Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Critical Influence of the Processing Route on the Mechanical Properties of Zirconia Composites with Graphene Nanoplatelets
Gallardo-Lopez, A; Munoz-Ferreiro, C; Lopez-Pernia, C; Jimenez-Pique, E; Gutierrez-Mora, F; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Poyato, RMaterials, 14 (2021) 108 DOI: 10.3390/ma14010108
Abstract
Graphene-based nanostructures, used as potential reinforcement in ceramic composites, have a great tendency to agglomerate. This requires the use of homogenization techniques during the powder processing, posing the need to evaluate how these techniques affect the microstructure and the mechanical properties of the resulting composites. The influence of the processing route on the properties of 3YTZP (3 mol % yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystals) ceramic composites with 10 vol % cost-effective GNP (graphene nanoplatelets) has been addressed. Four different powder processing routines combining ultrasonic powder agitation (UA) and planetary ball milling (PBM) in wet and dry media have been used and all the composites were densified by spark plasma sintering (SPS). The mechanical properties at room temperature in the macroscale have been assessed by Vickers indentations, four-point bending tests and the impulse-echo technique, while instrumented indentation was used to measure the hardness and Young’s modulus at the nanoscale. The application of dry-PBM enhances greatly the mechanical and electrical isotropy of the composites, slightly increases the hardness and lowers the elastic modulus, independently of the application of UA. The combination of UA and dry-PBM enhances the flexure strength by 50%, which is desirable for structural applications.
January, 2021 · DOI: 10.3390/ma14010108
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Sol-gel synthesis of ZnWO4-(ZnO) composite materials. Characterization and photocatalytic properties
Jaramillo-Páez, C., Navío, J.A., Puga, F., Hidalgo, M.C.Journal of Photochemistry & Photobiology, A: Chemistry, 404 (2021) 112962 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112962
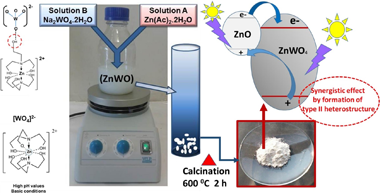
Abstract
ZnWO4 based powder photocatalyst have been successfully prepared by calcining a co-precipitated precursor (ZnWO) obtained from aqueous Zn2+ and WO4 2− solutions at pH = 7, without surfactants addition. The as-formed sample was characterized by XRD, N2-absorption, SEM, TEM, DRS and XPS. Both techniques, XRD and XPS results showed that prepared sample corresponds to a crystalline, Zn-enriched composition, ZnWO4 indicating the formation of a ZnWO4-(ZnO) composite, whit ca. 10 wt.-% of ZnO confirmed by XRF analysis. Photocatalytic activities towards degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB), Methyl Orange (MO) and Phenol, under UV-illumination, was investigated not only by monitoring the percentages of conversion of substrates, but also by estimating the corresponding percentages of mineralization that accompany the photocatalytic process. Comparative substrateconversion rates estimated per surface area unit of catalyst, showed that the activity for ZnWO4-(ZnO) composite is similar to that for TiO2(P25), at least for MO and RhB, and even higher that for TiO2(P25) in respect to phenol conversion. By adding TEA to the synthesis procedure, a composite named as ZnWO4-ZnO-(pH = 10)-600 is generated, which has a higher proportion of ZnO (ca. 39 %) and superior specific surface area than the so-called ZnWO4-(ZnO) sample. Furthermore, the photocatalytic degradation of MO using the former material indicates that it is superior to ZnWO4-(ZnO) and even that TiO2(P25) itself under the same operational conditions.
January, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112962
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Physicochemical surface analysis and germination at different irrigation conditions of DBD plasma‐treated wheat seeds
Molina, R; Lalueza, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Ghobeira, R; Cools, P; Morent, R; de Geyter, N; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Processes and Polymers, 18 (2021) e2000086 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202000086
Abstract
Plasma treatment is increasingly being explored as an effective presowing treatment improving seed germination. This study examines the synergetic effect of the irrigation condition and the physicochemical surface properties of wheat seeds subjected to atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge plasma activation on their water uptake and germination. Extensive surface analysis revealed a remarkably enhanced wettability of plasma-treated seeds due to the insertion of oxygen-containing functionalities on their surface. However, long plasma exposures damaged the outermost layers of the pericarp due to a pronounced oxidative etching effect. Although the seed germination capacity was not affected by the plasma treatments, short plasma exposures were shown to enhance water uptake and accelerate seed germination, especially under water-scarcity conditions.
January, 2021 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202000086
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Anisotropic Resistivity Surfaces Produced in ITO Films by Laser-Induced Nanoscale Self-organization
Lopez-Santos, C; Puerto, D; Siegel, J; Macias-Montero, M; Florian, C; Gil-Rostra, J; Lopez-Flores, V; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Solis, JAdvanced Optical Materials, 9 (2021) 2001086 DOI: 10.1002/adom.202001086
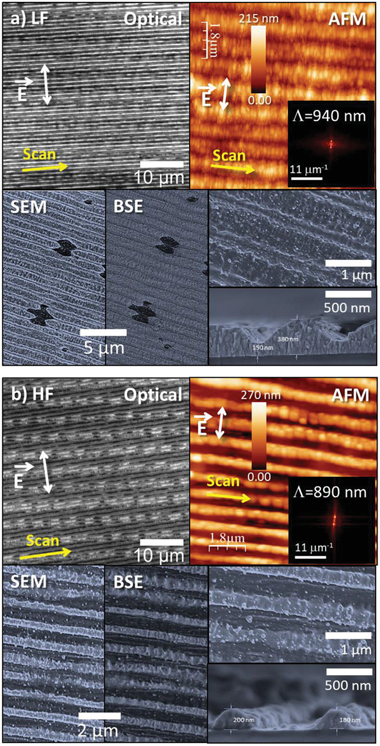
Abstract
Highly anisotropic resistivity surfaces are produced in indium tin oxide (ITO) films by nanoscale self-organization upon irradiation with a fs-laser beam operating at 1030 nm. Anisotropy is caused by the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) extended over cm-sized regions. Two types of optimized structures are observed. At high fluence, nearly complete ablation at the valleys of the LIPSS and strong ablation at their ridges lead to an insulating structure in the direction transverse to the LIPSS and conductive in the longitudinal one. A strong diminution of In content in the remaining material is then observed, leading to a longitudinal resistivity rho(L) approximate to 1.0 omega center dot cm. At a lower fluence, the material at the LIPSS ridges remains essentially unmodified while partial ablation is observed at the valleys. The structures show a longitudinal conductivity two times higher than the transverse one, and a resistivity similar to that of the pristine ITO film (rho approximate to 5 x 10(-4) omega center dot cm). A thorough characterization of these transparent structures is presented and discussed. The compositional changes induced as laser pulses accumulate, condition the LIPSS evolution and thus the result of the structuring process. Strategies to further improve the achieved anisotropic resistivity results are also provided.
January, 2021 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.202001086
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Sponge-like processed D-periodic self-assembled atelocollagen supports bone formation in vivo
Borrego-Gonzalez, S; Rico-Llanos, G; Becerra, J; Diaz-Cuenca, A; Visser, RMaterials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications, 120 (2021) art.111679 DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111679
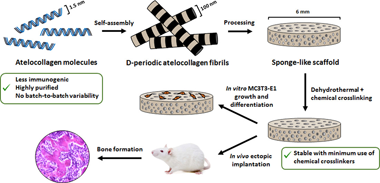
Abstract
Fibrous biopolymeric collagen extracted from animal tissues has been widely used for fabricating matrices for bone tissue engineering (BTE). However, animal extracted collagens can trigger immune reactions when implanted in vivo and the presence of native crosslinks leads to batch-to-batch variability. Atelocollagen, a monomeric form of collagen, is free of telopeptides, which are mainly responsible for the immunogenicity of collagen, and can self-assemble in vitro to obtain fibrils with the characteristic D-periodic staining pattern of native collagen. However, atelocollagen-based biomaterials have not extensively been studied and, hence, their suitability for BTE remains relatively unexplored. Besides, to stabilize collagen biomaterials, chemical and physical crosslinking are used, although chemical agents are cytotoxic while the physical methods yield a less effective crosslinking. A combination of physical and chemical crosslinking is a suitable alternative that has rarely been tested in BTE programs. In this work, a sponge-like biomaterial (DCol-S) was processed from D-periodic self-assembled atelocollagen and its stabilization was studied using the combination of a dehydrothermal treatment (DHT) and minimal glutaraldehyde (GTA) exposition crosslinking, to increase the resistance to degradation of the scaffold without a major effect on the biomaterial structure. The microstructural features of the final sponges were characterised and compared to a commercial biomaterial processed from native bovine collagen (Helistat (R), Integra Lifesciences, NJ, USA), demonstrating that a D-periodic nanostructure was obtained and maintained after processing of the sponges. MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast adhesion, proliferation and differentiation assays in vitro showed that DCol-S is biocompatible. Furthermore, intramuscular implantation of the biomaterials loaded with rhBMP-2 revealed that the double-crosslinked sponges were able to support ectopic bone formation, while sponges stabilised only with the DHT treatment were not. Altogether, these findings show that atelocollagen-based sponges stabilised with a DHT treatment followed by a mild GTA crosslinking are a suitable alternative to polymeric extracted collagen for BTE applications.
January, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111679
2020
2020
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Wetting and spreading of liquid lithium onto nanocolumnar tungsten coatings tailored through the topography of stainless steel substrates
Munoz-Pina, S; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Oyarzabal, E; Gil-Rostra, J; Rico, V; Alcala, G; Alvarez, R; Tabares, FL; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARNuclear Fusion, 60 (2020) 126033 DOI: 10.1088/1741-4326/abb53e
Abstract
The use of liquid metal as an alternative to cover the plasma-exposed areas of fusion reactors has called for the development of substrates where refilling and metal spreading occur readily and at reasonably low temperatures. In the search for common materials for this purpose, we show that nanostructured tungsten coatings deposited on stainless steel (SS) by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles (MS-OAD) is a good option, provided that the surface microstructure of substrate is properly engineered. Tungsten thin films with nominal thicknesses of 500 and 2500 nm were deposited onto SS plates subjected to conventional surface finishing treatments (sand blasting, sand paper abrasion and electrochemical polishing) to modify the surface topography and induce the appearance of different groove patterns. In the first part of this work we show how the topographical features of the SS substrates affect the typical nanocolumnar microstructure of OAD thin films of tungsten. Subsequently, we characterize the spreading behavior of liquid lithium onto these tungsten nanocolumnar surfaces and critically discuss whether nanocolumnar tungsten thin films are a suitable option for the wetting and spreading of molten lithium. As a result, we reveal that the features of the tungsten nanocolumnar coating, characterized by a given height and void spaces between nanocolumns in the order of 1–2 μm, is critical for the spreading of molten lithium, while the existence of wider channels affects it very weakly. Moreover, it is shown that tungsten films deposited by MS-OAD on SS substrates subjected to conventional finishing procedures represent a good alternative to other more complex surface engineering procedures utilized for this purpose.
