Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction as effective photocatalyst for the degradation of diclofenac and ketoprofen
Sacco, O.l; Murcia, J.J.; Lara, A.E.; Hernández-Laverde, M.; Rojas, H.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Vaiano, V.Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 107 (2020) 104839
Show abstract ▽
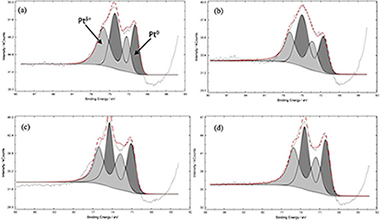
Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction was synthetized and studied for the photocatalytic removal of diclofenac (DCF) and ketoprofen (KTF) under UV light irradiation. The physical-chemical properties of the prepared catalysts were analysed by different characterization techniques revealing that the lowest platinum nanoparticle size and the better metal distribution was observed in Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 sample. The Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction possessed the best photocatalytic activity toward both the photodegradation and mineralization of the two selected pollutants. The optimal photocatalyst showed a DCF and KTF mineralization rate of 0.0555 and 0.0746 min−1, respectively, which were higher than those of Pt–TiO2 (0.0321 min−1 for DCF and 0.0597 min−1 for KTF). The experiments driven to analyse the effects of free radical capture showed that ·OH, ·O2− and h+ have a primary role in reactive during the photocatalytic reaction. The improved photocatalytic performances of the Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction could be argue by a direct Z-scheme mechanism in which the Pt0 nanoparticles could act as a bridge between TiO2 and Nb2O5, improving the electron-hole separation and, ultimately, enhancing the photocatalytic removal rate of both DCF and KTF.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104839
Reactividad de Sólidos
Role of particle size on the multicycle calcium looping activity of limestone for thermochemical energy storage
Duran-Martin, JD; Jimenez, PES; Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; Arcenegui-Troya, J; Trinanes, PG; Maqueda, LAPJournal of Advanced Research, 22 (2020) 67-76
Show abstract ▽
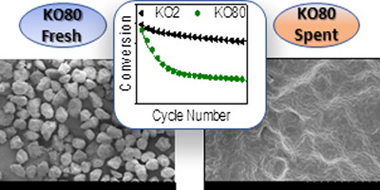
The calcium looping process, based on the reversible reaction between CaCO3 and CaO, is recently attracting a great deal of interest as a promising thermochemical energy storage system to be integrated in Concentrated Solar Power plants (CaL-CSP). The main drawbacks of the system are the incomplete conversion of CaO and its sintering-induced deactivation. In this work, the influence of particle size in these deactivation mechanisms has been assessed by performing experimental multicycle tests using standard limestone particles of well-defined and narrow particle size distributions. The results indicate that CaO multicycle conversion benefits from the use of small particles mainly when the calcination is carried out in helium at low temperature. Yet, the enhancement is only significant for particles below 15 μm. On the other hand, the strong sintering induced by calcining in CO2 at high temperatures makes particle size much less relevant for the multicycle performance. Finally, SEM imaging reveals that the mechanism responsible for the loss of activity is mainly pore-plugging when calcination is performed in helium, whereas extensive loss of surface area due to sintering is responsible for the deactivation when calcination is carried out in CO2 at high temperature.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2019.10.008
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
An insight on the design of mercapto functionalized swelling brittle micas
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 561 (2020) 533-541
Show abstract ▽
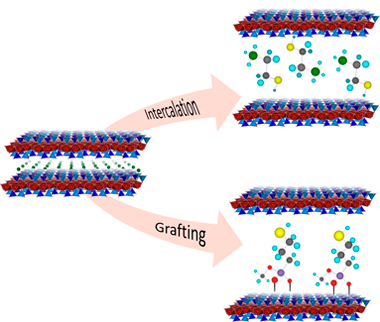
Surface modification of natural clay minerals with reagents containing metal chelating groups has great environmental value. The functionalization by adsorption or grafting guarantees a durable immobilization of the reactive organic groups, preventing their leaching when they are used in liquid media. The aim of this research was the designed mercapto functionalization of swelling brittle micas, Na-Mn, thorough both chemical and physical mechanisms. Na-Mn were functionalized with 2-mercaptoethylammonium (MEA), 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanol (BAL) and (3-mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane (MPTMS). The thiol concentration on swelling brittle micas is higher than the observed value for others adsorbents. The cation exchange reaction with MEA and one-step grafting with MPTMS in acid medium are the most efficient mercapto functionalization mechanism.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.028
