Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Thermo-optic response of MEH-PPV films incorporated to monolithic Fabry-Perot microresonators
Rostra, JG; Soler-Carracedo, K; Martin, LL; Lahoz, F; Yubero, FDyes and Pigments, 182 (2020) 108625
Show abstract ▽
Poly[2-methoxy-5-(2'-ethylhexyloxy)-1,4-phenylene vinylene] (MEH-PPV) is a semiconducting optically active polymer widely used in optoelectronics research. MEH-PPV can be commercially acquired in a large range of molecular weights. However, the influence of this property on the optical performance of the polymer is often disregarded. In this paper, the thermal dependence of the refractive index of MEH-PPV thin films prepared from high and medium molecular weight polymers is investigated. Thus, monolithic Fabry-Perot (FP) microcavities are fabricated, in which the active polymer film is part of their defect layer. It is found that when these devices are used as optical temperature sensors, the position of the emission band of the microcavities excited with a blue diode laser shifts to lower wavelengths when temperature increases with sensitivities in the 0.2-0.3 nm/degrees C range. This effect is ascribed to the variation in the refractive index of the polymer active layer within the resonator with temperature. According to theoretical simulations of optical transmittance by classical transfer matrix method and the evaluation of the optical eigenmodes by finite element methods of the manufactured FP resonator cavities, it is found that the MEH-PPV films present negative thermo-optic coefficients of about-0.018 K-1 and-0.0022 K-1 for high and medium molecular weight polymers, respectively, in the temperature range between 20 and 60 degrees C. These values are about the highest reported so far, to the best of our knowledge, and points to high performance thermal sensor applications.
November, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2020.108625
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Upgrading the PtCu intermetallic compounds: The role of Pt and Cu in the alloy
Castillo, R; Garcia, ED; Santos, JL; Centeno, MA; Sarria, FR; Daturi, M; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 356 (2020) 390-398
Show abstract ▽
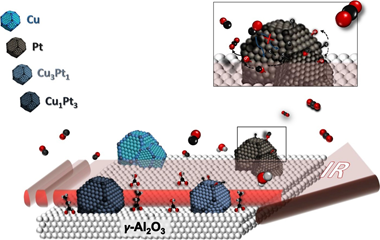
This work is devoted to the study of the role of both metals in the intermetallic PtxCuy/ γ Al2O3 catalysts commonly employed in CO-PROX reaction. Therefore, monometallic Pt and Cu based catalysts and PtCu intermetallic compound with different molar ratios (Pt3Cu1 and Pt1Cu3) supported catalysts were carefully synthesized and deeply characterized. Room temperature CO adsorptions by FTIR spectroscopy were carried out on the mono- and intermetallic catalysts being the monometallic catalyst determinant for the study. From the analysis of the nature of the platinum surface in Pt/ γ Al2O3, we have demonstrated that the role of Pt sites is based in the CO dissociation for the CO2 formation and also how the platinum surface is partially blocked by leftovers from the synthesis. Moreover, the study of the Cu/ γ Al2O3 and the bimetallic catalysts PtxCuy/ γ Al2O3 allowed elucidating the effect of the copper in the metallic site and support interphase as well as the role of copper in the hydrocarbon oxidation.
October, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2019.11.026
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Tribological performance of Nb-C thin films prepared by DC and HiPIMS
Sala, N; Abad, MD; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Cruz, M; Caro, J; Colominas, CMaterials Letters, 277 (2020) 12834
Show abstract ▽
Nanostructured NbC thin films with variable contents of Nb and C were prepared by direct current (DC) magnetron sputtering, and for the first time, via high power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) searching for an improvement in the tribological properties. X-ray diffraction shows that increasing the carbon incorporation, the crystalline composition evolves from Nb2C to NbC phase. Further carbon enrichment leads to a nanocomposite structure formed by small NbC crystals (8-14 nm) dispersed in a-C matrix. The friction coefficient varied from high friction (0.8) to low friction (0.25) and the hardness values between 20 and 11 GPa depending on the film composition. A densification of the coatings by changing the methodology from DC to HiPIMS was not observed.
October, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128334
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Microstructure and thermal conductivity of Si-Al-C-O fiber bonded ceramics joined to refractory metals
Vera, MC; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Singh, M; Casalegno, V; Balagna, C; Ramirez-Rico, JMaterials Letters, 276 (2020) 128203
Show abstract ▽
We explore joining Si-Al-C-O fiber-bonded ceramics to Cu-clad-Mo using an Ag-Ti-Cu brazing alloy. A temperature of 900 degrees C and times in the range of 10-20 min are required to obtain sound joints irrespectively of the fiber orientation. The reaction layer is 1-2 mu m thick and free of pores and defects. The thermal conductivity of the joined samples is well described considering that the metal and the ceramic are in series for thermal resistance. This implies that the joint is highly conductive and forms an almost perfect
October, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128203
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Unraveling Discharge and Surface Mechanisms in Plasma-Assisted Ammonia Reactions
Navascues, P; Obrero-Perez, JM; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Gomez-Ramirez, AACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 8 (2020) 14855-14866
Show abstract ▽
Current studies on ammonia synthesis by means of atmospheric pressure plasmas respond to the urgent need of developing less environmentally aggressive processes than the conventional Haber-Bosch catalytic reaction. Herein, we systematically study the plasma synthesis of ammonia and the much less investigated reverse reaction (decomposition of ammonia into nitrogen and hydrogen). Besides analyzing the efficiency of both processes in a packed-bed plasma reactor, we apply an isotope-exchange approach (using D-2 instead of H-2) to study the reaction mechanisms. Isotope labeling has been rarely applied to investigate atmospheric plasma reactions, and we demonstrate that this methodology may provide unique information about intermediate reactions that, consuming energy and diminishing the process efficiency, do not effectively contribute to the overall synthesis/decomposition of ammonia. In addition, the same methodology has demonstrated the active participation of the interelectrode material surface in the plasma-activated synthesis/decomposition of ammonia. These results about the involvement of surface reactions in packed-bed plasma processes, complemented with data obtained by optical emission spectroscopy analysis of the plasma phase, have evidenced the occurrence of inefficient intermediate reaction mechanisms that limit the efficiency and shown that the rate-limiting step for the ammonia synthesis and decomposition reactions are the formation of NH* species in the plasma phase and the electron impact dissociation of the molecule, respectively.
October, 2020 | DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c04461
- ‹ previous
- 92 of 410
- next ›














