Scientific Papers in SCI
2022
2022
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
CO2 methanation on Ni/YMn1-xAlxO3 perovskite catalysts
Safdar, M; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Penkova, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Arellano-Garcia, HApplied Materials Today, 29 (2022) 101577
Show abstract ▽
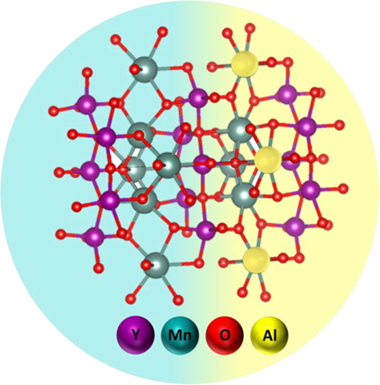
Seeking for advanced catalytic systems for the CO2 methanation reaction, the use of Ni supported catalysts over redox materials is often proposed. Profiting the superior redox properties described for layered perovskite systems, this work has investigated a series Ni supported YMn1-xAlxO3 (x = 0, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 1) perovskite catalysts. The obtained results evidenced the impact of the support nature on the systems redox properties and Ni-support interactions. Within the catalysts series, the greater methanation rates displayed by Ni/YMn0.5Al0.5O3 catalyst (0.748 mmol(CO2,conv.)s(-1) g(Ni)(-1) at 400 ? and 60 L/gh) were associated to the interplay between the support redox properties and superior Ni dispersion. The improved redox behavior attained through the Al-incorporation (up to x = 0.5) was associated to the layered perovskite structures which, being distorted and constituted by smaller crystal sizes, facilitated the behavior of Mn redox couples as surface species readily interconverted. Exhibiting catalytic performances comparable to precious metals based catalysts, this work proposes the Ni/YMn0.5Al0.5O3 catalyst as an effective system for the CO2 methanation reaction.
December, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apmt.2022.101577
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Assessment of pilot-plant scale solar photocatalytic hydrogen generation with multiple approaches: Valorization, water decontamination and disinfection
Ruiz-Aguirre, A; Villachica-Llamosas, JG; Polo-Lopez, MI; Cabrera-Reina, A; Colon, G; Peral, J; Malato, SEnergy, 260 (2022) e10272
Show abstract ▽
The main goal of the present study was to explore pilot-scale combination of H-2 generation with simultaneous water disinfection or decontamination. Performance of a TiO2-CuO mixture for solar-to-hydrogen (STH) con-version was studied, focusing on treatment optimization (catalyst dose, proportion of semiconductors in the mixture and concentration of the sacrificial agent). Experiments were performed in a 25-L compound parabolic collector (2 m(2)) solar pilot plant specifically designed for photocatalytic hydrogen generation. The best operating conditions were 100 mg L-1 TiO2-CuO (10:1) with 0.075 M glycerol as the sacrificial agent. The best STH conversion attained was 0.9%. 25 mg L-1 imidacloprid was completely degraded (over 99%). The synergetic effect of anoxic conditions, TiO2:CuO and solar radiation caused a significant reduction (> 5 Log) in concen-tration of E. coli, used as a model waterborne pathogen, in less than 10 min.
December, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.125199
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
High-Quality SiO2/O-Terminated Diamond Interface: Band-Gap, Band-Offset and Interfacial Chemistry
Canas, J; Reyes, DF; Zakhtser, A; Dussarrat, C; Teramoto, T; Gutierrez, M; Gheeraert, ENanomaterials, 12 (2022) 4125
Show abstract ▽
Silicon oxide atomic layer deposition synthesis development over the last few years has open the route to its use as a dielectric within diamond electronics. Its great band-gap makes it a promising material for the fabrication of diamond-metal-oxide field effects transistor gates. Having a sufficiently high barrier both for holes and electrons is mandatory to work in accumulation and inversion regimes without leakage currents, and no other oxide can fulfil this requisite due to the wide diamond band-gap. In this work, the heterojunction of atomic-layer-deposited silicon oxide and (100)-oriented p-type oxygen-terminated diamond is studied using scanning transmission electron microscopy in its energy loss spectroscopy mode and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The amorphous phase of silicon oxide was successfully synthesized with a homogeneous band-gap of 9.4 eV. The interface between the oxide and diamond consisted mainly of single- and double-carbon-oxygen bonds with a low density of interface states and a straddling band setting with a 2.0 eV valence band-offset and 1.9 eV conduction band-offset.
December, 2022 | DOI: 10.3390/nano12234125
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Nanoantennas Patterned by Colloidal Lithography for Enhanced Nanophosphor Light Emission
Viana, JM; Romero, M; Lozano, G; Míguez, HACS Applied Nano Materials, 5(11) (2022) 16242-16249
Show abstract ▽
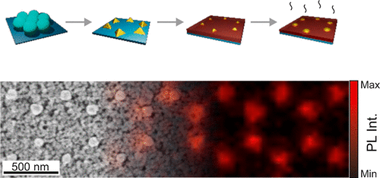
Transparent coatings made of rare-earth doped nanocrystals, also known as nanophosphors, feature efficient photoluminescence and excellent thermal and optical stabi l i t y . Herein, we demonstrate that the optical antennas prepared by colloidal lithography render thin nanophosphor films with a brighter emission. In particular, we fabricate gold nanostructures in the proximity of GdVO4:Eu3+ nanophosphors by metal evaporation using a mask made of a monolayer of polymer beads arranged in a triangular lattice. Optical modes supported by the antennas can be controlled by tuning the diameter of the polymer spheres in the colloidal mask, which determines the shape of the gold nanostructure, as confirmed by numerical simulations. Confocal microscopy reveals that metallic antennas induce brighter photoluminescence at specific spatial regions of the nanophosphor film at targeted frequencies as a result of the coupling between gold nanostructures and nanophosphors. Patterning of nanophosphor thin layers with arrays of metallic antennas offers an inexpensive nanophotonic solution to develop bright emitting coatings of interest for color conversion, labeling , or anti-counterfeiting.
November, 2022 | DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.2c03258
Reactividad de Sólidos
Reactive flash sintering of SrFe12O19 ceramic permanent magnets
Manchon-Gordon, AF; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Blazquez, JS; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 922 (2022) 166203
Show abstract ▽
Reactive flash-sintering technique has been used in order to obtain strontium ferrite magnets from a mixture of SrCO3 and Fe2O3 commercial powders. This technique allows preparing sintered SrFe12O19 at a furnace temperature of just 973 K during just 2 min by applying a modest field of 40 V cm(-1), instead of the conventional sintering process employed in ferrite magnet manufacturing that demands high temperature and long dwell times. Analysis of structural and magnetic properties were performed as a function of time in which the flash event was held. Mossbauer spectra show the existence of five different kinds of local environments, confirming the formation of strontium hexaferrite. The resulting samples exhibit comparable magnetic properties to the state-of-the-art ferrite magnets. In particular, produced samples reach a coercivity of 0.4 T and a specific saturation magnetization of 70 Am-2 kg(-1).
November, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166203
- ‹ previous
- 37 of 410
- next ›














