in thin-film light-emitting devices is key to maximize their brightness.
January, 2020 · DOI: 10.1039/c9cp05505c
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Effect of synthesis pH on the physicochemical properties of a synthesized Bi2WO6 and the type of substrate chosen, in assessing its photo-catalytic activities
Jaramillo-Páez, C.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 13 (2020) 431-443 DOI: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.014

Abstract
Crystalline orthorhombic Bi2WO6 powders were synthesized by a hydrothermal method from aqueous solutions of Bi(NO3)35H2O and Na2WO42H2O over a range of three selected pH values (2.0, 5.0 and 7.0), using NaOH as precipitating agent. The as-prepared catalysts were characterized by XRD, BET, FE-SEM, TEM, XPS and UV-vis spectroscopy. The effect of pH-synthesis on crystallinity, morphologies, surface area and optical absorption properties, were investigated.
Although the pH has a marked influence on morphology, the nature of the precipitating agent (NaOH or TEA) also influences the morphology and surface structure composition, as it is observed in the present work. Three different probe molecules were used to evaluate the photocatalytic properties under two illumination conditions (UV and Visible): Methyl Orange and Rhodamine B were chosen as dye substrates and Phenol as a transparent substrate. The photo-catalytic activities are strongly dependent not only on the pH used in the synthesis but also on the nature of the chosen substrate in assessing the photo-catalytic activities. Results were compared with those obtained when using TiO2(P25, Evonik) in the same experimental conditions. The photocatalytic activity of one of the synthesised samples has been evaluated by exposing a mixture of Rhodamine B and Phenol in water, to different illumination conditions. Our results provide new evidences about the issue of whether dyes are suitable substrates to assess the activity of a photo-catalyst.
January, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.014
Reactividad de Sólidos
Development of Ti(C,N)-based cermets with (Co,Fe,Ni)-based high entropy alloys as binder phase
de la Obra, AG; Sayagues, MJ; Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 814 (2020) 152218 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152218
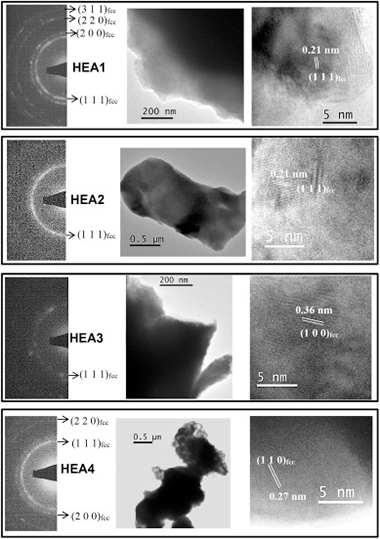
Abstract
High entropy alloys have been proposed as novel binder phases in cemented carbides and cermets. Many aspects related to the stability of these alloys during the liquid phase sintering process are still unclear and were addressed in this work. Consolidated Ti(C,N)-based cermets using four different (Co,Fe,Ni)based high entropy alloys as the binder phase were obtained. The chosen alloys - CoCrCuFeNi, CoCrFeNiV, CoCrFeMnNi and CoFeMnNiV - were previously synthesized through mechanical alloying and a single alloyed solid solution phase with fcc structure and nanometric character was always obtained. The powdered alloys and the consolidated cermets were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray energy dispersive spectrometry and transmission electron microscopy. Differential thermal analysis was employed to determine the melting point of the four high entropy alloys that ranged between 1310 degrees C and 1375 degrees C. Although a high temperature of 1575 degrees C was required to obtain the highest cermet densification by pressureless sintering, porosity still remained in most of the cermets. Best densification was achieved when CoCrFeNiV was used as the binder phase. During liquid phase sintering, different compositional changes were observed in the ceramic and binder phases. A core-rim microstructure was observed in cermets containing V in the alloys (CoCrFeNiV and CoFeMnNiV), since this element was incorporated to the carbonitride structure during sintering. A slight Cr segregation was detected in cermets containing Cr, leading to CrTi-rich alloys in small binder regions. However, a great Cu segregation was produced when CoCrCuFeNi was used, and the formation of two different fcc alloys -a Cu-rich and a Cu-depleted- was observed. Finally, a loss of Mn was also evidenced in CoCrFeMnNi and CoFeMnNiV, probably due to its sublimation at the sintering temperature.
January, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152218
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Preparation and Characterization of Bio-Based PLA/PBAT and Cinnamon Essential Oil Polymer Fibers and Life-Cycle Assessment from Hydrolytic Degradation
Correa-Pacheco, ZN; Black-Solis, JD; Ortega-Gudino, P; Sabino-Gutierrez, MA; Benitez-Jimenez, JJ; Barajas-Cervantes, A; Bautista-Banos, S; Hurtado-Colmenares, LBPolymers, 12 (2020) 38 DOI: 10.3390/polym12010038

Abstract
Nowadays, the need to reduce the dependence on fuel products and to achieve a sustainable development is of special importance due to environmental concerns. Therefore, new alternatives must be sought. In this work, extruded fibers from poly (lactic acid) (PLA) and poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) added with cinnamon essential oil (CEO) were prepared and characterized, and the hydrolytic degradation was assessed. A two-phase system was observed with spherical particles of PBAT embedded in the PLA matrix. The thermal analysis showed partial miscibility between PLA and PBAT. Mechanically, Young's modulus decreased and the elongation at break increased with the incorporation of PBAT and CEO into the blends. The variation in weight loss for the fibers was below 5% during the period of hydrolytic degradation studied with the most important changes at 37 degrees C and pH 8.50. From microscopy, the formation of cracks in the fiber surface was evidenced, especially for PLA fibers in alkaline medium at 37 degrees C. This study shows the importance of the variables that influence the performance of polyester-cinnamon essential oil-based fibers in agro-industrial applications for horticultural product preservation.
January, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/polym12010038
Reactividad de Sólidos
Processing and properties of Bi0.98R0.02FeO3 (R = La, Sm, Y) ceramics flash sintered at similar to 650 degrees C in <5 s
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Raj, R; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 103 (2020) 136-144 DOI: 10.1111/jace.16718
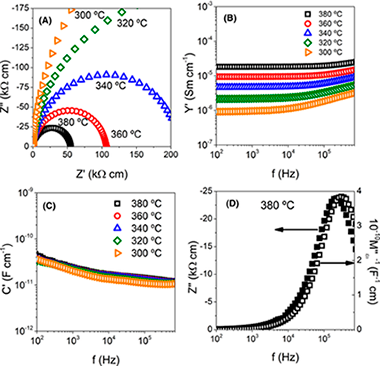
Abstract
We show that flash sintering produces single‐phase, nanograin‐sized polycrystals of isovalent‐substituted multiferroic ceramics of complex compositions. Single‐phase polycrystals of Bi0.98R0.02FeO3 (R = La, Sm, Y) were produced at a furnace temperature of ~650°C in a few seconds by the application of an electric field of 50 V cm−1, with the current limit set to 40 mA mm−2. The dielectric and insulating properties compared favorably with expected values. Impedance spectroscopy suggests electrically homogenous microstructure, except for the sample Bi0.98La0.02FeO3 that shows a small grain boundary contribution to the impedance. These results reinforce the enabling nature of flash sintering for ceramics which pose difficulties in conventional sintering because they contain low melting constituents or develop secondary phases during the sintering protocol.
January, 2020 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.16718
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Finite Size Effects on Light Propagation throughout Random Media: Relation between Optical Properties and Scattering Event Statistics
Miranda-Munoz, JM; Esteso, V; Jimenez-Solano, A; Lozano, G; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, 8 (2020) 1901196 DOI: 10.1002/adom.201901196
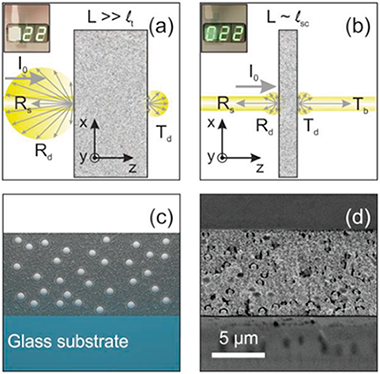
Abstract
This work introduces a thorough analysis of light transport in thin optically disordered media. The diffusive properties of a turbid material are generally dictated by the transport mean free path, lt. For depths larger than this characteristic length, light propagation can be considered fully randomized. There is however a range of thicknesses for which light becomes only partly randomized, as it only undergoes a single or very few scattering events. The effects of such finitude are experimentally and theoretically studied on the optical properties of the material, such as the angular distribution of scattered light. Simulations provide insight into the phenomena that occur within the optically disordered slab, like the number of scattering events that photons undergo during propagation throughout the material, as a function of the built‐in wavelength dependent scattering mean free path, lsc. This approach provides fundamental information about photon transport in finite optically random media, which can be put into practice to design diffusers with specific requirements in terms of the spectral and angular properties of the scattered light.
