Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of the Test Configuration and Temperature on the Mechanical Behaviour of WC-Co
Gonzalez, LM; Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJ; Bermejo, R; Llanes, L; Torres, YMetals, 10 (2020) 322
Show abstract ▽

In this work, the effect of the test configuration and temperature on the mechanical behaviour of cemented carbides (WC-Co) with different carbide grain sizes (d(WC)) and cobalt volume fractions (V-Co), implying different binder mean free paths (lambda (Co)), was studied. The mechanical strength was measured at 600 degrees C with bar-shaped specimens subjected to uniaxial four-point bending (4PB) tests and with disc specimens subjected to biaxial ball-on-three-balls (B3B) tests. The results were analysed within the frame of the Weibull theory and compared with strength measurements performed at room temperature under the same loading conditions. A mechanical degradation greater than 30% was observed when the samples were tested at 600 degrees C due to oxidation phenomena, but higher Weibull moduli were obtained as a result of narrower defect size distributions. A fractographic analysis was conducted with broken specimens from each test configuration. The number of fragments (N-f) and the macroscopic fracture surface were related to the flexural strength and fracture toughness of WC-Co. For a given number of fragments, higher mechanical strength values were always obtained for WC-Co grades with higher K-Ic. The observed differences were discussed based on a linear elastic fracture mechanics (LEFM) model, taking into account the effect of the temperature and microstructure of the cemented carbides on the mechanical strength.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/met10030322
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction as effective photocatalyst for the degradation of diclofenac and ketoprofen
Sacco, O.l; Murcia, J.J.; Lara, A.E.; Hernández-Laverde, M.; Rojas, H.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Vaiano, V.Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 107 (2020) 104839
Show abstract ▽
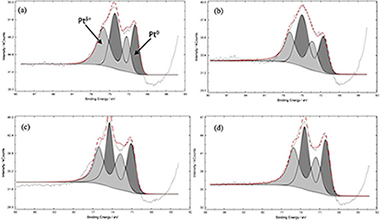
Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction was synthetized and studied for the photocatalytic removal of diclofenac (DCF) and ketoprofen (KTF) under UV light irradiation. The physical-chemical properties of the prepared catalysts were analysed by different characterization techniques revealing that the lowest platinum nanoparticle size and the better metal distribution was observed in Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 sample. The Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction possessed the best photocatalytic activity toward both the photodegradation and mineralization of the two selected pollutants. The optimal photocatalyst showed a DCF and KTF mineralization rate of 0.0555 and 0.0746 min−1, respectively, which were higher than those of Pt–TiO2 (0.0321 min−1 for DCF and 0.0597 min−1 for KTF). The experiments driven to analyse the effects of free radical capture showed that ·OH, ·O2− and h+ have a primary role in reactive during the photocatalytic reaction. The improved photocatalytic performances of the Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction could be argue by a direct Z-scheme mechanism in which the Pt0 nanoparticles could act as a bridge between TiO2 and Nb2O5, improving the electron-hole separation and, ultimately, enhancing the photocatalytic removal rate of both DCF and KTF.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104839
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Hybrid ZnO/Ag3PO4 photocatalysts, with low and high phosphate molar percentages
Martín-Gómez, A.N.;Navío, J.A.;Jaramillo-Páeza, C.;Sánchez-Cid, P.;Hidalgo, M.C.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, (2020) 112196
Show abstract ▽
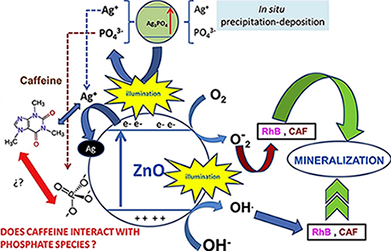
In this work, a previously optimized synthesized ZnO photocatalyst was modified with different molar percentages of Ag3PO4 through a facile in situ precipitation–deposition method and then characterized by different techniques (XRD, XRF, BET, UV–vis DRS, SEM, TEM and XPS). The incorporation of Ag3PO4 produces important changes in the light absorption properties with a significant absorbance in the visible region observed for ZnO modified with different amounts of Ag3PO4; the optical absorption intensity in the visible region of the coupled ZnO/Ag3PO4 increases as the molar percentages of Ag3PO4 increases, evidencing a clear dependence on the content of Ag3PO4. However, this work shows that the incorporation of Ag3PO4 in almost all cases reduces the photocatalytic capacity of ZnO, except when it is used in a specific percentage of 10 % and only being more active against rhodamine B and not on the