Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Role of Fe(III) in aqueous solution or deposited on ZnO surface in the photoassisted degradation of rhodamine B and caffeine
Tanji, Karim; Navio, J A; Martin-Gomez, A N; Hidalgo, M C; Jaramillo-Paez, C; Naja, Jamal; Hassoune, Hicham; Kherbeche, AbdelhakChemosphere, 241 (2020) 125009
Show abstract ▽
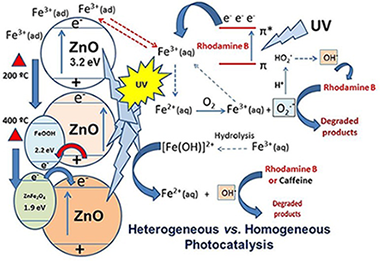
Iron (III) was incorporated, to the surface of a synthesized ZnO, using two nominal molar percentages of Fe (III): 1% and 5% Fe relative to ZnO. Samples dried and calcined at 200 °C and 400 °C for 2 h, were characterized by XRD, XPS, XRF, N2-adsorption-BET and (UV–vis)-DRS. Photocatalytic activities of the catalysts were assessed based on the degradation of rhodamine B (RhB) and caffeine (CAF) in aqueous solution under two irradiation conditions: UV and visible light illumination. Prior to the photocatalytic tests, the interaction of each one of the substrates with either Fe(III) or Fe(II) was studied in homogeneous medium under UV-illumination and oxygenated environment. It was found that Fe (III) can play an important role in homogeneous media in the photoassisted degradation, both of rhodamine B and caffeine, while Fe (II) does not exert a relevant role in the photoassisted degradation of the referred substrates. Fe–ZnO samples display similar or poorer performance than pure ZnO in the presence of UV light for both studied substrates. The phenomenon can be attributed to the formation of either goethite or ZnFe2O4 at the ZnO surface where the coupled Fe3+/Fe2+ can act as recombination centers for the photogenerated charges. On the contrary, all Fe–ZnO samples showed enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible illumination which seems to be independent of the iron content. In this context, the mechanisms for photoassisted degradation of both the substrates in homogeneous medium and photocatalytic degradation are discussed, as well as the role of Fe in the photodegradation processes.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125009
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Monolithic stirrer reactor: The selective lactose oxidation in liquid phase over Au/Al2O3 nanostructured catalysts
Regenhardt, SA; Meyer, CI; Sanz, O; Sebastian, V; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Montes, M; Marchi, AJ; Garetto, TFMolecular Catalysis, 481 (2020) 110219
Show abstract ▽
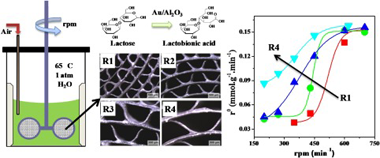
The performance of rotating metallic monolith stirrer reactor was studied for selective lactose oxidation in liquid phase at 65 degrees C, atmospheric pressure and with air as oxidant agent. The Au/Al(2)O(3)deposition on metallic substrates was performed by wash-coating, producing catalyst coating thicknesses between 5 and 20 mu m. Monoliths with different configuration (channel size between 0.36 and 1.06 mm) were used as stirrer blades in a batch reactor. Internal and external mass transfer limitations were observed during liquid phase lactose oxidation. For stirring rates equal or higher than 600 rpm there were no important external diffusional restrictions and this was also independent of the monolith configuration. Coating with thickness higher than 15 mu m presents loss of catalyst effectiveness due to internal diffusional restrictions. Excellent stability in the catalytic tests was obtained after three regeneration-reaction cycles. Regeneration was carried out at 400 degrees C in air flow. Gold particle size distribution in the monolith washcoat, determined by TEM before and after reaction, was homogeneous with a medium size of around 5 nm. This is in agreement with the very good reproducibility and stability obtained in the catalytic tests. After calcination at 500 degrees C, some sintering and a heterogeneous distribution of metal particle size was observed, accompanied by a slight loss in catalyst activity. It is concluded that metallic monolith stirrer reactors are a promising application for selective lactose oxidation in liquid phase.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.10.014
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis of Mn2+-doped ZnS by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Aviles, MA; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, FJJournal of Materials Science, 55 (2020) 1603-1613
Show abstract ▽
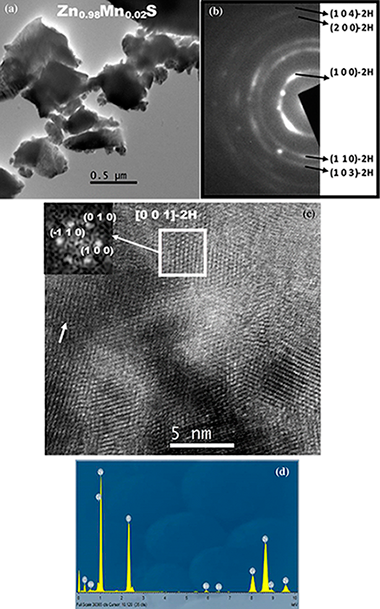