Reactividad de Sólidos
Development by Mechanochemistry of La0.8Sr0.2Ga0.8Mg0.2O2.8 Electrolyte for SOFCs
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Tang, YQ; Gotor, FJ; Sayagues, MJMaterials, 13 (2020)
Show abstract ▽
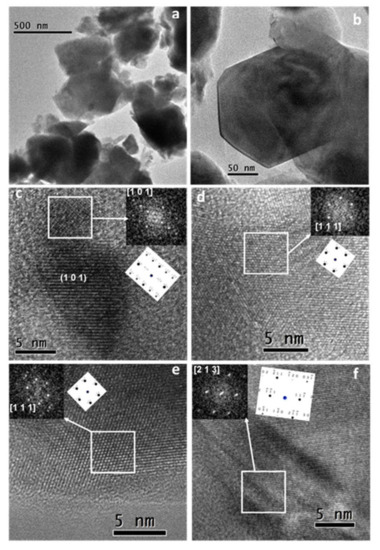
In this work, a mechanochemical process using high-energy milling conditions was employed to synthesize La0.8Sr0.2Ga0.8Mg0.2O3-δ (LSGM) powders from the corresponding stoichiometric amounts of La2O3, SrO, Ga2O3, and MgO in a short time. After 60 min of milling, the desired final product was obtained without the need for any subsequent annealing treatment. A half solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) was then developed using LSGM as an electrolyte and La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 (LSM) as an electrode, both obtained by mechanochemistry. The characterization by X-ray diffraction of as-prepared powders showed that LSGM and LSM present a perovskite structure and pseudo-cubic symmetry. The thermal and chemical stability between the electrolyte (LSGM) and the electrode (LSM) were analyzed by dynamic X-ray diffraction as a function of temperature. The electrolyte (LSGM) is thermally stable up to 800 and from 900 °C, where the secondary phases of LaSrGa3O7 and LaSrGaO4 appear. The best sintering temperature for the electrolyte is 1400 °C, since at this temperature, LaSrGaO4 disappears and the percentage of LaSrGa3O7 is minimized. The electrolyte is chemically compatible with the electrode up to 800 °C. The powder sample of the electrolyte (LSGM) at 1400 °C observed by HRTEM indicates that the cubic symmetry Pm-3m is preserved. The SOFC was constructed using the brush-painting technique; the electrode–electrolyte interface characterized by SEM presented good adhesion at 800 °C. The electrical properties of the electrolyte and the half-cell were analyzed by complex impedance spectroscopy. It was found that LSGM is a good candidate to be used as an electrolyte in SOFC, with an Ea value of 0.9 eV, and the LSM sample is a good candidate to be used as cathode
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/ma13061366
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Platinum nanoparticles stabilized by N-heterocyclic thiones. Synthesis and catalytic activity in mono- and di-hydroboration of alkynes
Moraes, LCC; Figueiredo, RCC; Espinos, JPP; Vattier, F; Franconetti, A; Jaime, C; Lacroix, B; Rojo, J; Lara, P; Conejero, SNanoscale, 12 (2020) 6821-6831
Show abstract ▽
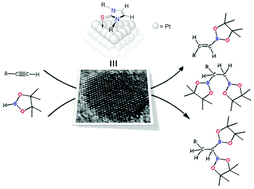
N-Heterocyclic Thiones (NHT) proved to be efficient ligands for the stabilization of small platinum nanoparticles (1.3-1.7 nm), synthesized by decomposition of [Pt(dba)(2)], under a H-2 atmosphere, in the presence of variable sub-stoichiometric amounts of the NHT. Full characterization by means of TEM, HR-TEM, NMR, ICP, TGA and XPS have been carried out, providing information about the nature of the metal nanoparticles and the interaction of the NHT ligands to the metal surface. Importantly, DFT calculations indicate that some NHT ligands interact with the metal through the C & xe001;C double bond of the imidazole fragment in addition to the sulfur atom, thus providing additional stabilization to the nanoparticles. According to XPS, TGA and ICP techniques, the surface coverage by the ligand increases by decreasing the size of the substituents on the nitrogen atom. The platinum nanoparticles have been used as catalyst in the hydroboration of alkynes. The most active system is that with a less covered surface area lacking an interaction of the ligand by means of the C & xe001;C double bond. This catalyst hydroborates alkynes with excellent selectivities towards the monoborylated anti-Markovnikov product (vinyl-boronate) when one equiv. of borane is used. Very interestingly, aliphatic alkynes undergo a second hydroborylation process leading to the corresponding 1,1- and 1,2-diboroylated species with good selectivities towards the former.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1039/d0nr00251h
- ‹ previous
- 103 of 410
- next ›