December, 2020 · DOI: 10.1088/1741-4326/abb53e
Materiales Avanzados
Characterization, thermal and ceramic properties of phyllite clays from southeast Spain
Garzon, Eduardo; Perez-Villarejo, Luis; Sanchez-Soto, Pedro J.Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 142 (2020) 1659-1670 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-020-10160-9
Abstract
The present research studied a set of phyllite clays from several deposits in southeast Spain. These phyllite clays have traditionally been used as sealing material to impermeabilize roofs, embankments, ponds, construction and waste landfill, with recent applications in the preparation of new mortars. However, studies on thermal behaviour and ceramic properties of phyllite clays have been scarce. The present research showed a summary of previous characterization studies on representative phyllite clays from these deposits with additional results. Mineralogical, by X-ray diffraction, and chemical, by X-ray fluorescence characterization of these samples were summarized. Thermal analysis methods (DTA-TG and thermal diffractometry) were applied to achieve a more complete mineralogical characterization. Several phyllite clay samples were selected for a ceramic study by firing pressed powdered samples up to 1300 degrees C. Sintered or vitrified materials, with porosities almost zero, were obtained from these phyllite clays after firing at 1100-1200 degrees C, with apparent densities between 2.1 and 2.4 g cm(-3). Higher firing temperatures (> 1250 degrees C) produced deformation and expansion of the ceramic bodies. These results allowed obtain the vitrification temperature (T-v) and the temperature of the maximum bulk density (T-d). According to the previous mineralogical and chemical characterization and the values of these parameters, the phyllite clay samples were classified in three varieties, as follows: (1)Micaceous, characterized by predominant layer silicates, mainly muscovite or illite, alkaline elements (mainly K2O higher than 3.5 mass%) and lower values of both T(v)and T-d, (2)Quartzitic, with predominant quartz and SiO(2)and intermediate values of T(v)and T-d, and (3)Carbonaceous, characterized by predominant dolomite, medium contents of CaO and MgO and higher values of both T(v)and T-d. These results are interesting for the application of these phyllite clays as ceramic raw materials.
December, 2020 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-020-10160-9
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Robust anti-icing superhydrophobic aluminum alloy surfaces by grafting fluorocarbon molecular chains
Rico, V; Mora, J; Garcia, P; Aguero, A; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Lopez-Santos, CApplied Materials Today, 21 (2020) 100815 DOI: 10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100815
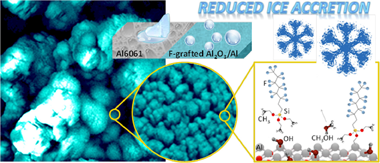
Abstract
Infusion of low surface tension liquids in nanostructured surfaces is currently used to promote an anti icing response, although the long term stability of these systems is often jeopardized by losses of the infused liquid. In this work, we propose an alternative to the infusion procedure to induce a more effective and long lasting anti-icing capacity. The method consists of a combination of surface nanostructuration with the chemical grafting of fluorocarbon molecules. Al6061 substrates have been subjected to laser roughening and further modified with a nanostructured Al2O3 thin film to achieve a dual roughness and porous surface state. These surfaces have been subjected to a grafting treatment with perfluorooctyltriethoxysilane (PFOTES) vapor or, for comparative purposes, infused with a low surface tension liquid. A comparative analysis of the wetting, water condensation and anti-icing properties of these two systems showed an outstandingly better performance for the grafted surfaces with respect to the infused ones. Grafted surfaces were markedly superhydrophobic and required higher water vapor pressures to induce condensation. When looking for their anti-icing capacity, they presented quite long freezing delay times for supercooled water droplets (i.e. almost four hours) and exhibited a notably low ice accretion in a wind tunnel test. The high aging resistance and durability of these grafted surfaces and the reproducibility of the results obtained when subjected to successive ice accretion cycles show that molecular grafting is an efficient anti-icing methodology that, in aggressive media, may outperform the classical infusion procedures. The role of the fluorocarbon chains anchored on the surface in inducing an anti-icing functionality is discussed.
December, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100815
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
(NH4)4[NiMo6O24H6].5H2O / g-C3N4 materials for selective photo-oxidation of Csingle bondO and Cdouble bondC bonds
Caudillo-Flores, U; Ansari, F; Bachiller-Baeza, B; Colon, G; Fernandez-Garcia, M; Kubacka, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 278 (2020) 119299 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119299
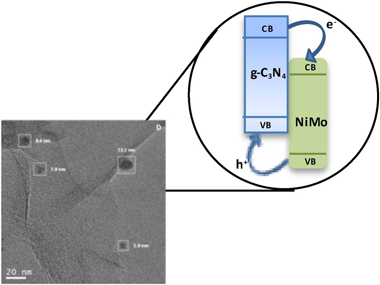
Abstract
Novel composite photo-catalysts having (NH4)(4)[NiMo6O24H6]center dot 5H(2)O Polyoxometalate (POM) species deposited over g-C3N4 are synthesized. Materials were characterized through a multitechnique approach showing the stability of the carbon nitride component both through the synthesis process and under reaction. Contrarily, the POM component evolves under reaction conditions to maximize the interaction with the support. Such a behavior renders, as measured by the quantum efficiency, highly active photo-catalysts in the photo-oxidation of 2-propanol and styrene both under UV and sunlight illumination, setting up the basis for a green catalytic process. The material having a 4 wt. % POM showed improved activity with respect to both parent constituents but also higher selectivity to the partial oxidation of the alcohol and the aromatic hydrocarbon to generate added value chemical compounds. A multitechnique approach investigating charge carrier fate demonstrates the key role played by the interaction between components to promote activity and selectivity in selective oxidation reactions.
December, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119299
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Influence of Water on the Oxidation of NO on Pd/TiO2 Photocatalysts
M.J. Hernández Rodríguez; E. Pulido Melián; J. Araña; J.A. Navío; O.M. González Díaz; Dunia E. Santiago; J.M. Doña RodríguezNanomaterials, 10 (2020) 2354 DOI: 10.3390/nano10122354
Abstract
Two series of new photocatalysts were synthesized based on modification with Pd of the commercial P25 photocatalyst (EVONIK®). Two techniques were employed to incorporate Pd nanoparticles on the P25 surface: photodeposition (series Pd-P) and impregnation (series Pd-I). Both series were characterized in depth using a variety of instrumental techniques: BET, DRS, XRD, XPS, TEM, FTIR and FESEM. The modified series exhibited a significant change in pore size distribution, but no differences compared to the original P25 with respect to crystalline phase ratio or particle size were observed. The Pd0 oxidation state was predominant in the Pd-P series, while the presence of the Pd2+ oxidation state was additionally observed in the Pd-I series. The photoactivity tests were performed in a continuous photoreactor with the photocatalysts deposited, by dip-coating, on borosilicate glass plates. A total of 500 ppb of NO was used as input flow at a volumetric flow rate of 1.2 L·min−1, and different relative humidities from 0 to 65% were tested. The results obtained show that under UV-vis or Vis radiation, the presence of Pd nanoparticles favors NO removal independently of the Pd incorporation method employed and independently of the tested relative humidity conditions. This improvement seems to be related to the different interaction of the water with the surface of the photocatalysts in the presence or absence of Pd. It was found in the catalyst without Pd that disproportionation of NO2 is favored through its reaction with water, with faster surface saturation. In contrast, in the catalysts with Pd, disproportionation took place through nitro-chelates and adsorbed NO2 formed from the photocatalytic oxidation of the NO. This different mechanism explains the greater efficiency in NOx removal in the catalysts with Pd. Comparing the two series of catalysts with Pd, Pd-P and Pd-I, greater activity of the Pd-P series was observed under both UV-vis and Vis radiation. It was shown that the Pd0 oxidation state is responsible for this greater activity as the Pd-I series improves its activity in successive cycles due to a reduction in Pd2+ species during the photoactivity tests.
December, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/nano10122354
Reactividad de Sólidos
Control of experimental conditions in reaction flash-sintering of complex stoichiometry ceramics
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Roman-Gonzalez, D; Perez-Maqueda, LACeramics International, 46 (2020) 29413-29420 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.091
Abstract
The inherent potential of reaction flash-sintering for the preparation of complex oxides is evidenced by the one-step synthesis and densification of a ceramic of complex stoichiometry. The system Bi0.93La0.07FeO3, a multi-ferroic ceramic with promising technological applications, has been chosen. This system presents three different metals in its composition and it is extremely challenging to prepare by conventional procedures. Non-stoichiometric materials with unwilling secondary phases are usually obtained by conventional methods, due to the high volatility of bismuth oxide at the temperatures required for inducing the solid-solid reactions. Here, it is demonstrated that a careful control of the experimental flash conditions (applied electric field and selected current density limit) is required to obtain a high quality ceramic. Small deviations from the optimum conditions result in either non-stoichometric or poorly densified samples.
December, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.091
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Thin film electroluminescent device based on magnetron sputtered Tb doped ZnGa2O4 layers
Gil-Rostra, J; Valencia, FY; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Luminescence, 228 (2020) 117617 DOI: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2020.117617
Abstract
Photoluminescent (PL) layers and electroluminescent (EL) systems prepared by different methods have been systematically studied for the fabrication of flat panel displays, monitoring screens, and lighting systems. In this work we report about a new procedure of preparing Tb doped ZnGa2O4 green luminescent thin films at low temperature that consists of the simultaneous reactive magnetron sputtering (R-MS) deposition of a Zn-Ga mixed oxide acting as a matrix and the plasma decomposition (PD) of evaporated terbium acetylacetonate. The resulting films were transparent and presented a high PL efficiency making them good candidates for EL applications. Layers of this phosphor film with thickness in the order of hundreds nanometers were sandwiched between two dielectric layers of Y2O3 and AlSiNxOy that were also prepared by R-MS. The response of the resulting EL device was characterized as a function of the applied voltage and the type of AC excitation signal. The high luminance and long-term stability of these thin film electroluminescent devices (TFELDs) proves the reliability and efficiency of this kind of transparent R-MS multilayer system (with a total thickness in order of 650 nm) for display and lighting applications.
December, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2020.117617
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Efficient third harmonic generation from FAPbBr(3) perovskite nanocrystals
Rubino, A; Huq, T; Dranczewski, J; Lozano, G; Calvo, ME; Vezzoli, S; Miguez, H; Sapienza, RJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 8 (2020) 15990-15995 DOI: 10.1039/d0tc04790b
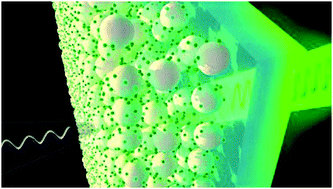
Abstract
The development of versatile nanostructured materials with enhanced nonlinear optical properties is relevant for integrated and energy efficient photonics. In this work, we report third harmonic generation from organic lead halide perovskite nanocrystals, and more specifically from formamidinium lead bromide nanocrystals, ncFAPbBr(3), dispersed in an optically transparent silica film. Efficient third order conversion is attained for excitation in a wide spectral range in the near infrared (1425 nm to 1650 nm). The maximum absolute value of the modulus of the third order nonlinear susceptibility of ncFAPbBr(3), chi((3)NC), is derived from modelling both the linear and nonlinear behaviour of the film and is found to be chi((3)NC) = 1.46 x 10(-19) m(2) V-2 (or 1.04 x 10(-11) esu) at 1560 nm excitation wavelength, which is of the same order as the highest previously reported for purely inorganic lead halide perovskite nanocrystals (3.78 x 10(-11) esu for ncCsPbBr(3)). Comparison with the experimentally determined optical constants demonstrates that maximum nonlinear conversion is attained at the excitonic resonance of the perovskite nanocrystals where the electron density of states is largest. The ease of synthesis, the robustness and the stability provided by the matrix make this material platform attractive for integrated nonlinear devices.