The mechanochemical process denoted as a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction was successfully applied in obtaining Mn-doped ZnS samples with Mn content between 0 and 5 mol%. The process consists in milling Zn/Mn/S powder elemental mixtures with the appropriate stoichiometry, which promotes after approximately 80 min the induction of a combustion reaction. The doping level was properly adjusted by controlling the atomic ratio of the starting mixture. A complete characterization of samples was carried out, including X-ray diffraction, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, selected area electron diffraction, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, diffuse reflectance UV-Vis spectroscopy and emission and excitation photoluminescence measurements. A wurtzite structure, in which Mn2+ replaces Zn2+, was obtained with a nanometric character. The photoluminescence of samples showed the characteristic (Mn2+T1)-T-4-(6)A(1) emission that was highly dependent on the doping level. The maximum luminescence efficiency through the ZnS excitation was found for a doping value of 1 mol%. The photoluminescence showed virtually no contribution from the host emission, which confirmed that samples were properly doped.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1007/s10853-019-04138-8
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Catalytic Performance of Bulk and Al2O3-Supported Molybdenum Oxide for the Production of Biodiesel from Oil with High Free Fatty Acids Content
Navajas, A; Reyero, I; Jimenez-Barrera, E; Romero-Sarria, F; Llorca, J; Gandia, LMCatalysts, 10 (2020) 158
Show abstract ▽
Non-edible vegetable oils are characterized by high contents of free fatty acids (FFAs) that prevent from using the conventional basic catalysts for the production of biodiesel. In this work, solid acid catalysts are used for the simultaneous esterification and transesterification with methanol of the FFAs and triglycerides contained in sunflower oil acidified with oleic acid. Molybdenum oxide (MoO3), which has been seldom considered as a catalyst for the production of biodiesel, was used in bulk and alumina-supported forms. Results showed that bulk MoO3 is very active for both transesterification and esterification reactions, but it suffered from severe molybdenum leaching in the reaction medium. When supported on Al2O3, the MoO3 performance improved in terms of active phase utilization and stability though molybdenum leaching remained significant. The improvement of catalytic performance was ascribed to the establishment of MoO3-Al2O3 interactions that favored the anchorage of molybdenum to the support and the formation of new strong acidic centers, although this effect was offset by a decrease of specific surface area. It is concluded that the development of stable catalysts based on MoO3 offers an attractive route for the valorization of oils with high FFAs content.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/catal10020158
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Mesoporous Matrices as Hosts for Metal Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals
Rubino, A; Calio, L; Garcia-Bennett, A; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, (2020) 201901868
Show abstract ▽
Several works have recently demonstrated that perovskite nanocrystals can be controllably formed within a variety of porous matrices employing diverse synthetic strategies. By means of the fine tuning of the pore size distribution, the thickness and composition of the walls, the geometry of the void network and its topology, strict control over the structural and morphological parameters of the hosted semiconductor can be achieved, determining its optical absorption and emission properties. Furthermore, porous hosts provide the guest semiconductor with enhanced stability and versatility in terms of processing, which favors its integration in devices. This article provides a comprehensive review of the different approaches proposed, as well as a discussion on the relevance they may have for the development of nanostructured perovskite-based optoelectronics. A critical assessment of the optical quality of the hybrid perovskite nanomaterials so obtained is presented, as well as an analysis of the fundamental and applied aspects of the nanocrystal-matrix interaction and a projected prospect of their impact in the fields of artificial lighting and renewable energy.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.201901868
- ‹ previous
- 106 of 410
- next ›














