Scientific Papers in SCI
2023
2023
Reactividad de Sólidos
Thermal arrest analysis of the reverse martensitic transformation in a Ni55Fe19Ga26 Heusler alloy obtained by melt-spinning
Vidal-Crespo, A; Manchon-Gordon, AF; Blazquez, JS; Ipus, JJ; Svec, P; Conde, CFJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, (2023)
Show abstract ▽
Ni55Fe19Ga26 ribbons obtained by melt-spinning technique exhibit a martensitic transformation from L2(1) cubic austenite phase to 14 M martensite phase above room temperature. We have taken advantage of the existence of thermal hysteresis of the martensitic phase transition (similar to 11 K) to analyze the effect of isothermal treatments on the reverse martensitic transformation, which has been analyzed by means of interrupted heating using differential scanning calorimetry. The experimental findings clearly indicate a time-depending effect in the martensitic transformation at temperatures between the austenite start and finish temperatures. Moreover, it has been observed that two successive martensitic transformations take place after the isothermal arrest was performed.
January, 2023 | DOI: 10.1007/s10973-022-11889-1
Reactividad de Sólidos
A novel, green, cost-effective and fluidizable SiO2-decorated calcium-based adsorbent recovered from eggshell waste for the CO2 capture process
Imani, M; Tahmasebpoor, M; Sanchez-Jim, P; Valverde, J; Garcia, VMSeparation and Purification Technology, 305 (2023) 122523
Show abstract ▽
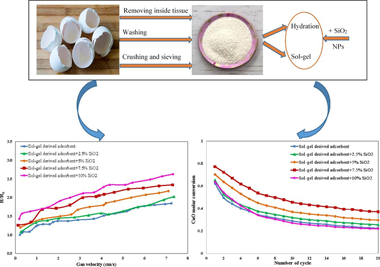
The reduction, storage, and reuse of greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) is a crucial concern in modern society. Bio-waste adsorbents have recently aroused the investigator's attention as auspicious materials for CO2 capture. However, the adsorption capacity decaying and poor fluidizability during carbonation/calcination cycles of all natural adsorbents used in the calcium-looping process (CaL) are important challenges. The current study ex-plores the performance of a novel SiO2-decorated calcium-based adsorbent recovered from eggshell waste in terms of both CO2 capture capacity and fluidity. Two preparation methods of hydration and sol-gel were used to obtain Ca-based adsorbents with different pore configurations and volumes. Modification of the adsorbents was applied by dry physically mixing with different weight percentages of hydrophobic SiO2 nanoparticles (NPs), in order to maintain stability and fluidity. The adsorbent prepared by the sol-gel method exhibited a fluffier structure with smaller grain sizes and higher porosity than that of prepared by the hydration method, leading to a 6.9 % increase in conversion at the end of the 20th cycle. Also, with the optimal amount of SiO2 nanoparticles, i. e. 7.5 wt%, the amount of CaO conversion obtained by sol-gel derived adsorbent was 27.59 % higher than that by pristine eggshell at the end of the 20th carbonation/calcination cycles. The fluidizability tests showed that the highest bed expansion ratio (2.29) was achieved for sol-gel derived adsorbent in the presence of 7.5 wt% silica nanoparticles which was considerably higher than the amount of 1.8 and 1.6 belonged to sol-gel derived adsorbent and pristine eggshell without silica at the gas velocity of approximate to 6.5 cm/s, respectively. The high adsorption capacity and proper fluidity of this novel and green calcium-based adsorbent promise its wide application.
January, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122523
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Engineering morphologies of yttrium oxide supported nickel catalysts for hydrogen production
Zhang, RB; Tu, ZA; Meng, S; Feng, G; Lu, ZH; Yu, YZ; Reina, TR; Hu, FY; Chen, XH; Ye, RPRare Metals, 42 (2023) 176-188
Show abstract ▽
The catalytic performance is highly related to the catalyst structure. Herein, a series of Ni nanoparticles supported on Y2O3 with different morphologies were successfully synthesized via hydrothermal process screening different pH environments. These Ni/Y2O3 catalysts were applied to efficiently produce COx-free H-2 through ammonia decomposition. We identify a significant impact of Y2O3 supports on nickel nanoclusters sizes and dispersion. The experimental results show that Ni/Y11 catalyst achieves 100% ammonia decomposition conversion under a gas hour space velocity (GHSV) of 12,000 ml.h(-1).g(cat)(-1) and temperature of 650 degrees C. Such a high level of activity over Ni/Y11 catalyst was attributed to a large specific surface area, appropriate alkalinity, and small Ni nanoparticles diameter with high dispersion.