December, 2020 · DOI: 10.1039/d0tc04790b
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
High-temperature solar-selective coatings based on Cr(Al)N. Part 2: Design, spectral properties and thermal stability of multilayer stacks
Rojas, TC; Caro, A; Escobar-Galindo, R; Sanchez-Lopez, JCSolar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 218 (2020) 110812 DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2020.110812
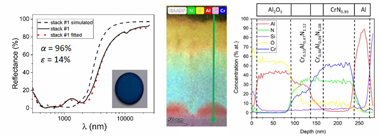
Abstract
Two multilayer solar selective absorber coatings [Al/CrN0.95/Cr0.96Al0.04N1.08/Cr0.53Al0.47N1.12/Al2O3 (stack #1) and Cr0.96Al0.04N0.89/Cr0.62Al0.38N1.00/Cr0.53Al0.47N1.12/Al2O3 (stack #2)] were deposited on 316L steel by combining direct current (DC) and high power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) technologies with the aim of increasing the working limit temperature. The composition and thickness of the constituent layers were optimized using CODE software to achieve a high solar absorptance (alpha) and low values of thermal emittance (epsilon) in the infrared region. The deposited multilayered stacks were heated during 2 h in air at 600, 700 and 800 degrees C to study their thermal stability and optical performance. Compositional, structural and optical characterization of the stacks (as-prepared and after thermal treatment) was performed. Both stacks presented a good solar selectivity with alpha > 95% and epsilon < 15%, were stable up to 600 degrees C and fulfilled the performance criterion PC < 5% after 600 and 700 degrees C treatments. Despite the stacks suffered chemical transformations above 600 degrees C, partial oxidation (stack #1) and Cr2N formation (stack #1 and #2), the optical properties were optimum up to 700 degrees C for stack #1 (alpha = 94%, epsilon((25 degrees C)) = 12%) and 600 degrees C for stack #2 (alpha = 93%, epsilon((25 degrees C)) = 13%). The solar-to-mechanical energy conversion efficiencies (eta) of the as-deposited and annealed (600 and 700 degrees C) samples were up to 20% points higher than the absorber paint commercially used (Pyromark). At 800 degrees C, they underwent a further structural transformation, provoked by the oxidation of the inner layers, and they consequently lost their solar selectivity.
December, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2020.110812
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Ru-Ni/MgAl2O4 structured catalyst for CO2 methanation
Navarro, Juan C.; Centeno, Miguel A.; Laguna, Oscar H.; Odriozola, Jose A.Renewabel Energy, 161 (2020) 120-132 DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.07.055
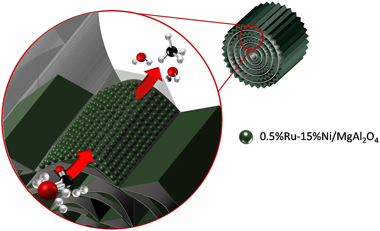
Abstract
Novel catalytic systems should be tested for the valorization of CO2 through the Sabatier reaction, since this process is gaining great importance within strategic sectors of the chemical industry. Therefore, this work explores the feasibility of structuring a catalyst (0.5%Ru-15%Ni/MgAl2O4) for CO2 methanation using metal micromonoliths. The coating of the catalyst over the surface of the micromonoliths is carried out by means of the washcoating procedure and different characterization techniques are applied to establish possible changes in the catalyst during structuring.
Regarding the performance in the Sabatier reaction, the structured systems are tested as well as the powder catalyst in order to establish the possible effects of the structuring processes. For this, variables such as catalyst loading, space velocity, inclusion of water in the feed-stream and the pressurization of the process were studied.
In general, the structuring of the proposed catalyst by the reported procedure is absolutely feasible. There are no substantial changes in the main features of the catalyst and this means that its catalytic performance is not altered after the structuring process either. Furthermore, the structured system exhibits high stability in a long-term test and is comparable with other CO2 methanation catalysts reported in research to date.
December, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.07.055
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Flexible syngas production using a La2Zr2-xNixO7-delta pyrochlore-double perovskite catalyst: Towards a direct route for gas phase CO2 recycling
le Sache, E; Pastor-Perez, L; Garcilaso, V; Watson, DJ; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TRCatalysis Today, 357 (2020) 583-589 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2019.05.039
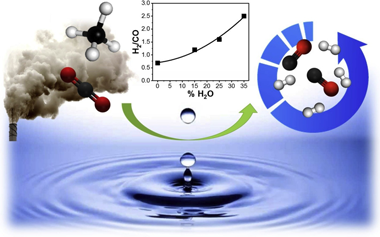
Abstract
The bi-reforming of methane (BRM) has the advantage of utilising greenhouse gases and producing H2 rich syngas. In this work Ni stabilised in a pyrochlore-double perovskite structure is reported as a viable catalyst for both Dry Reforming of Methane (DRM) and BRM. A 10 wt.% Ni-doped La2Zr2O7 pyrochlore catalyst was synthesised, characterised and tested under both reaction conditions and its performance was compared to a supported Ni/La2Zr2O7. In particular the effect of steam addition is investigated revealing that steam increases the H2 content in the syngas but limits reactants conversions. The effect of temperature, space velocity and time on stream was studied under BRM conditions and brought out the performance of the material in terms of activity and stability. No deactivation was observed, in fact the addition of steam helped to mitigate carbon deposition. Small and well dispersed Ni clusters, possibly resulting from the progressive exsolution of Ni from the mixed oxide structure could explain the enhanced performance of the catalyst.
November, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2019.05.039
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Thermo-optic response of MEH-PPV films incorporated to monolithic Fabry-Perot microresonators
Rostra, JG; Soler-Carracedo, K; Martin, LL; Lahoz, F; Yubero, FDyes and Pigments, 182 (2020) 108625 DOI: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2020.108625
Abstract
Poly[2-methoxy-5-(2'-ethylhexyloxy)-1,4-phenylene vinylene] (MEH-PPV) is a semiconducting optically active polymer widely used in optoelectronics research. MEH-PPV can be commercially acquired in a large range of molecular weights. However, the influence of this property on the optical performance of the polymer is often disregarded. In this paper, the thermal dependence of the refractive index of MEH-PPV thin films prepared from high and medium molecular weight polymers is investigated. Thus, monolithic Fabry-Perot (FP) microcavities are fabricated, in which the active polymer film is part of their defect layer. It is found that when these devices are used as optical temperature sensors, the position of the emission band of the microcavities excited with a blue diode laser shifts to lower wavelengths when temperature increases with sensitivities in the 0.2-0.3 nm/degrees C range. This effect is ascribed to the variation in the refractive index of the polymer active layer within the resonator with temperature. According to theoretical simulations of optical transmittance by classical transfer matrix method and the evaluation of the optical eigenmodes by finite element methods of the manufactured FP resonator cavities, it is found that the MEH-PPV films present negative thermo-optic coefficients of about-0.018 K-1 and-0.0022 K-1 for high and medium molecular weight polymers, respectively, in the temperature range between 20 and 60 degrees C. These values are about the highest reported so far, to the best of our knowledge, and points to high performance thermal sensor applications.
November, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2020.108625
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Tailoring CrNx stoichiometry and functionality by means of reactive HiPIMS
Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Caro, A; Alcala, G; Rojas, TCSurface & Coatings Technology, 401 (2020) 126235 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126235
Abstract
This work presents a complete study of the influence of HiPIMS pulse characteristics on the microstructure, chemical composition, mechanical and oxidation resistance properties of CrN thin films. The investigated parameters were frequency and pulse length at two different nitrogen fluxes, maintaining constant the duty cycle conditions (2%). The effect of a negative bias of 100 V was investigated in a particular case. By changing the synthesis conditions, it was possible to tailor the N/Cr ratio and thus to control the CrNx stoichiometry from x = 0.63 to 1.10. The selection of longer pulses (shorter frequencies) generates more disordered structures with lower N/Cr ratios. This is reflected in higher hardness and elastic modulus values on despite of a lower oxidation resistance due to existence of larger concentration of N vacancies. The best oxidation resistance is obtained at the highest peak current combined with additional ion bombardment provided by substrate biasing. The present results open the possibilities of modifying chemical composition and engineering surfaces by changing exclusively the pulse conditions in HiPIMS deposition processes.
November, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126235
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Advances in the implementation of PVD-based techniques for the preparation of metal catalysts for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride
Arzac, GM; Fernandez, AInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 58 (2020) 33288-33309 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.09.041
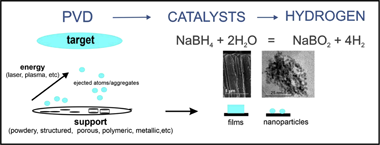
Abstract
Sodium borohydride constitutes a safe alternative for the storage of hydrogen with a high gravimetric content. Catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride permits on-demand hydrogen generation for multiple applications. In this field, the rational design of efficient metal catalysts deposited on structured supports is highly desirable. For most reactions, chemical methods are the most commonly used methods for the preparation of supported metal catalysts. Physical vapour deposition techniques are emerging as an alternative for the preparation of catalytic materials because of their multiple advantages. They permit the one-step deposition of catalysts on structured supports with controlled microstructure and composition, avoiding the multi-step procedures and the generation of hazardous by-products associated with chemical routes.
In this short review, we will describe the available literature on the application of physical vapour deposition techniques for the preparation of supported metal catalysts for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. The effects of the deposition parameters on the properties of the catalytic materials will be discussed, and strategies for further improvement will be proposed. Here, we also present our new results on the study of nanoporous Pt catalysts that are prepared through the chemical dealloying of magnetron sputtered Pt-Cu thin films for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. We discuss the capabilities of the technique to tune the microstructure from columnar to closed porous microstructures, which, coupled with dealloying, produces more active supported catalysts with lower noble metal loading. At the end, we briefly mention the application of PVD for the preparation of supported catalysts for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane, another hydrogen generating reaction of high interest nowadays.
November, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.09.041
Reactividad de Sólidos
Graphene-coated Ti-Nb-Ta-Mn foams: A promising approach towards a suitable biomaterial for bone replacement
Lascano, S; Chavez-Vasconez, R; Munoz-Rojas, D; Aristizabal, J; Arce, B; Parra, C; Acevedo, C; Orellana, N; Reyes-Valenzuela, M; Gotor, FJ; Arevalo, C; Torres, YSurface & Coatings Technology, 401 (2020) 126250 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126250
Abstract
The design of bone implants with proper biological and mechanical properties remains a challenge in medical implantology. The use of bioactive coatings has been shown to improve the biocompatibility of the implant surface. In this study, a new approach including porous scaffolds, beta-Ti alloys and nanocoatings to design new bone implants is presented. Porous Ti-Nb-Ta-xMn alloys (x: 2, 4, and 6 wt%) substrates were obtained by powder metallurgy and the effect of the porosity and Mn content on mechanical properties was studied. CVD single-layer graphene was transferred onto the porous substrates that presented the best mechanical response (x: 4 wt%) for further evaluation of in vitro cell behavior (biocompatibility and cell adhesion). Cytotoxicity and biocompatibility tests confirmed that cell adhesion and proliferation were successfully achieved on graphene-coated porous substrates, confirming these systems are potential candidates for using in partial bone tissue replacement.
November, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126250
Materiales Avanzados
Dust filter of secondary aluminium industry as raw material of geopolymer foams
Eliche-Quesada, D; Ruiz-Molina, S; Perez-Villarejo, L; Castro, E; Sanchez-Soto, PJHournal of Building Engineering, 32 (2020) 101656 DOI: 10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101656
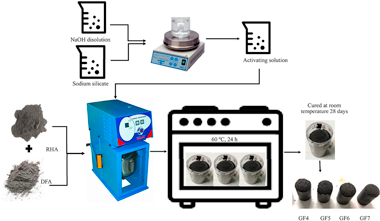
Abstract
In this work, the use of waste dust filter of secondary aluminum industry (DFA) to obtain geopolymer foams has been studied. The waste was used as source of alumina and foaming agent. As precursor and principal reactive silica supplier rice husk ash was used. Precursors were chemically activated by means of a sodium hydroxide aqueous solution and a commercial sodium silicate solution. The influence of the DFA content or Si/Al molar ratio (4-7) were determined by keeping the Si/Na molar ratio of 0.7 M constant and the concentration of sodium hydroxide in the activating solution equal to 8.5 M. The geopolymer foams obtained were studied by X-ray Diffraction (XRD), adsorption/desorption of nitrogen, infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and scanning electron microscope (SEM) techniques. The results indicated that geopolymer foams presented low values of bulk density (643-737 kg/m(3)) high values of apparent porosity (62-70%), low, but sufficient values of compressive strength (0.5-1.7 MPa) and good values of thermal conductivity (0.131-0.157 W/mK). Lower values of thermal conductivity were obtained for Si/Al = 4 and 5 M ratios, due to the highest apparent porosity and the highest total pore volume. These geopolymer foam materials have similar properties to other construction materials sector such as gypsum boards, foamed concrete, or insulating materials. In addition, its use in other applications of interest such as catalyst support or gas filtration materials could be investigated.
November, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101656
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Plasma-Enabled Amorphous TiO2 Nanotubes as Hydrophobic Support for Molecular Sensing by SERS
Filippin, N; Castillo-Seoane, J; Lopez-Santos, MC; Rojas, CT; Ostrikov, K; Barranco, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Borras, AACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 12 (2020) 50721-50733 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.0c14087
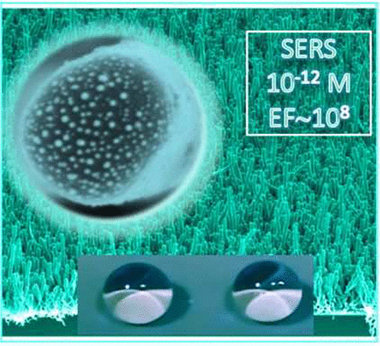
Abstract
We devise a unique heteronanostructure array to overcome a persistent issue of simultaneously utilizing the surface-enhanced Raman scattering, inexpensive, Earth-abundant materials, large surface areas, and multifunctionality to demonstrate near single-molecule detection. Room-temperature plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition and thermal evaporation provide high-density arrays of vertical TiO2 nanotubes decorated with Ag nanoparticles. The role of the TiO2 nanotubes is 3-fold: (i) providing a high surface area for the homogeneous distribution of supported Ag nanoparticles, (ii) increasing the water contact angle to achieve superhydrophobic limits, and (iii) enhancing the Raman signal by synergizing the localized electromagnetic field enhancement (Ag plasmons) and charge transfer chemical enhancement mechanisms (amorphous TiO2) and by increasing the light scattering because of the formation of vertically aligned nanoarchitectures. As a result, we reach a Raman enhancement factor of up to 9.4 × 107, satisfying the key practical device requirements. The enhancement mechanism is optimized through the interplay of the optimum microstructure, nanotube/shell thickness, Ag nanoparticles size distribution, and density. Vertically aligned amorphous TiO2 nanotubes decorated with Ag nanoparticles with a mean diameter of 10–12 nm provide enough sensitivity for near-instant concentration analysis with an ultralow few-molecule detection limit of 10–12 M (Rh6G in water) and the possibility to scale up device fabrication.
November, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.0c14087
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Internal quantum efficiency and time signals from intensity-modulated photocurrent spectra of perovskite solar cells
Riquelme, A; Galvez, FE; Contreras-Bernal, L; Miguez, H; Anta, JAJournal of Applied Physics, 128 (2020) 133103 DOI: 10.1063/5.0013317
Abstract
Intensity Modulated Photocurrent Spectroscopy (IMPS) is a small-perturbation optoelectronic technique that measures the quantum efficiency of a photoelectrochemical device as a function of optical excitation frequency. Metal Halide Perovskites (MHPs) are mixed electronic-ionic semiconductors with an extraordinary complex optoelectronic behavior and a record efficiency surpassing 25%. In this paper, we propose a simplified procedure to analyze IMPS data in MHPs based on the analysis of the internal quantum efficiency and the time signals featuring in the frequency spectra. In this procedure, we look at the change of each signal when optical excitation wavelength, photon flux, and temperature are varied for an archetypical methyl ammonium lead iodide solar cell. We use drift-diffusion modeling and comparison with relatively simpler dye-sensitized solar cells (DSC) with viscous and non-viscous electrolytes to help us to understand the origin of the three signals appearing in MHP cells and the measurement of the internal quantum efficiency.
October, 2020 · DOI: 10.1063/5.0013317
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Upgrading the PtCu intermetallic compounds: The role of Pt and Cu in the alloy
Castillo, R; Garcia, ED; Santos, JL; Centeno, MA; Sarria, FR; Daturi, M; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 356 (2020) 390-398 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2019.11.026
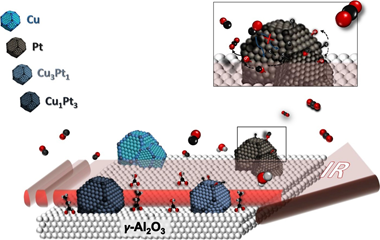
Abstract
This work is devoted to the study of the role of both metals in the intermetallic PtxCuy/ γ Al2O3 catalysts commonly employed in CO-PROX reaction. Therefore, monometallic Pt and Cu based catalysts and PtCu intermetallic compound with different molar ratios (Pt3Cu1 and Pt1Cu3) supported catalysts were carefully synthesized and deeply characterized. Room temperature CO adsorptions by FTIR spectroscopy were carried out on the mono- and intermetallic catalysts being the monometallic catalyst determinant for the study. From the analysis of the nature of the platinum surface in Pt/ γ Al2O3, we have demonstrated that the role of Pt sites is based in the CO dissociation for the CO2 formation and also how the platinum surface is partially blocked by leftovers from the synthesis. Moreover, the study of the Cu/ γ Al2O3 and the bimetallic catalysts PtxCuy/ γ Al2O3 allowed elucidating the effect of the copper in the metallic site and support interphase as well as the role of copper in the hydrocarbon oxidation.
October, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2019.11.026
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Tribological performance of Nb-C thin films prepared by DC and HiPIMS
Sala, N; Abad, MD; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Cruz, M; Caro, J; Colominas, CMaterials Letters, 277 (2020) 12834 DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128334
Abstract
Nanostructured NbC thin films with variable contents of Nb and C were prepared by direct current (DC) magnetron sputtering, and for the first time, via high power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) searching for an improvement in the tribological properties. X-ray diffraction shows that increasing the carbon incorporation, the crystalline composition evolves from Nb2C to NbC phase. Further carbon enrichment leads to a nanocomposite structure formed by small NbC crystals (8-14 nm) dispersed in a-C matrix. The friction coefficient varied from high friction (0.8) to low friction (0.25) and the hardness values between 20 and 11 GPa depending on the film composition. A densification of the coatings by changing the methodology from DC to HiPIMS was not observed.
October, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128334
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Microstructure and thermal conductivity of Si-Al-C-O fiber bonded ceramics joined to refractory metals
Vera, MC; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Singh, M; Casalegno, V; Balagna, C; Ramirez-Rico, JMaterials Letters, 276 (2020) 128203 DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128203
Abstract
We explore joining Si-Al-C-O fiber-bonded ceramics to Cu-clad-Mo using an Ag-Ti-Cu brazing alloy. A temperature of 900 degrees C and times in the range of 10-20 min are required to obtain sound joints irrespectively of the fiber orientation. The reaction layer is 1-2 mu m thick and free of pores and defects. The thermal conductivity of the joined samples is well described considering that the metal and the ceramic are in series for thermal resistance. This implies that the joint is highly conductive and forms an almost perfect
October, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128203
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Unraveling Discharge and Surface Mechanisms in Plasma-Assisted Ammonia Reactions
Navascues, P; Obrero-Perez, JM; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Gomez-Ramirez, AACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 8 (2020) 14855-14866 DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c04461
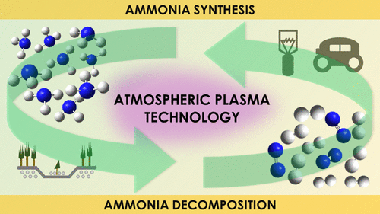
Abstract
Current studies on ammonia synthesis by means of atmospheric pressure plasmas respond to the urgent need of developing less environmentally aggressive processes than the conventional Haber-Bosch catalytic reaction. Herein, we systematically study the plasma synthesis of ammonia and the much less investigated reverse reaction (decomposition of ammonia into nitrogen and hydrogen). Besides analyzing the efficiency of both processes in a packed-bed plasma reactor, we apply an isotope-exchange approach (using D-2 instead of H-2) to study the reaction mechanisms. Isotope labeling has been rarely applied to investigate atmospheric plasma reactions, and we demonstrate that this methodology may provide unique information about intermediate reactions that, consuming energy and diminishing the process efficiency, do not effectively contribute to the overall synthesis/decomposition of ammonia. In addition, the same methodology has demonstrated the active participation of the interelectrode material surface in the plasma-activated synthesis/decomposition of ammonia. These results about the involvement of surface reactions in packed-bed plasma processes, complemented with data obtained by optical emission spectroscopy analysis of the plasma phase, have evidenced the occurrence of inefficient intermediate reaction mechanisms that limit the efficiency and shown that the rate-limiting step for the ammonia synthesis and decomposition reactions are the formation of NH* species in the plasma phase and the electron impact dissociation of the molecule, respectively.
October, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c04461
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Multiple pollutants removal by functionalized heterostructures based on Na-2-Mica
Pazos, MC; Bravo, LR; Ramos, SE; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 196 (2020) 105749 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2020.105749
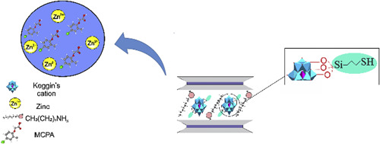
Abstract
Organomica, C8-2-Mica, was obtained from a high charged synthetic mica, Na-2-Mica, by cation exchange reaction with octylammonium cations and these were used to host other bulky guest species such as polyhydroxy aluminium cations, Al(13)20. The hydrolization of 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane (MPTMS) allowed the covalent attachment with hydroxyl groups of the oligomeric cation, providing thiol groups that create specific adsorption sites, Al(13)20/SH. The structure of the adsorbents was analysed by XRD and Infrared spectroscopy and these were tested as an adsorbent for the removal of zinc and herbicide MCPA from aqueous solutions. C8-2-Mica was the best adsorbent for MCPA and thiol groups favoured the adsorption of Zn2+. Moreover, Al(13)20/SH showed excellent adsorptive properties for the simultaneous adsorption of MCPA and Zn2+.
October, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2020.105749
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Bimetallic PdAu catalysts for formic acid dehydrogenation
Santos, JL; Leon, C; Monnier, G; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 45 (2020) 23056-23068 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.06.076
Abstract
A series of monometallic and bimetallic palladium gold catalyst were prepared and studied for the formic acid dehydrogenation reaction. Different Pd/Au compositions were employed (PdxAu100-x, where x = 25; 50 and 75) and their impact on alloy structure, particle size and dispersion was evaluated. Active phase composition and reaction parameters such as temperature, formic acid concentration or formate/formic acid ratio were adjusted to obtain active and selective catalyst for hydrogen production. An important particle size effect was observed and related to Pd/Au composition for all bimetallic catalysts.
September, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.06.076
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Free-Carbon Surface for PtCu Nanoparticles: An In Situ Near Ambient Pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Study
Castillo, R; Navarro-Jaen, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Perez-Dieste, V; Escudero, C; Centeno, MA; Daturi, M; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2020) 19046-19056 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c04713
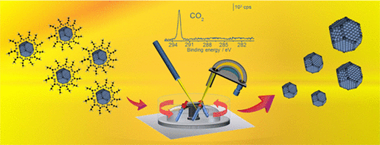
Abstract
Usually, nanoparticle synthesis methodologies require the use of organic molecules (capping agent, solvent molecules, etc.), which results in carbon deposits on the nanoparticle surface. These residues modify the surface properties mainly affecting the catalytic behavior. In this work, unsupported poly(vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP)-stabilized PtCu (1:3 molar ratio) bimetallic alloy nanoparticles were synthetized and characterized. An alternative surface cleaning method has been designed, which successfully removes the presence of organic fragments. To address this key issue, we have combined a first nanoparticle washing step with a near ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (NAPXPS) study in order to obtain a clean active site and the total understanding of the carbon elimination mechanism. The dynamic evolution of the surface organic species composition under different gas mixtures at 750 mTorr and 350 degrees C has been studied, and only under CO2 exposure, NAPXPS analysis revealed a total availability of the active site by the removal of the organic nanoparticle coating.
September, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c04713
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The wrinkling concept applied to plasma-deposited polymer-like thin films: A promising method for the fabrication of flexible electrodes
Thiry, Damien; Vinx, Nathan; Damman, Pascal; Aparicio, Francisco F.J.; Tessier, Pierre-Yves; Moerman, David; Leclere, Philippe; Godfroid, Thomas; Deprez, Sylvain; Snyders, RonyPlasma Processes and Polymers, 17 (2020) e2000119 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202000119
Abstract
In this communication, we report on an innovative solvent-free method that allows for the design of nano-/micropatterns with tuneable dimensions. Our approach is based on the spontaneous wrinkling phenomenon taking place in a bilayer system formed by a mechanically responsive bottom plasma polymer layer and a top aluminum thin film. The dimensions of the wrinkles can be adjusted in a wide range (i.e., from nanometer to micrometer range) by modulating the cross-linking density as well as the thickness of the plasma polymer layer. Finally, it is demonstrated that these wrinkled surfaces could efficiently be used as flexible electrodes. The whole set of our data unambiguously reveals the attractiveness of our method for the fabrication of the micro-/nanopattern with dimensions on demand.
September, 2020 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202000119
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Mg2SiO4-MgAl2O4 directionally solidified eutectics: Hardness dependence modelled through an array of screw dislocations
Moshtaghioun, BM; Gomez-Garcia, D; Pena, JIJournal of The European Ceramic Society, 40 (2020) 4171-4176 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.05.015
Abstract
Mg2SiO4-MgAl2O4 eutectic ceramics have been fabricated by means of the laser floating zone (LFZ) technique. The microstructure has revealed as an unusual one at lower growth rate, composed of broken lamellae of MgAl2O4 distributed randomly along one matrix, composed of Mg2SiO4. At higher growth rates, a cell structure with intra-cell lamella structure is dominant. Contrary to most eutectic systems, hardness is not dependent upon the inter-spacing, but it does depend on one characteristic length of lamellae: their perimeter. One simple model based upon the dislocation is proposed, which successfully accounts for such extraordinary hardness law. Accordingly, Mg2SiO4-MgAl2O4 eutectic ceramics fabricated at 50 mm/h growth rate with the smallest MgAl2O4 lamella perimeter favorably showed more elevated hardness (13.4 GPa from Vickers indentation and 15.3 GPa from nanoindentation) and strength (430 MPa) than those found in the monolithic Mg2SiO4 matrix.
September, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.05.015
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis of all equiatomic five-transition metals High Entropy Carbides of the IVB (Ti, Zr, Hf) and VB (V, Nb, Ta) groups by a low temperature route
Chicardi, E; Garcia-Garrido, C; Hernandez-Saz, J; Gotor, FJCeramics International, 46 (2020) 21421-21430 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.240
Abstract
The six possible equiatomic five-transition metal High Entropy Carbides (HECs) of the IVB (Ti, Zr, Hf) and VB (V, Nb, Ta) groups of the periodic table, i.e., TiZrHfVNbC5, TiZrHfVTaC5, TiZrHfNbTaC5, TiZrVNbTaC5, TiHfVNbTaC5 and ZrHfVNbTaC5, were successfully obtained via a powder metallurgy route at room temperature, specifically, by one-step diffusion mechanosynthesis starting from the elemental constituents (using graphite as the carbon source). Three of those HECs, TiZrHfVTaC5, TiZrVNbTaC5 and ZrHfVNbTaC5, were developed for the first time. Their development was possible without any subsequent thermal treatment, in contrast to the usual way (reactive sintering at 1800-2200 degrees C), and in a powder form, make them potential advanced raw ceramics for hard, refractory and oxidation resistance coatings or matrix phase composites.
September, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.240
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Experimental evidence of HCO species as intermediate in the fischer tropsch reaction using operando techniques
Diaz-Sanchez, RM; de-Paz-Carrion, A; Serrera-Figallo, MA; Torres-Lagares, D; Barranco, A; Leon-Ramos, JR; Gutierrez-Perez, JLApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 272 (2020) 119032 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119032
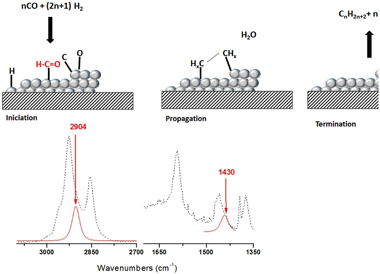
Abstract
Fischer Tropsch's reaction, known from 1925, receives special attention nowadays due to its key role in the CO2 or biomass valorization to liquid fuels and chemicals. Several aspects on the exact mechanism or the role of water in this reaction are not yet completely clear. Formyl species, HCO, have been proposed as the most probable reaction intermediate, but they have never been observed under operation conditions closed to the real ones. In this work, using DRIFTS-MS operando techniques, HCO intermediates are detected under a H2/CO flow and 200 °C. IR bands at 2900 cm−1 and 1440 cm−1 attributed to ν(C–H) and δ(HCO) vibrations modes characterize these species. Evolution of these bands with the reaction time evidences its high reactivity with OH groups, which explains the positive effect of water on the CO conversion previously observed.
September, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119032
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Novel procedure for laboratory scale production of composite functional filaments for additive manufacturing
Diaz-Garcia, A; Law, JY; Cota, A; Bellido-Correa, A; Ramirez-Rico, J; Schafer, R; Franco, VMaterials Today Communications, 24 (2020) 101049 DOI: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101049
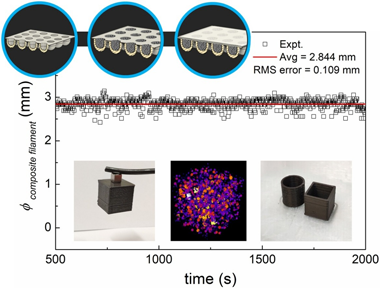
Abstract
Successful 3D printing by material extrusion of functional parts for new devices requires high quality filaments. Uniform homogeneity and good dispersion of particles embedded in filaments typically takes several cycles of extrusion or well-prepared feedstock by injection molding, industrial kneaders or twin-screw compounding. These methods need specific production devices that are not available in many laboratories non-specialized in polymer research, such as those working on different material science and technology topics that try to connect with additive manufacturing. Therefore, laboratory studies are usually limited to compositions and filler concentrations provided by commercial companies. Here, we present an original laboratory scale methodology to custom-prepare the feedstock for extruding magnetic composite filaments for fused filament fabrication (FFF), which is attainable by a desktop single-screw extruder. It consists in encapsulating the fillers in custom made capsules that are used as feedstock and reach the melting area of the extruder maintaining the same concentration of fillers. Results have shown that our approach can create smooth and continuous composite filaments with good homogeneity and printability with fine level of dimensional control. We further show the good dispersion of the particles in the composite filament using X-Ray Tomography, which enabled a 3D reconstruction of the spacial distribution of the embedded magnetic particles. The major advantage of this new way of preparing the composite feedstock is that it avoids the hassle of multiple extrusion runs and industrial machinery, yet providing uniform filaments of well controlled filler concentration, which is predictable and reproducible. The proposed methodology is suitable for different polymer matrices and applicable to other functional particle types, not just limited to magnetic ones. This opens an avenue for further laboratory scale development of novel functional composite filaments, useful for any community. This democratization of complex filament preparation, including consumers preparing their own desired uniform novel filaments, will facilitate to unify efforts nearing 3D printing of new functional devices.
September, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101049
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tailoring materials by high-energy ball milling: TiO2 mixtures for catalyst support application
Rinaudo, MG; Beltran, AM; Fernandez, MA; Cadus, LE; Morales, MRMaterials Today Chemistry, 17 (2020) 100340 DOI: 10.1016/j.mtchem.2020.100340
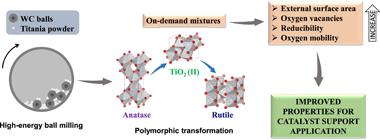
Abstract
We carried out a rational design of catalyst supports by high-energy ball milling. Tailored mixtures of TiO2 crystalline phases were obtained using rotational speed and milling time as variable parameters. Polymorphic transformation from anatase to rutile through high-pressure TiO2 (II) as intermediate was confirmed by X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Raman Spectroscopy and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM). Also, starting material doubled its specific surface area due to particle fragmentation, as confirmed by surface area of Brunauer-Emmet-Teller (S-BET) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). Defects introduced during milling process generated oxygen vacancies in the surface and bulk of supports, as evidenced by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) and Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR). Furthermore, longer milling time increased reducibility and oxygen mobility of supports, as observed by H-2 Temperature Programmed Reduction (H-2-TPR) and O-2 Temperature Programmed Desorption (O-2-TPD). Phase composition remained unchanged even under extreme conditions, highlighting the stability of unusual TiO2 (II) phase. Properties achieved in present materials could benefit metal-support interactions and play a major role in supported catalysts.
September, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mtchem.2020.100340
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Elucidating esterification reaction during deposition of cutin monomers from classical molecular dynamics simulations
Bueno, OVM; Benitez, JJ; San-Miguel, MAJournal of Molecular Modeling, 26 (2020) 280 DOI: 10.1007/s00894-020-04544-9
Abstract
The structural behavior of some cutin monomers, when deposited on mica support, was extensively investigated by our research group. However, other events, such as esterification reaction (ER), are still a way to explore. In this paper, we explore possible ER that could occur when these monomers adsorb on support. Although classical molecular dynamics simulations are not able to capture reactive effects, here, we show that they become valuable strategies to analyze the initial structural configurations to predict the most favorable reaction routes. Thus, when depositing aleuritic acid (ALE), it is observed that the loss of capacity to form self-assembled (SA) systems favors different routes to occur ER. In pure ALE bilayers systems, an ER is given exclusively through the -COOH and primary -OH groups. In pure ALE monolayers systems, the ER does not happen when the system is self-assembled. However, for disorganized systems, it is able to occur by two possible routes: -COOH and primary -OH (route 1) and -COOH and secondary -OH (route 2). When palmitic acid (PAL) is added in small quantities, ALE SAMs can now form an ER. In this case, ER occurs mostly through the -COOH and secondary -OH groups. However, when the presence of PAL is dominant, ER can occur with either of both possibilities, that is, routes 1 and 2.