January, 2020 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.201901196
Materiales Avanzados
New waste-based clinkers for the preparation of low-energy cements. A step forward toward circular economy
Martinez-Martinez, S; Perez-Villarejo, L; Eliche-Quesada, D; Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Christogerou, A; Kanellopoulou, DG; Angelopoulos, GNInternational Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 17 (2020) 12-21 DOI: 10.1111/ijac.13390
Abstract
This paper describes the use of industrial wastes arising from different production processes of the ceramic and marble industries as raw materials for the design and formulation of new cement clinkers with a high content of dicalcium silicate (Belite). The aim was to reintroduce these wastes in the industrial sector and take advantage of them for a greater environmental benefit, as indicated by the principles of the circular economy. Formulations containing 2.5, 5 and 10 wt% of chamotte and marble sludge, respectively, and a waste-free formulation have been designed to obtain clinkers with a content of dicalcium silicate higher than 60 wt%. The different blends have been studied up to a maximum temperature of 1390 degrees C by Thermal Analysis. Other techniques such as XRD, XRF, Modified Bogue Equation, Quality Indexes (LSF, AM, SM) and Optical Microscopy have been used for the study and characterization of industrial wastes, the raw materials and the high belite-type cement dosages. The results indicate that this type of cements can be designed using different types of wastes and in this way reduce the environmental impacts caused by the extraction of raw materials and the deposition of the wastes in landfills, improving the circular economy of the construction industry.
January, 2020 · DOI: 10.1111/ijac.13390
Reactividad de Sólidos
Obituary: Prof. José Manuel Criado
Perez-Maqueda, LA; Real, C; Gotor, FJ; Alcala, MD; Malek, J; Koga, NJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, (2020) DOI: 10.1007/s10973-019-09207-3
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of DSC thermal lag on evaluation of crystallization kinetics
Svoboda, R; Maqueda, LP; Podzemna, V; Perejon, A; Svoboda, OJournal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 528 (2020) 119738 DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.119738
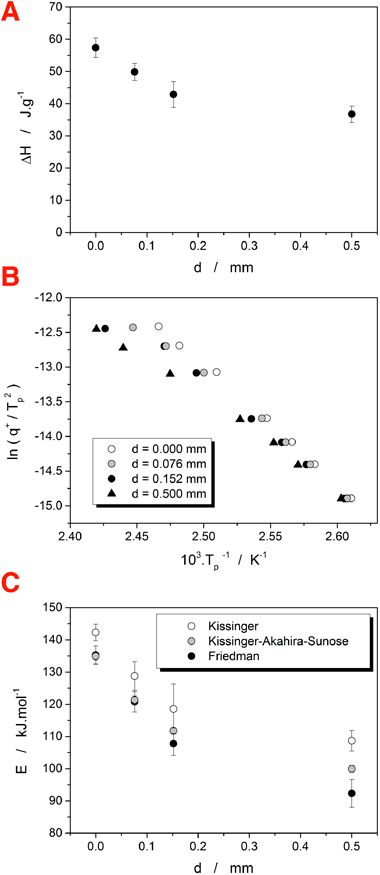
Abstract
Influence of added thermal resistance on crystallization kinetics, as measured by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), of the Se70Te30 glass was studied. The increase of thermal resistance was achieved by adding polytetrafluorethylene discs of different thicknesses (up to 0.5 mm) in-between the DSC platform and the pan with sample. Increase of the thermal resistance led to an apparent decrease (by more than 30%) in the crystallization enthalpy. Significant change of model-free kinetics occurred: apparent activation energy E of the crystallization process decreased (by more than 20%) due to the DSC data being progressively shifted to higher temperatures with increasing heating rate. The model-based kinetics was changed only slightly; the DSC peaks retained their asymmetry and the choice of the appropriate model was not influenced by the added thermal resistance. The temperature shift caused by added thermal lag was modeled for the low-to-moderate heating rates.
January, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.119738
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Low gas consumption fabrication of He-3 solid targets for nuclear reactions
Fernandez, A; Hufschmidt, D; Colaux, JL; Valiente-Dobon, JJ; Godinho, V; de Haro, MCJ; Feria, D; Gadea, A; Lucas, SMaterials & Design, 186 (2020) 108337 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108337
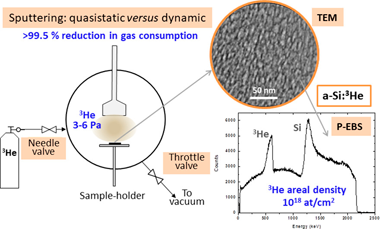
Abstract
Nanoporous solids that stabilize trapped gas nanobubbles open new possibilities to fabricate solid targets for nuclear reactions. A methodology is described based on the magnetron sputtering (MS) technique operated under quasistatic flux conditions to produce such nanocomposites films with He-3 contents of up to 16 at.% in an amorphous-silicon matrix. In addition to the characteristic low pressure (3-6 Pa) needed for the gas discharge, the method ensures almost complete reduction of the process gas flow during film fabrication. The method could produce similar materials to those obtained under classical dynamic flux conditions for MS. The drastic reduction (>99.5%) of the gas consumption is fundamental for the fabrication of targets with scarce and expensive gases. Si:He-3 and W:He-3 targets are presented together with their microstructural (scanning and transmission electron microscopy, SEM and TEM respectively) and compositional (Ion Beam Analysis, IBA) characterization. The He-3 content achieved was over 1 x 10(18) at/cm(2) for film thicknesses between 1.5 and 3 mu m for both Si and W matrices. First experiments to probe the stability of the targets for nuclear reaction studies in inverse kinematics configurations are presented.
January, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108337
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Enhanced Stability of Perovskite Solar Cells Incorporating Dopant-Free Crystalline Spiro-OMeTAD Layers by Vacuum Sublimation
Barranco, A; Lopez-Santos, MC; Idigoras, J; Aparicio, FJ; Obrero-Perez, J; Lopez-Flores, V; Contreras-Bernal, L; Rico, V; Ferrer, J; Espinos, JP; Borras, A; Anta, JA; Sanchez-Valencia, JRAdvanced Energy Materials, (2020) 1901524 DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201901524
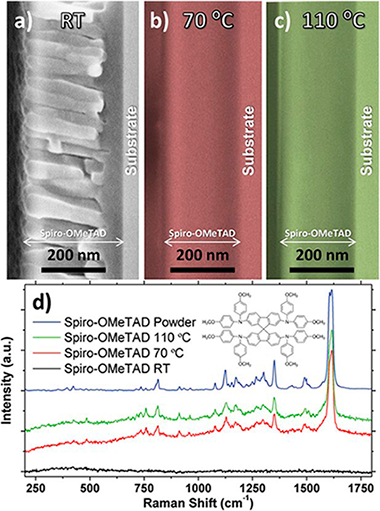
Abstract
The main handicap still hindering the eventual exploitation of organometal halide perovskite-based solar cells is their poor stability under prolonged illumination, ambient conditions, and increased temperatures. This article shows for the first time the vacuum processing of the most widely used solid-state hole conductor (SSHC), i.e., the Spiro-OMeTAD [2,2 ',7,7 '-tetrakis (N,N-di-p-methoxyphenyl-amine) 9,9 '-spirobifluorene], and how its dopant-free crystalline formation unprecedently improves perovskite solar cell (PSC) stability under continuous illumination by about two orders of magnitude with respect to the solution-processed reference and after annealing in air up to 200 degrees C. It is demonstrated that the control over the temperature of the samples during the vacuum deposition enhances the crystallinity of the SSHC, obtaining a preferential orientation along the pi-pi stacking direction. These results may represent a milestone toward the full vacuum processing of hybrid organic halide PSCs as well as light-emitting diodes, with promising impacts on the development of durable devices. The microstructure, purity, and crystallinity of the vacuum sublimated Spiro-OMeTAD layers are fully elucidated by applying an unparalleled set of complementary characterization techniques, including scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, grazing-incidence small-angle X-ray scattering and grazing-incidence wide-angle X-ray scattering, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy.