Caffeine. SEM images and elemental mapping indicate that Ag3PO4 disperses very well in the ZnO particles, exhibiting an almost homogeneous distribution, showing zones with cumulus of Ag3PO4 (rich in P-Ag) in contact with ZnO-zones (rich in Zn). All the prepared photocatalysts were tested in the photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B as a dye, and caffeine as a toxic and persistent emerging compound under UV and visible light illumination. It is reported that not only the ZnO:Ag3PO4 ratio is an important factor that influences the photocatalytic process of substrate degradation, but also the nature of the substrate has an important influence on the photocatalytic behavior of the materials under both UV and visible illumination. Thus, pristine Ag3PO4 showed high photocatalytic degradation for rhodamine B, while for caffeine negligible photocatalytic degradation was found in both the UV and visible regions. The thermal- and photo-stability of the coupled system was also studied. At least, for rhodamine B no loss of photocatalytic activity has been observed after five recycles although the mineralization degree progressively diminished along the recycles.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112196
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Modulation of the acidity of a vermiculite and its potential use as a catalytic support
Amaya, J; Bobadilla, L; Azancot, L; Centeno, M; Moreno, S; Molina, RJournal of Materials Science, 55 (2020) 6482-6501
Show abstract ▽
The modulation and characterization of the acidity of a vermiculite were carried out, which was modified by delamination by means of hydrothermal and acid treatments with the subsequent incorporation of AlZr and AlCe species to modulate the acidity. The effect of these species was evaluated regarding the structural (XRD, XPS and IR), textural (N-2 sortometry) and acidity properties (NH3-TPD, NH3-DRIFTS and CO adsorption at low temperature). The catalytic performance was studied in the dehydration-dehydrogenation reactions of 2-propanol and the hydroconversion of decane, which generate important information about the acidity properties such as the type, number and strength of acidic sites. The correlation between the number, type and acid strength with the catalytic behavior allowed to establish the important effect regarding the nature of the mineral, its method of delamination and the nature of the incorporated cation, thus generating tools for controlled processes for the potentiation of the acidity of new supports from raw vermiculite.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1007/s10853-020-04445-5
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Robust label-free CuxCoyOz electrochemical sensors for hexose detection during fermentation process monitoring
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez, R; Yubero, F; de Lucas-Consuegra, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSensors and Actuators B-Chemical, 304 (2020) 127360
Show abstract ▽

Label free electrochemical sensors of glucose are used whenever long-term operation and stable response are required. For this purpose, various metals and oxides of the first transition series have been proposed as alternative to more expensive noble metal electrochemical sensors. In this work we propose a new formulation consisting of copper-cobalt mixed oxides which, in the form of porous and nanostructured thin films with well controlled Co/Cu ratio, are prepared at room temperature in one step by a modification of the magnetron sputtering oblique angle deposition procedure. Films with various compositions were electrochemically characterized by cyclic voltammetry to determine their amperometric response to glucose as a function of voltage and NaOH electrolyte concentration. This analysis showed that films with a Co/Cu atomic ratio equal 3.4 presented a maximum sensitivity (0.710 A M−1 cm−2), a small limit of detection (0.105 μM) and a resilient behaviour upon cycling operation and long storage periods that clearly overpassed the performance of copper and cobalt single oxides. The CuxCoyO electrocatalysts also presented a good selectivity towards glucose and fructose in the presence of common interference compounds found in biological fluids (e.g., ascorbic acid, acetaminophen and uric acid), sucrose and ethanol, this latter present in many agrofood liquids. The possibilities of this sensor electrocatalyst have been tested for the analysis of a wine synthetic fermentation process. The comparison of the electrochemical results with conventional analytical methods showed a lineal amperometric response with respect hexose contents in a must at different stages of its transformation into wine.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.127360
- ‹ previous
- 105 of 410
- next ›