January, 2023 | DOI: 10.1007/s12598-022-02136-5
Materiales Avanzados
Sintering behaviour of a clay containing pyrophyllite, sericite and kaolinite as ceramic raw materials: Looking for the optimum firing conditions
Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Garzon, E; Perez-Villarejo, L; Eliche-Quesada, DBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Ceramica y Vidrio, 62 (2023) 26-39
Show abstract ▽
The sintering behaviour of a pyrophyllite clay has been investigated. The mineralogical composition by X-ray diffraction (XRD) of this sample was -35 wt.% pyrophyllite, -25 wt.% sericite/illite, -15 wt.% kaolinite and -20 wt.% quartz. The chemical composition was consistent with these results, with a total flux content of 4.18 wt.%. Prismatic bars were prepared by dry pressing using this sample and fired in the range 800-1500 degrees C with 0.5-5 h of soaking times. Sintering diagrams were obtained using the results of linear firing shrinkage, water absorption capacity, bulk density and apparent porosity determined in the ceramic bodies as a function of firing temperatures. It was found a trend of slight variations of bulk density values firing in the range 1000-1150 degrees C, with marked decreases of these values for these bodies fired at 1200 degrees C and 1300 degrees C. The temperature of maximum bulk density was determined as -1200 degrees C and the vitrification temperature was -1300 degrees C where the apparent porosity becomes almost zero. The vitrification process of the pyrophyllite clay sample was investigated using a method previously described in the literature, which considered an Arrhenius approach under isothermal conditions and a first order kinetic. It was determined an activation energy (Ea) of -45 kJ/mol with a linear correlation coefficient of 0.998. The relative rates of vitrification were calculated. It was found that the contribution of vitrification due to the heating was relatively small compared to the vitrification during soaking. Mullite and quartz are forming the ceramic bodies besides a vitreous or glassy phase. The thermally treated pyrophyllite clay showed a dense network of rod-shaped and elongated needle-like crystals, being characteristic features of mullite as a dense felt. The vitrification rate equation, as deduced in this study by first time, can be a useful tool to estimate the optimum firing conditions of the pyrophyllite clays applied as ceramic raw materials.
January, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.bsecv.2021.09.001
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Is the RWGS a viable route for CO2 conversion to added value products? A techno-economic study to understand the optimal RWGS conditions
Portillo, E; Gandara-Loe, J; Reina, TR; Pastor-Perez, LScience of the Total Environment, 857 (2023) 159394
Show abstract ▽
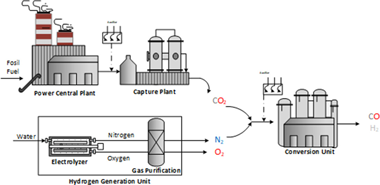
Understanding the viability of the RWGS from a thermodynamic and techno-economic angle opens new horizons within CO2 conversion technologies. Unfortunately, profitability studies of this technology are scarce in literature and mainly focused on overall conversion and selectivity trends with tangential remarks on energy demands and pro-cess costs. To address this research gap, herein we present a comprehensive techno-economic study of the RWGS reac-tion when coupling with Fischer-Tropsch synthesis is envisaged to produced fuels and chemicals using CO2 as building block. We showcase a remarkable impact of operating conditions in the final syngas product and both CAPEX and OPEX. From a capital investment perspective, optimal situations involve RWGS unit running at low temperatures and high pressures as evidenced by our results. However, from the running cost angle, operating at 4 bar is the most favorable alternative within the studied scenarios. Our findings showcase that, no matter the selected temperature the RWGS unit should be preferentially run at intermediate pressures. Ultimately, our work maps out multiple operat-ing scenarios in terms of energy demand and process cost serving as guideline to set optimal reaction conditions to un-lock the potential of the RWGS for chemical CO2 recycling.
January, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159394
- ‹ previous
- 32 of 410
- next ›