January, 2020 · DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201901524
Materiales Coloidales
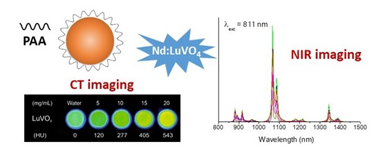
Bimodal Nd-Doped LuVO4 Nanoprobes Functionalized with Polyacrilic Acid for X-Ray Computed Tomography and NIR Luminescent Imaging
Nuñez, NO; Cusso, F; Cantelar, E; Martin-Gracia, B; de la Fuente, JM; Corral, A; Balcerzyk, M; Ocaña, MNanomaterials, 10 (2020) 149 DOI: 10.3390/nano10010149
Abstract
Uniform Nd3+-doped LuVO4 nanophosphors have been synthesized for the first time in literature by using a poliol-based method at 120 degrees C from Nd3+ and vanadate precursors. After optimizing the Nd doping level, these phosphors present intense luminescence in the near-infrared biological windows. The X-ray attenuation capacity of the optimum nanophosphor has been found to be higher than that of a commercial X-ray computed tomography contrast agent. After surface coating with polyacrylic acid, such nanoparticles present high colloidal stability in physiological pH medium and high cell viability. Because of these properties, the developed Nd3+-doped LuVO4 nanoparticles have potential applications as a bimodal probe for NIR luminescent bioimaging and X-ray computed tomography.
January, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/nano10010149
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Tribomechanical properties of hard Cr-doped DLC coatings deposited by low-frequency HiPIMS
Santiago, JA; Fernandez-Martinez, I; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Rojas, TC; Wennberg, A; Bellido-Gonzalez, V; Molina-Aldareguia, JM; Monclus, MA; Gonzalez-Arrabal, RSurface & Coatings Technology, 382 (2020) 124899 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.124899
Abstract
Cr-doped diamond-like carbon (Cr-DLC) films with Cr contents ranging from 3 up to 20 at. % were synthesised in a codeposition process with HiPIMS (Cr deposition) and DC-pulsed technology (C deposition). The application of HiPIMS at low frequencies was observed to significantly enhance the energy density during the Cr plasma discharge due to the interaction of Cr-C species. The higher energy bombardment at low HiPIMS frequencies allowed doping with Cr the DLC structure avoiding the graphitization of the carbon structure. EELS spectroscopy was used to evaluate sp(3) content and Raman was used for sp(2) structural characterization of the films. Enhanced mechanical properties (hardness up to 30 GPa) were observed with nanoindentation for Cr-doped DLC at low frequencies. High temperature nanoindentation tests were also performed from room temperature to 425 degrees C in order to evaluate the evolution of hardness and Young Modulus with temperature. The results showed that the mechanical properties at high temperature mainly depend on the initial sp(3)-sp(2) structure. Tribological tests were carried out in air from room temperature to 250 degrees C. Cr-doped DLC coatings deposited by low-frequency HiPIMS showed lower friction and wear compared to undoped DLC.
January, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.124899
2019
2019
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Design swelling micas: Insights on heavy metals cation exchange reaction
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 182 (2019) 105298 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2019.105298
Abstract
Heavy metal pollution has become one of the most serious environmental problems, demanding specialized remediation mechanisms. Among the studied treatments, ion-exchange processes have been widely used due to their high remediation capacity, efficiency and fast kinetic. Here, the potential use of a new family of design micas as cation exchanger has been analysed. Micas with a layer charge in the range of brittle micas have been synthesized and their heavy metals cation exchange capacity analysed as a function of the nature of the heavy metal cations (Pb2+, Cd2+ or Hg2+), the nature of the counterions (Cl− or NO3−), concentration of the solutions and the micas layer charge. A cation exchange ratio between 35% and 154% of their cation exchange capacity (CEC) was achieved, being more efficient when mica layer charge diminished. In general, the maximum adsorption capacity followed the trend: Hg2+ > Pb2+ > Cd2+. The efficiency of the cation exchange and adsorption mechanism of the synthetic micas depended on the experimental conditions and they were more efficient than raw and modified natural clay minerals.
December, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2019.105298
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Understanding segregation processes in SAMs formed by mixtures of hydroxylated and non-hydroxylated fatty acids
Bueno, OVM; Benitez, JJ; San-Miguel, MARSC Advances, 9 (2019) 39252-39263 DOI: 10.1039/c9ra06799j
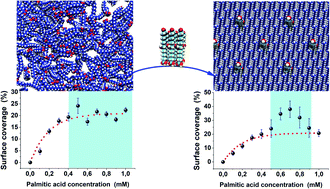
Abstract
In this paper, we focus on the segregation processes emerging when preparing mixtures with different compositions of aleuritic (9,10,16 trihydroxyhexadecanoic) (ALE) and palmitic (hexadecanoic) (PAL) acids. The combination of atomic force microscopy (AFM) and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations enabled us to prove the role of the functional groups in the formation of self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) on muscovite mica surfaces. MD simulations indicate that segregation processes are favored in high ALE composition mixtures in agreement with the experimental evidence, whereas low ALE compositions promote the co-existence between segregated and dispersed systems. The secondary hydroxyl groups play a central role in the self-assembling mechanism because they control the formation of hydrogen bonding networks guarantying system stability.
December, 2019 · DOI: 10.1039/c9ra06799j
Reactividad de Sólidos
Low temperature synthesis of an equiatomic (TiZrHfVNb)C5 high entropy carbide by a mechanically-induced carbon diffusion route
Chicardi, E; Garcia-Garrido, C; Gotor, FJCeramics International, 45 (2019) 21858-21863 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.07.195
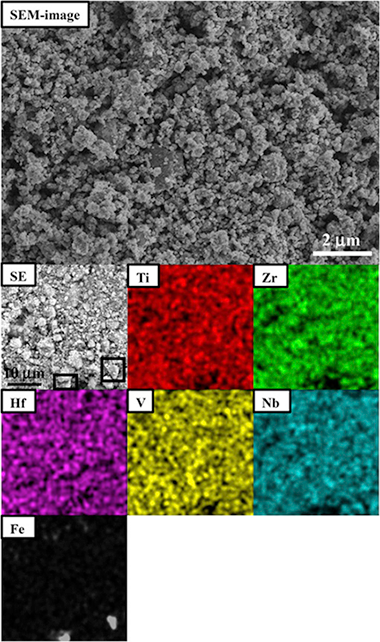
Abstract
A novel, homogeneous, nanostructured and equiatomic (TiZrHfVNb)C-5 High Entropy Carbide (HEC) was successfully synthesised in a powder form by a mechanosynthesis process from the elemental mixture. This synthesis method for HECs, not previously reported, is simple, reproducible and carried out at room temperature. During milling, the transition metals (Ti, Zr, Hf, V and Nb) alloying and the diffusion of carbon (introduced as graphite) into the alloy structure are simultaneously induced, obtaining the expected (TiZrHfVNb)C-5 HEC. The room temperature method employed contrasts with those reported in the bibliography from binary carbides that are carried out at a very high temperature (1800-2200 degrees C), with the consequent energy savings.
December, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.07.195
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Graphene Formation Mechanism by the Electrochemical Promotion of a Ni Catalyst
Espinos, JP; Rico, VJ; Gonzalez-Cobos, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Perez-Dieste, V; Escudero, C; de Lucas-Consuegra, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Catalysis, 9 (2019) 11447-11454 DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.9b03820
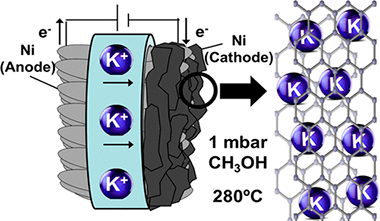
Abstract
In this work, we show that multilayer graphene forms by methanol decomposition at 280 degrees C on an electrochemically promoted nickel catalyst film supported on a K-beta Al2O3 solid electrolyte. In operando near ambient pressure photoemission spectroscopy and electrochemical measurements have shown that polarizing negatively the Ni electrode induces the electrochemical reduction and migration of potassium to the nickel surface. This elemental potassium promotes the catalytic decomposition of methanol into graphene and also stabilizes the graphene formed via diffusion and direct K-C interaction. Experiments reveal that adsorbed methoxy radicals are intermediate species in this process and that, once formed, multilayer graphene remains stable after electrochemical oxidation and back migration of potassium to the solid electrolyte upon positive polarization. The reversible diffusion of ca. 100 equivalent monolayers of potassium through the carbon layers and the unprecedented low-temperature formation of graphene and other carbon forms are mechanistic pathways of high potential impact for applications where mild synthesis and operation conditions are required.
