Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optofluidic liquid sensing on electromicrofluidic devices
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Wang, SL; Rico-Gavira, V; Lopez-Santos, C; Fan, SK; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARMaterials Research Express, 7 (2020) 036407
Show abstract ▽
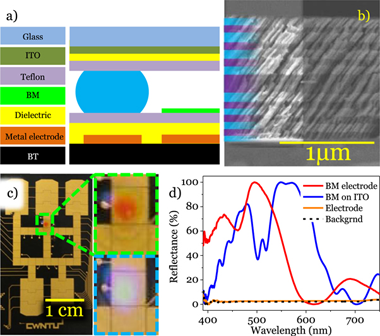
Electromicrofluidic (EMF) devices are used to handle and move tiny amounts of liquids by electrical actuation, including electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD) and dielectrophoresis (DEP). Monitoring the liquid characteristics in one of these devices requires suitable sensing transducers incorporated within the microfluidic structure. In the present work, we describe the incorporation of an optofluidic photonic transducer in an EMF device to monitor the refractive index of a liquid during its manipulation. The incorporated transducer consists of a responsive porous Bragg Microcavity (BM) deposited via physical vapor oblique angle deposition. Besides reporting the manufacturing procedure of the sensing-EMF device combining liquid handling and monitoring, the performance of the BM is verified by infiltrating several liquids dripped on its surface and comparing the responses with those of liquid droplets electrically moved from the delivery part of the chip to the BM location. This study proved that modified EMF devices can incorporate photonic structures to analyze very low liquid volumes (similar to 0.2 mu L) during its handling.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab7fdf
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction as effective photocatalyst for the degradation of diclofenac and ketoprofen
Sacco, O.l; Murcia, J.J.; Lara, A.E.; Hernández-Laverde, M.; Rojas, H.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Vaiano, V.Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 107 (2020) 104839
Show abstract ▽
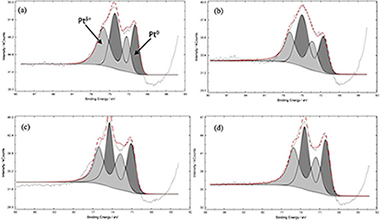
Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction was synthetized and studied for the photocatalytic removal of diclofenac (DCF) and ketoprofen (KTF) under UV light irradiation. The physical-chemical properties of the prepared catalysts were analysed by different characterization techniques revealing that the lowest platinum nanoparticle size and the better metal distribution was observed in Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 sample. The Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction possessed the best photocatalytic activity toward both the photodegradation and mineralization of the two selected pollutants. The optimal photocatalyst showed a DCF and KTF mineralization rate of 0.0555 and 0.0746 min−1, respectively, which were higher than those of Pt–TiO2 (0.0321 min−1 for DCF and 0.0597 min−1 for KTF). The experiments driven to analyse the effects of free radical capture showed that ·OH, ·O2− and h+ have a primary role in reactive during the photocatalytic reaction. The improved photocatalytic performances of the Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction could be argue by a direct Z-scheme mechanism in which the Pt0 nanoparticles could act as a bridge between TiO2 and Nb2O5, improving the electron-hole separation and, ultimately, enhancing the photocatalytic removal rate of both DCF and KTF.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104839
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Optical Responses of Localized and Extended Modes in a Mesoporous Layer on Plasmonic Array to Isopropanol Vapor
Murai, S; Cabello-Olmo, E; Kamakura, R; Calvo, ME; Lozano, G; Atsumi, T; Miguez, H; Tanaka, KJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2020) 5772-5779
Show abstract ▽
Mesoporous silica features open and accessible pores that can intake substances from the outside. The combination of mesoporous silica with plasmonic nanostructures represents an interesting platform for an optical sensor based on the dependence of plasmonic modes on the refractive index of the medium in which metallic nanoparticles are embedded. However, so far only a limited number of plasmonic nanostructures are combined with mesoporous silica, including random dispersion of metallic nanoparticles and flat metallic thin films. In this study, we make a mesoporous silica layer on an aluminum nanocylinder array. Such plasmonic arrangements support both localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPRs) and extended modes which are the result of the hybridization of LSPRs and photonic modes extending into the mesoporous layer. We investigate in situ optical reflectance of this system under controlled pressure of isopropanol vapor. Upon exposure, the capillary condensation in the mesopores results in a gradual spectral shift of the reflectance. Our analysis demonstrates that such shifts depend largely on the nature of the modes; that is, the extended modes show larger shifts compared to localized ones. Our materials represent a useful platform for the field of environmental sensing.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b10999
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
An insight on the design of mercapto functionalized swelling brittle micas
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 561 (2020) 533-541
Show abstract ▽
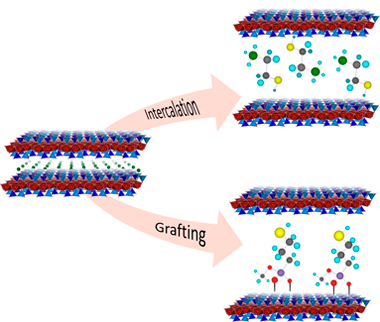
Surface modification of natural clay minerals with reagents containing metal chelating groups has great environmental value. The functionalization by adsorption or grafting guarantees a durable immobilization of the reactive organic groups, preventing their leaching when they are used in liquid media. The aim of this research was the designed mercapto functionalization of swelling brittle micas, Na-Mn, thorough both chemical and physical mechanisms. Na-Mn were functionalized with 2-mercaptoethylammonium (MEA), 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanol (BAL) and (3-mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane (MPTMS). The thiol concentration on swelling brittle micas is higher than the observed value for others adsorbents. The cation exchange reaction with MEA and one-step grafting with MPTMS in acid medium are the most efficient mercapto functionalization mechanism.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.028
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Optical interference effects on the Casimir-Lifshitz force in multilayer structures
Esteso, V; Carretero-Palacios, S; Miguez, HPhysical Review A, 101 (2020) 033815
Show abstract ▽
The Casimir-Lifshitz force F(C-L) between planar objects when one of them is stratified at the nanoscale is herein investigated. Layering results in optical interference effects that give rise to a modification of the optical losses, which, as stated by the fluctuation-dissipation theorem, should affect the Casimir-Lifshitz interaction. On these grounds, we demonstrate that, by nanostructuring the same volume of dielectric materials in diverse multilayer configurations, it is possible to access F(C-L) of attractive or repulsive nature, even getting canceled, at specific separation distances.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.101.033815
- ‹ previous
- 104 of 410
- next ›














