Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Study of the influence of the precursors on the sensing properties of ZnO:Cu system
Ramos, A; Urbieta, A; Escalante, G; Hidalgo, P; Espinos, JP; Fernandez, PCeramics International, 46 (2020) 8358-8367
Show abstract ▽
The properties of ZnO based materials for ethanol detection have been studied. Cu doped samples obtained from different precursors have been investigated. ZnO and ZnS have been used as host and Cu and CuO as dopant sources.
The sensing measurements have been mostly performed at room temperature. To monitor the effect of the presence of gas, resistivity and photoluminescence experiments with and without sensing gas have been carried out. The sensing behaviour is affected by the nature of the precursors used. For ZnO:Cu and ZnO:CuO series, a higher sensitivity is obtained at the lower gas concentrations, the better response is obtained for the sample ZnO:Cu with wt.1% of metallic copper. Strong segregation effects observed in these samples could be deleterious for the sensing properties. In the series ZnS:CuO, no segregation is observed, however the sensing behaviour is erratic and attributed to the reduction of Cu ions to the metallic state.
April, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.12.068
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Vegetable hierarchical structures as template for bone regeneration: New bio‐ceramization process for the development of a bone scaffold applied to an experimental sheep model
Filardo, G; Roffi, A; Fey, T; Fini, M; Giavaresi, G; Marcacci, M; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Martini, L; Ramirez-Rico, J; Salamanna, F; Sandri, M; Sprio, S; Tampieri, A; Kon, EJournal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B-Applied Materials, 108 (2020) 600-611
Show abstract ▽
Long bone defects still represent a major clinical challenge in orthopedics, with the inherent loss of function considerably impairing the quality of life of the affected patients. Thus, the purpose of this study was to assess the safety and potential of bone regeneration offered by a load‐bearing scaffold characterized by unique hierarchical architecture and high strength, with active surface facilitating new bone penetration and osseointegration in critical size bone defects. The results of this study showed the potential of bio‐ceramization processes applied to vegetable hierarchical structures for the production of new wood‐derived bone scaffolds, further improved by surface functionalization, with good biological and mechanical properties leading to successful treatment of critical size bone defects in the sheep model. Future studies are needed to evaluate if these scaffolds prototypes, as either biomaterial alone or in combination with augmentation strategies, may represent an optimal solution to enhance bone regeneration in humans.
April, 2020 | DOI: 10.1002/jbm.b.34414
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
A Microstructure Insight of MTA Repair HP of Rapid Setting Capacity and Bioactive Response
Jimenez-Sanchez, MC; Segura-Egea, JJ; Diaz-Cuenca, AMaterials, 13 (2020) 1641
Show abstract ▽
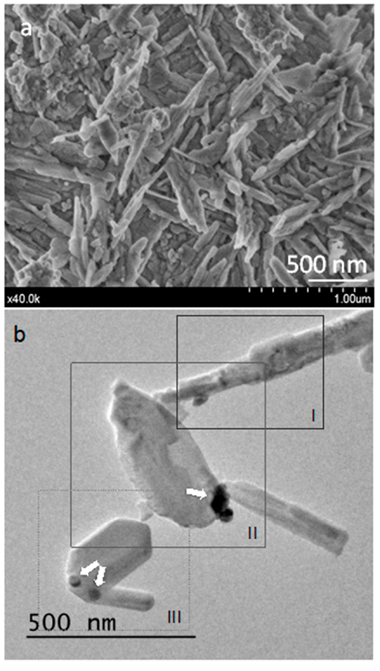
Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) is considered a bioactive endodontic material, which promotes natural mineralization at the material-tooth tissue interface. MTA Repair HP stands out because of the short setting time and the quick and effective bioactive response in vitro. The bioactivity, depens on material composition and microstructure. This work is devoted to analyze MTA Repair HP microstructural features, of both the powder precursor and set material, to get insights into the material physicochemical parameters-functionality performance relationships. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM) coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) analyses were performed. X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements were carried out at different times to investigate setting process. Bioactivity evaluation in vitro was carried out by soaking the processed cement disk in simulated body fluid (SBF). The presented results point out those MTA Repair HP precursor material characteristics of tricalcium silicate particles of nanometric size and high aspect ratio, which provide an elevated surface area and maximized components dispersion of calcium silicate and very reactive calcium aluminate. The MTA Repair HP precursor powder nanostructure and formulation, allows a hydration process comprising silicate hydrate structures, which are very effective to achieve both fast setting and efficient bioactive response.
April, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/ma13071641
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Positron annihilation analysis of nanopores and growth mechanism of oblique angle evaporated TiO2 and SiO2 thin films and multilayers
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Butterling, M; Liedke, MO; Hirschmann, E; Trinh, TT; Attallah, AG; Wagner, A; Alvarez, R; Gil-Rostra, J; Rico, V; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 295 (2020) 109968
Show abstract ▽
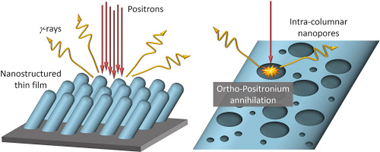
The nano-porosity embedded into the tilted and separated nanocolumns characteristic of the microstructure of evaporated thin films at oblique angles has been critically assessed by various variants of the positron annihilation spectroscopy. This technique represents a powerful tool for the analysis of porosity, defects and internal interfaces of materials, and has been applied to different as-deposited SiO2 and TiO2 thin films as well as SiO2/TiO2 multilayers prepared by electron beam evaporation at 70 and 85 zenithal angles. It is shown that, under same deposition conditions, the concentration of internal nano-pores in SiO2 is higher than in TiO2 nanocolumns, while the situation is closer to this latter in TiO2/SiO2 multilayers. These features have been compared with the predictions of a Monte Carlo simulation of the film growth and explained by considering the influence of the chemical composition on the growth mechanism and, ultimately, on the structure of the films.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109968
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Binder-free supercapacitor electrodes: Optimization of monolithic graphitized carbons by reflux acid treatment
Gomez-Martin, A; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Ramirez-Rico, JFuel Processing Technology, 199 (2020) 106279
Show abstract ▽

The rational design of electrodes mimicking the cellular structure of natural bio-resources has been a matter of increasing interest for applications in energy storage. Due to their anisotropic and hierarchical porosity, monolithic carbon materials from natural wood precursors are appealing as electrodes for supercapacitor applications due to their interconnected channels, relatively low cost and environmentally friendly synthesis process. In this work, a liquid-phase oxidative treatment with refluxing nitric acid at 100 degrees C for 8 h was performed to enhance the surface properties of beech-derived graphitized carbons treated with an iron catalyst. Microstructural, textural and surface investigations revealed that this strategy was successful in removing amorphous carbon and in functionalizing their surfaces. The crystallinity, accessible surface area, micropore volume and surface functionality of beech-derived carbons were increased upon the reflux treatment. The resulting porous carbon materials were evaluated as binderless monolithic electrodes for supercapacitors applications in aqueous KOH electrolyte. A maximum specific capacitance of 179 F.g(-1) and a volumetric capacitance of 89 Fcm(-3) in galvanostatic charge/discharge experiments were reached. Monolithic electrodes exhibited good cycling stability, with a capacitance retention over 95% after 10,000 cycles.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.106279
- ‹ previous
- 102 of 410
- next ›














