Scientific Papers in SCI
2023
2023
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Microstructural Characterization and Self-Propagation Properties of Reactive Al/Ni Multilayers Deposited onto Wavelike Surface Morphologies: Influence on the Propagation Front Velocity
Camposano, YHS; Bartsch, H; Matthes, S; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Jaekel, K; Schaaf, PPhysica Status Solidi A-Applications and Materials Science (2023) 2200765
Show abstract ▽
Reactive multilayer systems are nanostructures of great interest for various technological applications because of their high energy release rate during the self-propagating reaction of their components. Therefore, many efforts are aimed at controlling the propagation velocity of these reactions. Herein, reactive multilayer systems of Al/Ni in the shape of free-standing foils with a wavelike surface morphology prepared by using sacrificial substrates with well-aligned waves are presented and the propagation of the reaction along different directions of the reproduced waves is analyzed. During the ignition test, the propagation front is recorded with a high-speed camera, and the maximum temperature is measured using a pyrometer. The propagation of the reaction is favored in the direction of the waves, which points out the influence of the anisotropy generated by this morphology and how it affects the propagation dynamics and the resulting microstructure. Furthermore, compared to their counterparts fabricated on flat substrates, these reactive multilayers with wavelike morphology exhibit a remarkable reduction in the propagation velocity of the reaction of about 50%, without significantly affecting the maximum temperature registered during the reaction.
March, 2023 | DOI: 10.1002/pssa.202200765
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Incorporation of a Metal Catalyst for the Ammonia Synthesis in a Ferroelectric Packed-Bed Plasma Reactor: Does It Really Matter?
Navascues, P; Garrido-Garcia, J; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Gomez-Ramirez, AACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 11 (2023) 3621-3632
Show abstract ▽
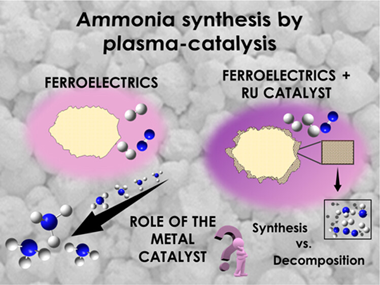
Plasma-catalysis has been proposed as a potential alternative for the synthesis of ammonia. Studies in this area focus on the reaction mechanisms and the apparent synergy existing between processes occurring in the plasma phase and on the surface of the catalytic material. In the present study, we approach this problem using a parallel-plate packed-bed reactor with the gap between the electrodes filled with pellets of lead zirconate titanate (PZT), with this ferroelectric material modified with a coating layer of alumina (i.e., Al2O3/PZT) and the same alumina layer incorporating ruthenium nanoparticles (i.e., Ru-Al2O3/PZT). At ambient temperature, the electrical behavior of the ferroelectric packed-bed reactor differed for these three types of barriers, with the plasma current reaching a maximum when using Ru-Al2O3/PZT pellets. A systematic analysis of the reaction yield and energy efficiency for the ammonia synthesis reaction, at ambient temperature and at 190 °C and various electrical operating conditions, has demonstrated that the yield and the energy efficiency for the ammonia synthesis do not significantly improve when including ruthenium particles, even at temperatures at which an incipient catalytic activity could be inferred. Besides disregarding a net plasma-catalysis effect, reaction results highlight the positive role of the ferroelectric PZT as moderator of the discharge, that of Ru particles as plasma hot points, and that of the Al2O3 coating as a plasma cooling dielectric layer.
February, 2023 | DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c05877
Reactividad de Sólidos
Flexible Kinetic Model Determination of Reactions in Materials under Isothermal Conditions
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Perejón, A; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; Pérez-Maqueda, LAMaterials, 16 (2023) 1851
Show abstract ▽
Kinetic analysis remains a powerful tool for studying a large variety of reactions, which lies at the core of material science and industry. It aims at obtaining the kinetic parameters and model that best describe a given process and using that information to make reliable predictions in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, kinetic analysis often relies on mathematical models derived assuming ideal conditions that are not necessarily met in real processes. The existence of nonideal conditions causes large modifications to the functional form of kinetic models. Therefore, in many cases, experimental data hardly obey any of these ideal models. In this work, we present a novel method for the analysis of integral data obtained under isothermal conditions without any type of assumption about the kinetic model. The method is valid both for processes that follow and for those that do not follow ideal kinetic models. It consists of using a general kinetic equation to find the functional form of the kinetic model via numerical integration and optimization. The procedure has been tested both with simulated data affected by nonuniform particle size and experimental data corresponding to the pyrolysis of ethylene-propylene-diene.
February, 2023 | DOI: 10.3390/ma16051851
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Flexible NiRu Systems for CO2 Methanation: From Efficient Catalysts to Advanced Dual-Function Materials
Merkouri, LP; Martin-Espejo, JL; Bobadilla, LF; Odriozola, JA; Duyar, MS; Reina, TRNanomaterials, 13 (2023) 506
Show abstract ▽
CO2 emissions in the atmosphere have been increasing rapidly in recent years, causing global warming. CO2 methanation reaction is deemed to be a way to combat these emissions by converting CO2 into synthetic natural gas, i.e., CH4. NiRu/CeAl and NiRu/CeZr both demonstrated favourable activity for CO2 methanation, with NiRu/CeAl approaching equilibrium conversion at 350 degrees C with 100% CH4 selectivity. Its stability under high space velocity (400 L center dot g(-1)center dot h(-1)) was also commendable. By adding an adsorbent, potassium, the CO2 adsorption capability of NiRu/CeAl was boosted, allowing it to function as a dual-function material (DFM) for integrated CO2 capture and utilisation, producing 0.264 mol of CH4/kg of sample from captured CO2. Furthermore, time-resolved operando DRIFTS-MS measurements were performed to gain insights into the process mechanism. The obtained results demonstrate that CO2 was captured on basic sites and was also dissociated on metallic sites in such a way that during the reduction step, methane was produced by two different pathways. This study reveals that by adding an adsorbent to the formulation of an effective NiRu methanation catalyst, advanced dual-function materials can be designed.
February, 2023 | DOI: 10.3390/nano13030506
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Improved stability of design clay minerals at high temperature: A comparison study with natural ones
Osuna, FJ; Chaparro, JR; Pavon, E; Alba, MDCeramics International, 49 (2023) 5279-5291
Show abstract ▽
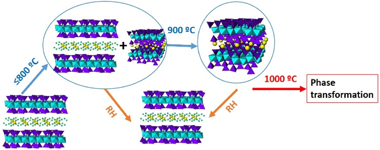
Clay minerals are ceramics materials that are involved in a wide range of economic uses. But, their structure and composition are modified by heating and, consequently, compromise their final applications. The actual tem-peratures at which changes occur vary greatly from one group to another group and even for different specimens within a given group. The aim of this research has been to evaluate the thermal behaviour of a set of design swelling micas, Na-Mica -n (Mn) and compare them with a set of natural smectites. All samples were heated in the range 200 degrees C to 1000 degrees C; afterwards, they were rehydrated thorough water suspension (0.4% wt). The results have shown that swelling micas have better property of hydration/dehydration than natural clay minerals and those with higher layer charge exhibited higher rehydration ability and dehydration temperature.
February, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.10.046
- ‹ previous
- 30 of 412
- next ›