September, 2020 · DOI: 10.1007/s00894-020-04544-9
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
An electrochemical evaluation of nitrogen-doped carbons as anodes for lithium ion batteries
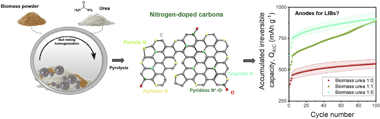
Gomez-Martin, A; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Ruttert, M; Winter, M; Placke, T; Ramirez-Rico, JCarbon, 164 (2020) 261-271 DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.04.003
Abstract
New anode materials beyond graphite are needed to improve the performance of lithium ion batteries (LIBs). Chemical doping with nitrogen has emerged as a simple strategy for enhancing lithium storage in carbon-based anodes. While specific capacity and rate capability are improved by doping, little is known about other key electrochemical properties relevant to practical applications. This work presents a systematic evaluation of electrochemical characteristics of nitrogen-doped carbons derived from a biomass source and urea powder as anodes in LIB half- and full-cells. Results show that doped carbons suffer from a continuous loss in capacity upon cycling that is more severe for higher nitrogen contents. Nitrogen negatively impacts the voltage and energy efficiencies at low charge/discharge current densities. However, as the charge/discharge rate increases, the voltage and energy efficiencies of the doped carbons outperform the non-doped ones. We provide insights towards a fundamental understanding of the requirements needed for practical applications and reveal drawbacks to be overcome by novel doped carbon-based anode materials in LIB applications. With this work, we also want to encourage other researchers to evaluate electrochemical characteristics besides capacity and cycling stability which are mandatory to assess the practicality of novel materials.
August, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.04.003
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Disclination dipoles are the Holy Grail for high temperature superplasticity in ceramics
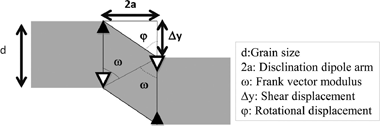
Moshtaghioun, BM; Bejarano-Palma, JA; Garcia, DGScripta Materialia, 185 (2020) 21-24 DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.03.049
Abstract
A model for high-temperature plasticity of polycrystals controlled by disclination dipoles is proposed that predict a parabolic dependence of the strain rate versus the applied stress. The presence of a precise stationary disclination density explains the origin of plasticity without microstructural invariance, commonly known as superplasticity. The disclination mechanism is universal, although other processes, such as dislocation glide, are superposed to this one in many systems such as metals or metallic alloys. While, in ceramics it is likely to be the only operative mechanism. Activation of disclination dipoles is a necessary condition for plasticity and sufficient one for superplastic yielding.
August, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.03.049
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Thermo-Photocatalytic Methanol Reforming for Hydrogen Production over a CuPd-TiO2 Catalyst
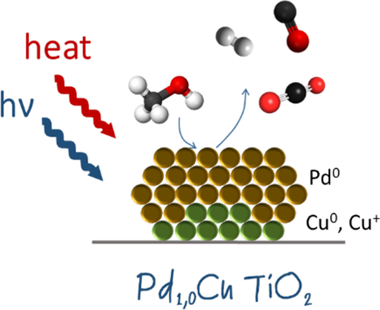
Lopez-Martin, A; Platero, F; Caballero, A; Colon, GChemPhotoChem, 4 (2020) 630-637 DOI: 10.1002/cptc.202000010
Abstract
A bimetallic CuPd/TiO2 system has been prepared by a two-step synthesis and was used for a methanol steam photoreforming reaction. By sequential deposition, palladium is deposited over copper nanoclusters through a galvanic replacement process. Hydrogen production by steam reforming from methanol was achieved by both thermo-photocatalytic and photocatalytic processes. It appears that H-2 production on the bimetallic system is notably higher than the Pd monometallic reference. Moreover this difference in the catalytic performance could be related to the higher CO evolution observed for the monometallic Pd-1.0 TiO2 system which is partially inhibited in the bimetallic catalyst. In addition, an important thermal effect can be envisaged in all cases. Nevertheless, this improved effect in the thermo-photocatalytic process is accompanied by a remarkable CO evolution and SMSI effect (important strong metal-support interactions) that hindered the efficiency as temperature increases. On this basis, optimal operational conditions for H-2 production are obtained for thermo-photocatalytic reforming at 100 degrees C, for which the synergetic effect is higher with lower CO production (H-2/CO=4)
August, 2020 · DOI: 10.1002/cptc.202000010
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Elucidation of Water Promoter Effect of Proton Conductor in WGS Reaction over Pt-Based Catalyst: An Operando DRIFTS Study
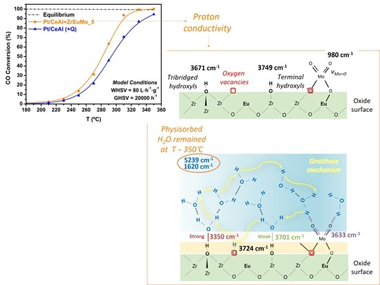
Jurado, L; Garcia-Moncada, N; Bobadilla, LF; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JACatalysts, 10 (2020) 841 DOI: 10.3390/catal10080841
Abstract
A conventional Pt/CeO2/Al(2)O(3)catalyst physically mixed with an ionic conductor (Mo- or Eu-doped ZrO2) was tested at high space velocity (20,000 h(-1)and 80 L h(-1)g(cat)(-1)) under model conditions (only with CO and H2O) and industrial conditions, with a realistic feed. The promoted system with the ionic conductor physically mixed showed better catalytic activity associated with better water dissociation and mobility, considered as a rate-determining step. The water activation was assessed by operando diffuse reflectance infrared fourier transformed spectroscopy (DRIFTS) studies under reaction conditions and the Mo-containing ionic conductor exhibited the presence of both dissociated (3724 cm(-1)) and physisorbed (5239 cm(-1)) water on the Eu-doped ZrO(2)solid solution, which supports the appearance of proton conductivity by Grotthuss mechanism. Moreover, the band at 3633 cm(-1)ascribed to hydrated Mo oxide, which increases with the temperature, explains the increase of catalytic activity when the physical mixture was used in a water gas shift (WGS) reaction.
August, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/catal10080841
Materiales Coloidales
Design of a nanoprobe for high field magnetic resonance imaging, dual energy X-ray computed tomography and luminescent imaging
Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Corral, A; Garcia-Embid, S; Balcerzyk, M; Garcia-Martin, ML; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 573 (2020) 278-286 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.101
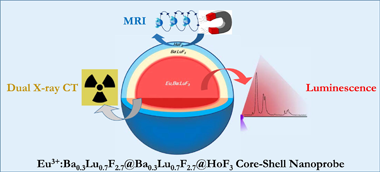
Abstract
The combination of different bioimaging techniques, mainly in the field of oncology, allows circumventing the defects associated with the individual imaging modalities, thus providing a more reliable diagnosis. The development of multimodal endogenous probes that are simultaneously suitable for various imaging modalities, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), X-ray computed tomography (CT) and luminescent imaging (LI) is, therefore, highly recommended. Such probes should operate in the conditions imposed by the newest imaging equipment, such as MRI operating at high magnetic fields and dual-energy CT. They should show, as well, high photoluminescence emission intensity for their use in optical imaging and present good biocompatibility. In this context, we have designed a single nanoprobe, based on a core-shell architecture, composed of a luminescent Eu3+:Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 core surrounded by an external HoF3 shell that confers the probe with very high magnetic transverse relaxivity at high field. An intermediate, optically inert Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 layer was interposed between the core and the shell to hinder Eu3+-Ho3+ cross-relaxation and avoid luminescence quenching. The presence of Ba and Lu, with different K-edges, allows for good X-ray attenuation at high and low voltages. The core-shell nanoparticles synthesized are good potential candidates as trimodal bioprobes for MRI at high field, dual-energy CT and luminescent imaging.
August, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.101
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Hydrodeoxygenation of vanillin over noble metal catalyst supported on biochars: Part II: Catalytic behaviour
Santos, JL; Maki-Arvela, P; Warna, J; Monzon, A; Centeno, MA; Murzin, DYApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 268 (2020) 118425 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118425
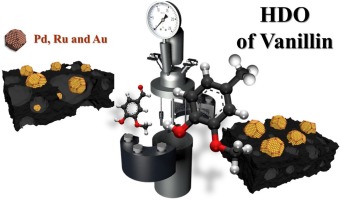
Abstract
Vanillin hydrodeoxygenation was investigated using noble metal (Pd, Au, Ru) supported on active carbon prepared from waste derived biochars, which were produced via pyrolysis in CO2 atmosphere. Chemical activation with ZnCl2 and HNO3 was also used in the preparation of active carbon to enhance the specific surface area and demineralize material, respectively. Both fresh and spent catalysts were characterized with X-ray diffraction, DRIFTS, zeta potential measurement and HR-TEM. The highest selectivity to p-creosol, 92 % selectivity at complete vanillin conversion after 3 h was obtained in vanillin hydrodeoxygenation at 100 degrees C under 30 bar in hydrogen in water with Pd/C catalyst prepared via pyrolysis under CO2 from wine waste and using ZnCl2 as a chemical activation agent. Hydrodeoxygenation activity increased with increasing metal dispersion. A kinetic model including adsorption of vanillin described well the experimental data.
July, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118425
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Performance trends in wall-flow diesel particulate filters: Comparative analysis of their filtration efficiency and pressure drop
Orihuela, MP; Chacartegui, R; Gomez-Martin, A; Ramirez-Rico, J; Villanueva, JABJournal of Cleaner Production, 60 (2020) 12063 DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120863
Abstract
Soot and particulate emissions from the transport sector are a major concern worldwide, given their harmful effects on public health and the environment. On-road vehicles are the main contributing source to this kind of pollution. They are strictly regulated in many countries, with limitations on the number and concentration of released particles, and they must be equipped with particle abatement systems. Wall-flow particulate filters are the most popular and effective devices to reduce particulate emissions from diesel and gasoline vehicles. Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs) have been a recurrent research topic since the last century. There are different research studies analysing different aspects of these systems, at different levels, using different methodologies and different approaches. Their results are not always comparable. This work analyses the latest advances and trends in this technology by comparing two relevant performance parameters: their filtration efficiency and pressure drop. The findings of this study suggest that, in order to be competitive, upcoming DPFs should have filtration efficiencies above 80%, and pressure drops below 10 kPa, for space velocities of 1.5.10(5) h(-1) or more at the clean state. They should reach similar to 100% efficiency after a short operation period, before the soot load reaches 0.2 g/L. Later, they should keep a low pressure drop for a longer time, with a reference of no more than 13 kPa for 6 g/L of soot load. Based on this analysis, this work proposes some test criteria and suggestions for the main parameters.
July, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120863
Reactividad de Sólidos
Calcium-Looping Performance of Biomineralized CaCO3 for CO2 Capture and Thermochemical Energy Storage
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Valverde, JM; Chacartegui, R; Perez-Maqueda, LAIndustrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 59 (2020) 12924-12933 DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05997
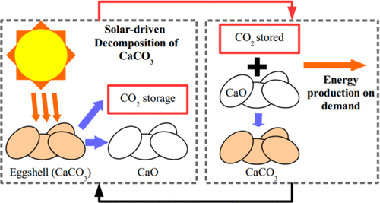
Abstract
The commercial deployment of calcium-looping (CaL)-based technologies relies on the availability of nontoxic, widely available and cheap CaCO3 rich materials. Biomineralized CaCO3 from waste amply fulfills the aforementioned requirements. In the present work, we study the performance of eggshell and snail shell from food waste as CaO precursors for CaL applications. The results obtained suggest the feasible use of these waste materials. The multicyclic conversion exhibited by biomineralized CaCO3 was comparable to that demonstrated by limestone, which is a commonly proposed material for CaL applications. In addition, the temperature needed to completely calcine biomineralized CaCO3 in short residence times is lower than that required to fully calcine limestone. This would mitigate the energy cost of the technology.
July, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05997
Reactividad de Sólidos
ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for analysis of multi-step kinetics
Vyazovkin, S; Burnham, AK; Favergeon, L; Koga, N; Moukhina, E; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sbirrazzuoli, NThermochimica Acta, 689 (2020) 178597 DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2020.178597
Abstract
The present recommendations have been developed by the Kinetics Committee of the International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (ICTAC). The recommendations provide guidance on kinetic analysis of multi-step processes as measured by thermal analysis methods such as thermogravimetry (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Ways of detecting the multi-step kinetics are discussed first. Then, four different approaches to evaluation of kinetic parameters (the activation energy, the pre-exponential factor, and the reaction model) for individual steps are considered. The approaches considered include multi-step model-fitting as well as distributed reactivity, isoconversional, and deconvolution analyses. For each approach practical advice is offered on its effective usage. Due attention is also paid to the typical problems encountered and to the ways of resolving them. The objective of these recommendations is to help a non-expert with efficiently performing multi-step kinetic analysis and interpreting its results.
July, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2020.178597
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Influence of Sr-doping on structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of synthesized Ca3(PO4)2
Y.Naciri; A.Hsini; Z.Ajmal; A.Bouddouch; B.Bakiz; J.A.Navío; A.Albourine; J-C.Valmalette; M.Ezahri; A.BenlhachemiJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 572 (2020) 269-280 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.105
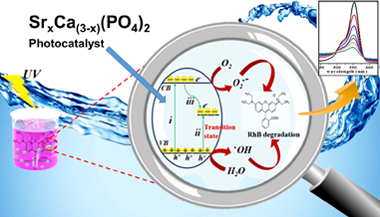
Abstract
Well-crystallized Ca3(PO4)2 doped and un-doped nano-particles with the maximum strontium content (40 wt% Sr) followed by calcination at 800 °C for 3 h were synthesized via facile co-precipitation method. DTA/TGA, X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive scanning electron microscopy (SEM/EDX), UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectrum (UV–vis DRS), Raman spectroscopy and photoluminescence (PL) techniques were used for material characterization. The (XRD) patterns of as-synthesized Sr-doped Ca3(PO4)2 solid solution samples exhibited a systematic shift toward lower angles by possessing a single rhombohedral crystal structure without any secondary phases. The UV light driven photocatalytic activity was assessed for rhodamine B (RhB) degradation. As a result, ultrafast photodegradation activity was observed after Sr doping. Moreover, the 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 sample showed the highest photocatalytic degradation among the Sr-doped Ca3(PO4)2 samples toward RhB. It was further suggested that as-synthesized 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 superior photocatalytic performance is ascribed to the more proficient partition of photogenerated electron-hole pairs. Furthermore, the involved mechanism of superior photocatalytic performance of the 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 solid solution was also investigated. In addition, regeneration cycles indicated the higher stability of the photocatalyst to be effectively recycled up to four times without any considerable reduction in photocatalytic performance. Thus, these informations further provides us a scalable pathway to fabricate Sr doped Ca3(PO4)2 and its consequent use as an efficient photocatalyst for rhodamine B (RhB) contaminated wastewater treatment.
July, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.105
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
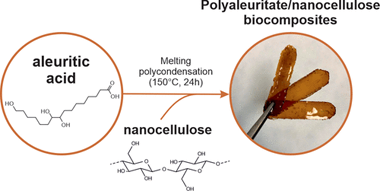
Sustainable, High-Barrier Polyaleuritate/Nanocellulose Biocomposites
Tedeschi, G; Guzman-Puyol, S; Ceseracciu, L; Benitez, JJ; Cataldi, P; Bissett, M; Heredia, A; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAACS Sistainable Chemistry & Engineering, 8 (2020) 10682-10690 DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00909
Abstract
Free-standing and flexible biocomposite films formed by a polyaleuritate matrix and nanocellulose fillers (i.e., cellulose nanofibrils) have been fabricated by a sustainable process. For this, 9,10,16-trihydroxyhexadecanoic (aleuritic) acid from shellac and nanocellulose were blended at different ratios in water through a sonication process. Polymerization of the polyhydroxylated fatty acid into polyaleuritate was induced by a solvent-free, melting polycondensation reaction in the oven. These biocomposites were characterized to evaluate their chemical (by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy) and physical (e.g., density, thermal stability, rigidity, gas permeability, surface energy, etc.) properties. The compatibility between the polyester matrix and the polysaccharide fillers was excellent due to the interaction by H bonds of the polar groups of both components. The addition of nanocellulose increased all determined mechanical parameters as well as the wettability and the barrier properties, while the thermal stability and the water uptake were determined by the polyaleuritate matrix. The physical properties of these biocomposites were compared to those of petroleum-based plastics and bio-based polymers, indicating that the developed materials can represent a sustainable alternative for different applications such as packaging.
July, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00909
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Evaluation of the Oxygen Mobility in CePO4-Supported Catalysts: Mechanistic Implications on the Water-Gas Shift Reaction
Navarro-Jaen, S; Bobadilla, LF; Romero-Sarria, F; Laguna, OH; Bion, N; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2020) 16391-16401 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c03649
Abstract
The hexagonal and monoclinic phases of CePO4 have been demonstrated to be excellent catalytic supports for Pt-based water-gas shift (WGS) catalysts. Consequently, the elucidation of the WGS reaction mechanism in these materials constitutes a fundamental aspect in order to explain their catalytic behavior. Because the observed WGS reaction path is closely related to the absence or presence of oxygen vacancies in the support, the study of the oxygen mobility in these solids constitutes a key factor for the understanding of the structure of the materials and its influence on the reaction mechanism. In this study, the oxygen mobility in CePO4 supports and the corresponding Pt catalysts has been evaluated by means of isotopic exchange experiments using O-18(2) and (CO2)-O-18 as probe molecules. Results demonstrate that the evaluated solids present a low exchange activity when O-18(2) is used, indicating the absence of oxygen vacancies in these solids, thus suggesting a poor influence of the WGS redox mechanism. On the contrary, a high oxygen exchange activity is observed using (CO2)-O-18, demonstrating that the exchange in these materials takes place through the formation of carbonate-like intermediates, thus suggesting the associative mechanism of the WGS reaction as the preferred path in these solids. Operando diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy experiments under WGS reaction conditions confirm these results, proving that the WGS reaction in the studied materials takes place through a formate-mediated associative mechanism.
July, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c03649
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Metal catalysts supported on biochars: Part I synthesis and characterization
Santos, JL; Maki-Arvela, P; Monzon, A; Murzin, DY; Centeno, MAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 268 (2020) 118423 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118423
Abstract
In the current study, synthesis and detailed characterization of cellulose biochars as a waste biomass model component and vine shoot biochars as a real waste biomass catalyst was performed. Although initially biochars exhibit poor textural properties, a simple activation process can make them much more suitable as a catalyst supports. A combination of physical (CO2) and chemical activation (ZnCl2) was evaluated. The characterization results indicated that the surface area and pore volume of the biochars have increased significantly by chemical activation treatment with ZnCl2. A series of metal catalysts (Pd, Au and Ru) supported on biochars was prepared and characterized. The prepared materials represent a set of noble metal catalysts supported on biochars with different textural and surface properties, which can be used to evaluate the catalytic role of the active phase and carbon support nature in catalytic reactions of interest, such as hydrodeoxygenation, described in the part II.
July, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118423
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Surface Modification of Rutile TiO2 with Alkaline-Earth Oxide Nanoclusters for Enhanced Oxygen Evolution
Rhatigan, S; Sukola, E; Nolan, M; Colon, GACS Applied Nano Materials, 3 (2020) 6017-6033 DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.0c01237
Abstract
The oxygen (O-2) evolution reaction (OER) is accepted as the bottleneck in the overall water splitting and has seen intense interest. In this work, we prepared rutile TiO2 modified with nanoclusters of alkaline-earth metal oxides for the OER. Photocatalytic OER was performed over rutile TiO2 surface-modified with alkaline-earth oxide nanoclusters, namely, CaO and MgO. The O-2 evolution activity is notably enhanced for MgO-modified systems at low loadings and a combination of characterization and first-principles simulations allows interpretation of the role of the nanocluster modification in improving the photocatalytic performance of alkaline-earth-modified rutile TiO2. At such low loadings, the nanocluster modifiers would be small, and this facilitates a close correlation with theoretical models. Structural and surface characterizations of the modified systems indicate that the integrity of the rutile phase is maintained after modification. However, charge-carrier separation is strongly affected by the presence of surface nanoclusters. This improved performance is related to surface features such as higher ion dispersion and surface hydroxylation, which are also discussed with first-principles simulations. The modified systems are reducible so that Ti3+ ions will be present. Water dissociation is favorable at cluster and interfacial sites of the stoichiometric and reduced modified surfaces. Pathways to water oxidation at interfacial sites of reduced MgO-modified rutile TiO2 are identified, requiring an overpotential of 0.68 V. In contrast, CaO-modified systems required overpotentials in excess of 0.85 V for the reaction to proceed.
June, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.0c01237
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Recent progress on the enhancement of photocatalytic properties of BiPO4 using π–conjugated materials
Naciri, Y., Hsini, A., Ajmal, Z., Navio, J.A., Bakiz, B., Albourine, A., Ezahri, M., Benlhachemi, A.Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 280 (2020) 102160 DOI: 10.1016/j.cis.2020.102160
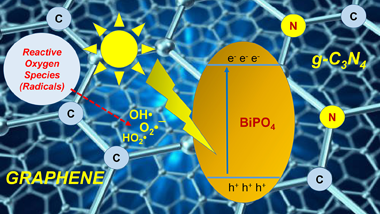
Abstract
Semiconductor photocatalysis is regarded as most privileged solution for energy conversion and environmental application. Recently, photocatalysis methods using bismuth-based photocatalysts, such as BiPO4, have been extensively investigated owing to their superior efficacy regarding organic pollutant degradation and their further mineralization into CO2 and H2O. It is well known that BiPO4 monoclinic phase exhibited better photocatalytic performance compared to Degussa (Evonik) P25 TiO2 in term of ultraviolet light driven organic pollutants degradation. However, its wide band gap, poor adsorptive performance and large size make BiPO4 less active under visible light irradiation. However, extensive research works have been conducted in the past with the aim of improving visible light driven BiPO4 activity by constructing a series of heterostructures, mainly coupled with π-conjugated architecture (e.g., conductive polymer, dye sensitization and carbonaceous materials). However, a critical review of modified BiPO4 systems using π-conjugated materials has not been published to date. Therefore, this current review article was designed with the aim of presenting a brief current state-of-the-art towards synthesis methods of BiPO4 in the first section, with an especial focuses onto its crystal-microstructure, optical and photocatalytic properties. Moreover, the most relevant strategies that have been employed to improve its photocatalytic activities are then addressed as the main part of this review. Finally, the last section presents ongoing challenges and perspectives for modified BiPO4 systems using π–conjugated materials
June, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cis.2020.102160
Reactividad de Sólidos
Electrochemically Exfoliated Graphene-Like Nanosheets for Use in Ceramic Nanocomposites
Poyato, R; Verdugo, R; Munoz-Ferreiro, C; Gallardo-Lopez, AMaterials, 13 (2020) 11 DOI: 10.3390/ma13112656
Abstract
In this work, the synthesis of graphene-like nanosheets (GNS) by an electrochemical exfoliation method, their microstructural characterization and their performance as fillers in a ceramic matrix composite have been assessed. To fabricate the composites, 3 mol % yttria tetragonal zirconia (3YTZP) powders with 1 vol % GNS were processed by planetary ball milling in tert-butanol to enhance the GNS distribution throughout the matrix, and densified by spark plasma sintering (SPS). According to a thorough Raman analysis and SEM observations, the electrochemically exfoliated GNS possessed less than 10 graphene layers and a lateral size lower than 1 mu m. However, they contained amorphous carbon and vacancy-like defects. In contrast the GNS in the sintered composite exhibited enhanced quality with a lower number of defects, and they were wavy, semi-transparent and with very low thickness. The obtained nanocomposite was fully dense with a homogeneous distribution of GNS into the matrix. The Vickers hardness of the nanocomposite showed similar values to those of a monolithic 3YTZP ceramic sintered in the same conditions, and to the reported ones for a 3YTZP composite with the same content of commercial graphene nanosheets.
June, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/ma13112656
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Local Rearrangement of the Iodide Defect Structure Determines the Phase Segregation Effect in Mixed-Halide Perovskites
Tiede, DO; Calvo, ME; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 11 (2020) 4911-4916 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c01127
Abstract
Mixed-halide perovskites represent a particularly relevant case within the family of lead-halide perovskites. Beyond their technological relevance for a variety of optoelectronic devices, photoinduced structural changes characteristic of this type of material lead to extreme photophysical changes that are currently the subject of intense debate. Herein we show that the conspicuous photoinduced phase segregation characteristic of these materials is primarily the result of the local and metastable rearrangement of the iodide sublattice. A local photophysical study comprising spectrally resolved laser scanning confocal microscopy is employed to find a correlation between the defect density and the dynamics of photoinduced changes, which extend far from the illuminated region. We observe that iodide-rich regions evolve much faster from highly defective regions. Also, by altering the material composition, we find evidence for the interplay between the iodide-related defect distribution and the intra- and interdomain migration dynamics giving rise to the complexity of this process.
June, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c01127
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Chemistry and Electrocatalytic Activity of Nanostructured Nickel Electrodes for Water Electrolysis
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Consuegra, AD; Yubero, FACS Catalysis, 10 (2020) 6159-6170 DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.0c00856
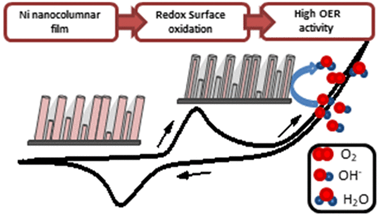
Abstract
Herein we have developed nanostructured nickel-based electrode films for anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE). The electrodes were prepared by magnetron sputtering (MS) in an oblique angle configuration and under various conditions aimed at preparing metallic, oxide, or oxyhydroxide films. Their electrochemical analysis has been complemented with a thorough physicochemical characterization to determine the effect of microstructure, chemical state, bilayer structure, and film thickness on the oxygen evolution reaction (OER). The maximum electrocatalytic activity was found for the metallic electrode, where analysis by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) demonstrated that the active catalytic phase at the surface after its electrochemical conditioning is a kind of oxidized nickel oxide/hydroxide layer with the thickness of a few nanometers. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis of these steady-state working electrodes supports that the enhanced performance of the metallic nickel anode vs other chemical states resides in the easier electron transfer through the electrode films and the various interlayers built up during their fabrication and activation. The long-term steady-state operation of the anodes and their efficiency for water splitting was proved in a full-cell AEMWE setup incorporating magnetron-sputtered metallic nickel as the cathode. This work proves that MS is a suitable technique to prepare active, stable, and low-cost electrodes for AEMWE and the capacity of this technique to control the chemical state of the electrocatalytically active layers involved in the OER.
June, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.0c00856
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Reductant atmospheres during slow pyrolysis of cellulose: First approach to obtaining efficient char -based catalysts in one pot
Santos, JL; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 148 (2020) 104821 DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2020.104821
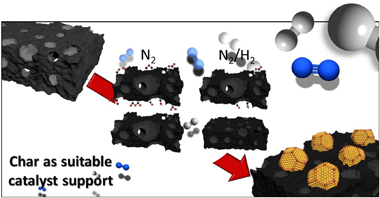
Abstract
Char based metallic (Pd-Au-Ru-Pt/C) catalysts have drawn increasing research interest due to their versatility in biomass related industrial reactions. Recent studies dealing with the synthesis of char-based catalysts in one single step (one-pot) use reductant atmospheres for biomass pyrolysis. In this work, the influence of the use of a reductant N2/H2 atmosphere on the physicochemical properties of the resulting chars was evaluated in comparison with the use of an inert N2 atmosphere. Specifically, the fundamental parameter of the pyrolysis process, the temperature, was evaluated in the 500−900 °C range. Produced chars were fully characterized by N2 isotherms, ultimate CHNS analysis, X-ray Diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, Diffuse Reflectance Infrared spectroscopy, X-ray Photoelectron spectroscopy, helium Temperature Programmed Decomposition and Isoelectric Point analysis. Slow pyrolysis under reductant atmosphere favours deoxygenation reaction against dehydrogenation ones, reduces the carbon yield and results in chars with a more hydrophobic and graphitic character, higher thermal stability and weak surface functionalization. The use of intermediates temperatures (700 °C) favours the obtaining of chars with suitable physicochemical properties and good surface functionalization, which will facilitate the anchoring of the active phase on the surface, improving the metallic dispersion of the resulting one pot catalyst. This leads us to affirm that the use of reducing atmospheres at intermediate temperatures, is superior to the use of inert atmospheres for this purpose. This analysis on the impact of the use of a reductant atmosphere during slow pyrolysis of microcrystalline cellulose opens a new working path for the optimization of char-based catalysts obtained in a single stage.
June, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2020.104821
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Cost-effective routes for catalytic biomass upgrading
Jin, W; Pastor-Perez, L; Yu, J; Odriozola, JA; Gu, S; Reina, TRCurrent Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 23 (2020) 1-9 DOI: 10.1016/j.cogsc.2019.12.008
Abstract
Catalytic hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) is a fundamental and promising route for bio-oil upgrading to produce petroleum-like hydrocarbon fuels or chemical building blocks. One of the main challenges of this technology is the demand of high-pressure H-2, which poses high costs and safety concerns. Accordingly, developing cost-effective routes for biomass or bio-oil upgrading without the supply of commercial H-2 is essential to implement the HDO at commercial scale. This article critically reviewed the very recent studies relating to the novel strategies for upgrading the biofeedstocks with 'green' H-2 generated from renewable sources. More precisely, catalytic transfer hydro-genation/hydrogenolysis, combined reforming and HDO, combined metal hydrolysis and HDO, water-assisted in-situ HDO and nonthermal plasma technology and self-supported hydrogenolysis are reviewed herein. Current challenges and research trends of each strategy are also proposed aiming to motivate further improvement of these novel routes to become competitive alternatives to conventional HDO technology.
June, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cogsc.2019.12.008
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
New biomorphic filters to face upcoming particulate emissions policies: A review of the FIL-BIO-DIESEL project
Orihuela, MP; Chacartegui, R; Martinez-Fernandez, JEnergy, 201 (2020) 117577 DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.117577
Abstract
With a high number of diesel vehicles worldwide, particulate emission control is an urgent issue with a global impact, from the health of citizens to commercial future of this technology in some transport segments. Particulate filters are widely used in automotive engines to comply emissions regulations, but current technologies have room for improvement as they add additional backpressure in the exhaust system, and efficient on-board regeneration process is challenging.
The Fil-Bio-Diesel Project is a R&D initiative to improve current particle filtration systems, based on the development of novel biomorphic substrates. By replicating the biologic tissue of a wood precursor, a biomorphic silicon carbide with hierarchic orthotropic microstructure can be produced. The porosity, the pore size, and pore orientation of this bioceramic material can be tailored through the selection of a suitable precursor, widening the initially narrow relationship between filtration efficiency and pressure drop that characterizes granular ceramic materials. In this paper the methodology and main results of the Fil-Bio-Diesel Project are presented. This work shows the peculiar advantages of biomorphic silicon carbide through several experimental studies. The results show the potential of this novel filter substrate to be used in future particulate abatement systems.
June, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.117577
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
5-Hydroxymethyl-2-Furfural Oxidation Over Au/Ce(x)Zr(1-x)O(2)Catalysts
Megias-Sayago, C; Bonincontro, D; Lolli, A; Ivanova, S; Albonetti, S; Cavani, F; Odriozola, JAFrontiers in Chemistry, 8 (2020) 461 DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00461
Abstract
A series of gold catalysts supported on pure CeO2, ZrO2, and two different Ce-Zr mixed oxides have been prepared and tested in the 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural oxidation reaction. All catalysts show high catalytic activity (100% conversion) and important selectivity (27-41%) to the desired product i.e., 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid at low base concentration. Products selectivity changes with the support nature as expected, however, the observed trend cannot be related neither to gold particle size, nor to catalyst reducibility and oxygen mobility. An important relation between the FDCA selectivity and the support textural properties is observed, conducing to the general requirement for optimal pore size for this reaction.
June, 2020 · DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00461
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Supported Porous Nanostructures Developed by Plasma Processing of Metal Phthalocyanines and Porphyrins
Obrero, JM; Filippin, AN; Alcaire, M; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Jacob, M; Matei, C; Aparicio, FJ; Macias-Montero, M; Rojas, TC; Espinos, JP; Saghi, Z; Barranco, A; Borras, AFrontiers in Chemistry, 8 (2020) 520 DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00520
Abstract
The large area scalable fabrication of supported porous metal and metal oxide nanomaterials is acknowledged as one of the greatest challenges for their eventual implementation in on-device applications. In this work, we will present a comprehensive revision and the latest results regarding the pioneering use of commercially available metal phthalocyanines and porphyrins as solid precursors for the plasma-assisted deposition of porous metal and metal oxide films and three-dimensional nanostructures (hierarchical nanowires and nanotubes). The most advanced features of this method relay on its ample general character from the point of view of the porous material composition and microstructure, mild deposition and processing temperature and energy constrictions and, finally, its straightforward compatibility with the direct deposition of the porous nanomaterials on processable substrates and device-architectures. Thus, taking advantage of the variety in the composition of commercially available metal porphyrins and phthalocyanines, we present the development of metal and metal oxides layers including Pt, CuO, Fe2O3, TiO2, and ZnO with morphologies ranging from nanoparticles to nanocolumnar films. In addition, we combine this method with the fabrication by low-pressure vapor transport of single-crystalline organic nanowires for the formation of hierarchical hybrid organic@metal/metal-oxide and @metal/metal-oxide nanotubes. We carry out a thorough characterization of the films and nanowires using SEM, TEM, FIB 3D, and electron tomography. The latest two techniques are revealed as critical for the elucidation of the inner porosity of the layers.
June, 2020 · DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00520
- ‹ previous
- 11 of 37
- next ›














