Artículos SCI
2024
2024
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synthetic natural gas production using CO2-rich waste stream from hydrothermal carbonization of biomass: Effect of impurities on the catalytic activity
González-Arias, J; Torres-Sempere, G; Villora-Picó, JJ; Reina, TR; Odriozola, JAJournal of CO2 Utilization, 79 (2024) 102653
Show abstract ▽
The utilization of biomass and bio-waste, particularly through hydrothermal processes, has shown promise as a technology for converting these materials into valuable products. While most research has traditionally focused on the solid and liquid byproducts of these hydrothermal treatments, the gaseous phase has often been over-looked. This study specifically investigates the conversion of off-gases produced during hydrothermal carbonation (HTC) into synthetic natural gas, offering a readily marketable product with economic potential. Although the methanation of conventional flue gases has been extensively studied, dealing with non-standard off-gases from processes like HTC presents challenges due to the presence of minor impurities like CO and CH4. This novel research seeks to experimentally evaluate the methanation of HTC off-gases using nickel-based catalysts and analyze how these impurities affect the catalytic performance. The studied catalysts include nickel supported by ceria and alumina, as well as alumina supported nickel-cobalt systems. The results demonstrate that these catalysts exhibit high CO2 conversion and CH4 selectivity under ideal gas conditions. However, when real gas compositions with impurities are considered, CO2 conversion decreases at lower temperatures (ca. 20% lower conversion for real gas vs. ideal), probably due to side reactions such as CH4 cracking. This difference becomes less pronounced at higher temperatures. Nevertheless, the catalysts perform satisfactorily, especially at temperatures exceeding 350 degrees C. In conclusion, this study sheds light on the methanation of HTC off-gases and underscores the significance of understanding how impurities in real gases impact the process, providing potential directions for future research.
January, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2023.102653
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Switchable catalysis for methanol and synthetic natural gas synthesis from CO2: A techno-economic investigation
Merkouri, LP; Mathew, J; Jacob, J; Reina, TR; Duyar, MSJournal of CO2 Utilization, 79 (2024) 102652
Show abstract ▽
The oil and gas sector produces a considerable volume of greenhouse gas emissions, mainly generated from flaring and venting natural gas. Herein, a techno-economic analysis has been performed of a switchable catalytic process to convert the CH4 and CO2 in flared/vented natural gas into syngas or methanol. Specifically, it was shown that depending on greenhouse gas composition, dry methane reforming (DRM), reverse water-gas shift (RWGS), and CO2 methanation could be chosen to valorise emissions in an overall profitable and flexible operation scenario. The switchable process produced methanol and synthetic natural gas as its products, resulting in an annual income of €687m and annual operating expenses of €452m. The pre-tax profit was calculated at €234m, and at the end of the project, the net present value was calculated as €1.9b with a profitability index of 4.7€/€. The expected payback time of this process was ca. 4 years, and with a 35% internal rate of return (IRR). Most importantly, this process consumed 42.8m tonnes of CO2 annually. The sensitivity analysis revealed that variations in operation time, green hydrogen price, and products' prices significantly impacted the profitability of the process. Overall, this techno-economic analysis demonstrated that switchable catalysis in greenhouse gas utilisation processes is profitable, and thus it could play an important role in achieving net zero emissions.
January, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2023.102652
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Evaluation of Pt/TiO2-Nb2O5 systems in the photocatalytic reforming of glucose for the generation of H2 from industrial effluents
Lara Sandoval, AE; Serafin, J; Murcia Mesa, JJ; Rojas Sarmiento, HA; Hernandez Niño, JS; Llorca, J; Navío Santos, JA; Hidalgo Lõpez; MCFuel, 363 (2024) 130932
Show abstract ▽
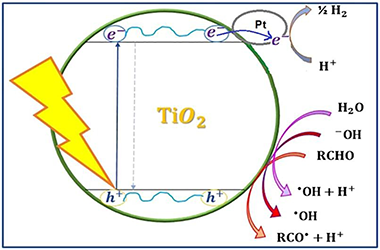
Different Pt-TiO2-Nb2O5 systems were synthesized and studied in the photocatalytic reforming of glucose for the generation of H2. The physicochemical properties of the synthesized photocatalysts were analyzed using different characterization techniques from which it was found that fluoridation and sulphation have different effects on the oxides under study such as a protective effect on the crystalline phase in anatase, and greater response in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The addition of fluorine or sulfates favors the reduction of platinum species on the surface of the semiconductor oxides and a better homogeneity of size and distribution of the particles of this metal. Studies were carried out in the gas phase that allowed the monitoring and quantification of the hydrogen produced from aqueous glucose solutions and it was determined that Pt-F-Nb2O5 and Pt-F-TiO2 are the most efficient materials for the production of hydrogen from this substrate. Similarly, liquid phase studies were carried out with a real sample from a confectionery industry where it was determined that with the material Pt-F-Nb2O5 the highest transformation of glucose is obtained, without the formation of any other sugar or intermediate compound, indicating the preferential production of hydrogen during the photocatalytic reaction. The foregoing demonstrates the potential of the evaluated process in obtaining this gas from the recovery of polluting residues derived from the samples under study.
May, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2024.130932
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Enhanced low-temperature CO2 methanation over La-promoted NiMgAl LDH derived catalyst: Fine-tuning La loading for an optimal performance
Wang, ZL; Zhang, TY; Reina, TR; Huang, L; Xie, WF; Musyoka, NM; Oboirien, B; Wang, QFuel, 366 (2024) 131383
Show abstract ▽
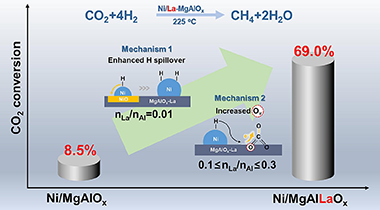
LDH-derived Ni-based catalysts are gathering momentum due to their excellent thermal stability but their lowtemperature CO2 methanation is limited. In this study, various concentrations of La were introduced into the LDH-derived Ni-based catalysts for CO2 methanation, and the underlying mechanisms were investigated. The optimal Ni/La-0.2-MgAlOx catalyst presented a CO(2)conversion level of 69.0 % at 225 C-degrees, which is over 7 times higher than that of conventional Ni/MgAlOx. The addition of small amounts of La could significantly enhance H spillover to promote the reduction of Ni species, but the oxygen vacancy concentration became the dominant factor causing changes in low -temperature activity as the La contents continue to increase. CO2 was found to be adsorbed at the oxygen vacancies in the form of bidentate carbonates, which are more reactive under an enhanced electron -rich environment. The research offers guidance to design effective and sustainable catalysts for low -temperature CO2 methanation.
June, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2024.131383
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Developing and understanding Leaching-Resistant cobalt nanoparticles via N/P incorporation for liquid phase hydroformylation
Galdeano-Ruano, C; Gutiérrez-Tarriño, S; Lopes, CW; Mazarío, J; Chinchilla, LE; Agostini, G; Calvino, JJ; Holgado, JP; Rodriguez-Castellón, E; Roldan, A; Oña-Burgos, PJournal of Catalysis, 431 (2024) 115374
Show abstract ▽
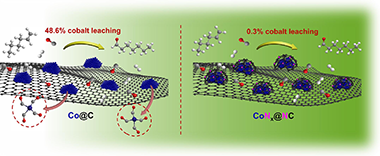
The ultimate target in heterogeneous catalysis is the achievement of robust, resilient and highly efficient materials capable of resisting industrial reaction conditions. Pursuing that goal in liquid -phase hydroformylation poses a unique challenge due to carbon monoxide -induced metal carbonyl species formation, which is directly related to the formation of active homogeneous catalysts by metal leaching. Herein, supported heteroatomincorporated (P and N) Co nanoparticles were developed to enhance the resistance compared with bare Co nanoparticles. The samples underwent characterization using operando XPS, XAS and HR electron microscopy. Overall, P- and N -doped catalysts increased reusability and suppressed leaching. Among the studied catalysts, the one with N as a dopant, CoNx@NC, presents excellent catalytic results for a Co -based catalyst, with a 94% conversion and a selectivity to aldehydes of 80% in only 7.5 h. Even under milder conditions, this catalyst outperformed existing benchmarks in Turnover Numbers (TON) and productivity. In addition, computational simulations provided atomistic insights, shedding light on the remarkable resistance of small Co clusters interacting with N -doped carbon patches.
March, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2024.115374
- ‹ anterior
- 3 of 412
- siguiente ›
icms