December, 2019 · DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.9b03820
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Hydrophobic and Icephobic Behaviour of Polyurethane-Based Nanocomposite Coatings
Przybyszewski, B; Boczkowska, A; Kozera, R; Mora, J; Garcia, P; Aguero, A; Borras, ACoatings, 9 (2019) 811 DOI: 10.3390/coatings9120811
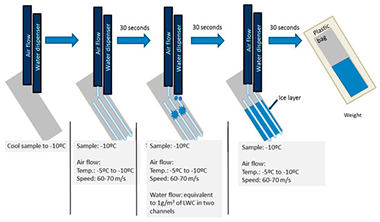
Abstract
In this paper, hydrophobic nanocomposite coatings based on polyurethane (PUR) modified by nano-silica and silane-based compounds were manufactured by spraying. The main challenge was to assess and improve the hydrophobic as well as anti-icing properties of initially hydrophilic polymer coatings. The prepared nanocomposite coatings were characterized by means of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), optical profilometry and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The results obtained showed that in order to achieve hydrophobicity, appropriate amounts of nano-silica must be incorporated in the coating, and complete coverage by nano-silica particles is necessary for achieving hydrophobicity. Coating adhesion and the durability of the hydrophobic behaviour were also studied by scratch test and frosting/defrosting cycles, respectively. The results show that use of both nano-silica and silane-based compounds improve the hydrophobic and anti-icing properties of the coating as compared to a non-modified PUR topcoat. A synergistic effect of both additives was observed. It was also found that the anti-icing behaviour does not necessarily correlate with surface roughness and the materials' wetting properties.
December, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/coatings9120811
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Porous Graphene-like Carbon from Fast Catalytic Decomposition of Biomass for Energy Storage Applications
Gomez-Martin, A; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Ruttert, M; Winter, M; Placke, T; Ramirez-Rico, JACS Omega, 4 (2019) 21446-21458 DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.9b03142

Abstract
A novel carbon material made of porous graphene-like nanosheets was synthesized from biomass resources by a simple catalytic graphitization process using nickel as a catalyst for applications in electrodes for energy storage devices. A recycled fiberboard precursor was impregnated with saturated nickel nitrate followed by high-temperature pyrolysis. The highly exothermic combustion of in situ formed nitrocellulose produces the expansion of the cellulose fibers and the reorganization of the carbon structure into a three-dimensional (3D) porous assembly of thin carbon nanosheets. After acid washing, nickel particles are fully removed, leaving nanosized holes in the wrinkled graphene-like sheets. These nanoholes confer the resulting carbon material with approximate to 75% capacitance retention, when applied as a supercapacitor electrode in aqueous media at a specific current of 100 A.g(-1) compared to the capacitance reached at 20 mA.g(-1), and approximate to 35% capacity retention, when applied as a negative electrode for lithium-ion battery cells at a specific current of 3720 mA.g(-1) compared to the specific capacity at 37.2 mA.g(-1). These findings suggest a novel way for synthesizing 3D nanocarbon networks from a cellulosic precursor requiring low temperatures and being amenable to large-scale production while using a sustainable starting precursor such as recycled fiberwood.
December, 2019 · DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.9b03142
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Dry Reforming of Ethanol and Glycerol: Mini-Review
Yu, J; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TRCatalysts, 9 (2019) art. 1015 DOI: 10.3390/catal9121015
Abstract
Dry reforming of ethanol and glycerol using CO2 are promising technologies for H-2 production while mitigating CO2 emission. Current studies mainly focused on steam reforming technology, while dry reforming has been typically less studied. Nevertheless, the urgent problem of CO2 emissions directly linked to global warming has sparked a renewed interest on the catalysis community to pursue dry reforming routes. Indeed, dry reforming represents a straightforward route to utilize CO2 while producing added value products such as syngas or hydrogen. In the absence of catalysts, the direct decomposition for H-2 production is less efficient. In this mini-review, ethanol and glycerol dry reforming processes have been discussed including their mechanistic aspects and strategies for catalysts successful design. The effect of support and promoters is addressed for better elucidating the catalytic mechanism of dry reforming of ethanol and glycerol. Activity and stability of state-of-the-art catalysts are comprehensively discussed in this review along with challenges and future opportunities to further develop the dry reforming routes as viable CO2 utilization alternatives.
December, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/catal9121015
- ‹ previous
- 12 of 37
- next ›














