Scientific Papers in SCI
2023
2023
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting with ITO/WO3/BiVO4/CoPi Multishell Nanotubes Enabled by a Vacuum and Plasma Soft- Template Synthesis
Gil-Rostra, J; Castillo-Seoane, J; Guo, Q; Sobrido, ABJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Borras, AACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 15 (2023) 9250-9262
Show abstract ▽
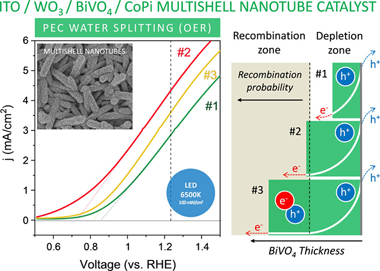
A common approach for the photoelectrochemical (PEC) splitting of water relies on the application of WO3 porous electrodes sensitized with BiVO4 acting as a visible photoanode semiconductor. In this work, we propose a new architecture of photoelectrodes consisting of supported multishell nanotubes (NTs) fabricated by a soft-template approach. These NTs are formed by a concentric layered structure of indium tin oxide (ITO), WO3, and BiVO4, together with a final thin layer of cobalt phosphate (CoPi) co-catalyst. The photoelectrode manufacturing procedure is easily implementable at a large scale and successively combines the thermal evaporation of single crystalline organic nanowires (ONWs), the magnetron sputtering deposition of ITO and WO3, and the solution dripping and electrochemical deposition of, respectively, BiVO4 and CoPi, plus the annealing in air under mild conditions. The obtained NT electrodes depict a large electrochemically active surface and outperform the efficiency of equivalent planar-layered electrodes by more than one order of magnitude. A thorough electrochemical analysis of the electrodes illuminated with blue and solar lights demonstrates that the characteristics of the WO3/BiVO4 Schottky barrier heterojunction control the NT electrode efficiency, which depended on the BiVO4 outer layer thickness and the incorporation of the CoPi electrocatalyst. These results support the high potential of the proposed soft-template methodology for the large-area fabrication of highly efficient multishell ITO/WO3/BiVO4/CoPi NT electrodes for the PEC splitting of water.
February, 2023 | DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c19868
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Determination of the optical constants of ligand-free organic lead halide perovskite quantum dots
Rubino, A; Lozano, G; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HNanoscale, 15 (2023) 2553-2560
Show abstract ▽
Precise knowledge of the optical constants of perovskite lead halide quantum dots (QDs) is required to both understand their interaction with light and to rationally design and optimize the devices based on them. However, their determination from colloidal nanocrystal suspensions, or films made out of them, remains elusive, as a result of the difficulty in disentangling the optical constants of the organic capping ligands and those of the semiconductor itself. In this work, we extract the refractive index and extinction coefficient of ligand-free methylammonium lead iodide (MAPbI(3)) and bromide (MAPbBr(3)) nanocrystals. In order to prevent the use of organic ligands in the preparation, we follow a scaffold assisted synthetic procedure, which yields a composite film of high optical quality that can be independently and precisely characterized and modelled. In this way, the contribution of the guest nanocrystals can be successfully discriminated from that of the host matrix. Using a Kramers-Kronig consistent dispersion model along with an effective medium approximation, it is possible to derive the optical constants of the QDs by fitting the spectral dependence of light transmitted and reflected at different angles and polarizations. Our results indicate a strong dependence of the optical constants on the QD size. Small nanocrystals show remarkably large values of the extinction coefficient compared to their bulk counterparts. This analysis opens the door to the rigorous modelling of solar cells and light-emitting diodes with active layers based on perovskite QDs.
February, 2023 | DOI: 10.1039/d2nr05109e
Materiales Avanzados
Effect of L-Glutamic Acid on the Composition and Morphology of Nanostructured Calcium Phosphate as Biomaterial
Takabait, F; Martinez-Martinez, S; Mahtout, L; Graba, Z; Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Perez-Villarejo, LMaterials, 16 (2023) 1262
Show abstract ▽
Calcium phosphate (CaP) with several chemical compositions and morphologies was prepared by precipitation using aqueous solutions of L-Glutamic acid (H(2)G) and calcium hydroxide, both mixed together with an aqueous solution (0.15 M) of phosphoric acid. Plate-shaped dicalcium phosphate dihydrate (brushite) particles were obtained and identified at a lower concentration of the solution of the reactants. The Ca/P ratio deduced by EDS was similar to 1, as expected. The nanoscale dimension of carbonate apatite and amorphous calcium phosphate, with variable Ca/P ratios, were revealed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis (SEM-EDS). They were characterized in medium and high concentrations of calcium hydroxide (0.15 M and 0.20 M). The equilibria involved in all the reactions in aqueous solution were determined. The thermodynamic calculations showed a decrease in the amount of chelate complexes with an increase in pH, being the opposite of [CaPO4-] and [CaHG(+)]. This fluctuation showed an evident influence on the morphology and polymorphism of CaP particles obtained under the present experimental conditions, with potential use as a biomaterial.
February, 2023 | DOI: 10.3390/ma16031262
Reactividad de Sólidos
Determination of the activation energy under isothermal conditions: revisited
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 148 (2023) 1679-1686
Show abstract ▽
The kinetic analysis of solid-state processes aims at obtaining fundamental information that can be used for predicting the time evolution of a process within a wide range of conditions. It is an extended belief that the determination of the kinetic parameters from the analysis of curves recorded under isothermal conditions is strongly conditioned by the kinetic model used to fit the experimental data. Thus, much effort is devoted to finding the model that truly describes a process in order to calculate the kinetic parameters with accuracy. In this work, we demonstrate that the value of activation energy determined from kinetic analysis of isothermal curves is independent of the kinetic model used to fit the experimental data and, taking advantage of the underlying reason for this, a method for determining the activation energy with two isothermal curves is proposed.
February, 2023 | DOI: 10.1007/s10973-022-11728-3
Materiales Coloidales
Carboxylate functionalized NaDy(MoO4)(2) nanoparticles with tunable size and shape as high magnetic field MRI contrast agents
Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Nuñez, NO; Caro, C; Garcia-Martin, ML; Ocaña, MJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 629 (2023) 310-321
Show abstract ▽
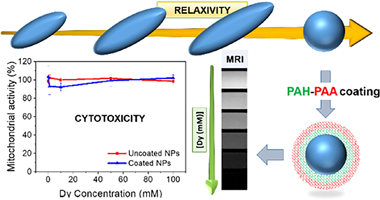
Uniform sodium-dysprosium double molybdate (NaDy(MoO4)(2)) nanoparticles having different morphologies (spheres and ellipsoids) and tunable size have been synthesized for the first time in literature. The procedure is based on a homogeneous precipitation process at moderated temperatures (<= 220 ?) from solutions containing appropriated precursors dissolved in ethylene glycol-water mixtures, in the absence (spheres) or the presence (ellipsoids) of tartrate anions. The effects of the morphological characteristics (size and shape) of the nanoparticles on the magnetic relaxivity at high field (9.4 T) have been evaluated finding that the latter magnitude was higher for the spheres than for the ellipsoids, indicating their better suitability as contrast agents for high-field magnetic resonance imaging. Such nanoparticles have been successfully coated with polymers bearing carboxylate functional groups through a layer-by -layer process, which improves the colloidal stability of the nanoparticles in physiological media. It has been also found that the coating layer had no significant effects on the nanoparticles relaxivity and that such coated nanoparticles exhibited a high biocompatibility and a high chemical stability. In summary, we have developed NaDy(MoO4)(2 )based bioprobes which meet the required criteria for their use as contrast agents for high-field magnetic resonance imaging.
January, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.08.130
- ‹ previous
- 31 of 410
- next ›














