Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
In Vitro and In Vivo Study of Titanium Grade IV and Titanium Grade V Implants with Different Surface Treatments
Diaz-Sanchez, RM; de-Paz-Carrion, A; Serrera-Figallo, MA; Torres-Lagares, D; Barranco, A; Leon-Ramos, JR; Gutierrez-Perez, JLMetals, 10 (2020) 449
Show abstract ▽
The aim of our study is to evaluate different implant surface treatments using TiIV and TiV in in vitro and in vivo studies. An in vitro study was established comprising four study groups with treated and untreated TiIV titanium discs (TiIVT and TiIVNT) and treated and untreated TiV titanium discs (TiVT and TiVNT). The surface treatment consisted in a grit blasting treatment with alumina and double acid passivation to modify surface roughness. The surface chemical composition and the surface microstructure of the samples were analyzed. The titanium discs were subjected to cell cultures to determine cell adhesion and proliferation of osteoblasts on them. The in vivo study was carried out on the tibia of three New Zealand rabbits in which 18 implants divided into three experimental groups were placed (TiIVT, TiIVNT, and TiVT). Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) was performed to determine bone density around the implants. The results showed that cell culture had minor adhesion and cell proliferation in TiIVT and TiVT within the first 6 and 24 h. However, no differences were found after 48 h. No statistically significant differences were found in the in vivo micro-CT and histological study; however, there was a positive trend in bone formation in the groups with a treated surface. Conclusions: All groups showed a similar response to in vitro cell proliferation cultures after 48 h. No statistically significant differences were found in the in vivo micro-CT and histological study
April, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/met10040449
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
A 4-view imaging to reveal microstructural differences in obliquely sputter-deposited tungsten films
El Beainou, R; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Raschetti, M; Cote, JM; Alvarez, R; Palmero, A; Potin, V; Martin, NMaterials Letters, 264 (2020) 127381
Show abstract ▽
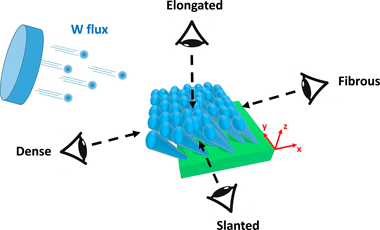
We report on the morphological disparity of the columnar growth in W thin films sputter-deposited by oblique angle deposition. Oriented tungsten thin films (400 +/- 50 nm thick) are prepared using a tilt angle alpha of 80 degrees and a sputtering pressure of 0.25 Pa. Inclined columns (beta = 38 +/- 2 degrees) are produced and the microstructure is observed by scanning electron microscopy. A 4-view imaging is performed in order to show inhomogeneous growing evolutions in the columns. Morphological features vs. viewing direction are also investigated from a growth simulation of these tilted W columns. Experimental and theoretical approaches are successfully compared and allow understanding how the direction of the W particle flux leads to dense or fibrous morphologies, as the column apexes are in front of the flux or in the shadowing zone.
April, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.127381
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Monitoring, Modeling, and Optimization of Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystal Growth within Porous Matrices
Tiede, DO; Rubino, A; Calvo, ME; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2020) 8041-8046
Show abstract ▽
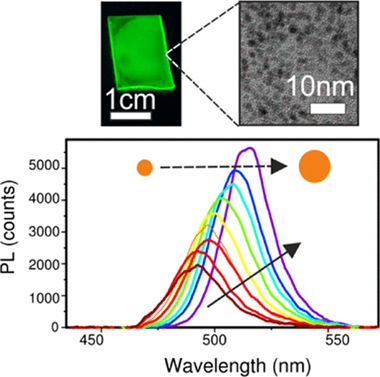
The growth of lead halide perovskites within metal-oxide nanoporous films has been recently considered as a means to obtain chemically and photostable ligand-free high-quality nanocrystals (NCs). The growth process, governed by the reactions taking place in nanoreactors dictated by the matrix pore size, has not been explored so far. In this work, we use photoluminescence as a tool to monitor the growth of perovskite NCs within the void network of an optically transparent matrix. We consider the effect of different external factors, such as temperature, light illumination, or precursor concentration, on the growth dynamics, and discuss a possible formation mechanism of the confined perovskite NCs. Based on this analysis, guidelines that could serve to improve the fabrication and optoelectronic quality of this type of NCs are also proposed.
April, 2020 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c01750
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Advanced Strategies in Thin Films Engineering by Magnetron Sputtering
Palmero, A; Martin, NCoatings, 10 (2020) 419
Show abstract ▽
This Special Issue contains a series of reviews and papers representing some recent results and some exciting perspectives focused on advanced strategies in thin films growth, thin films engineering by magnetron sputtering and related techniques. Innovative fundamental and applied research studies are then reported, emphasizing correlations between structuration process parameters, new ideas and approaches for thin films engineering and resulting properties of as-deposited coatings.
April, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/coatings10040419
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Bio-Based Coatings for Food Metal Packaging Inspired in Biopolyester Plant Cutin
Benitez, JJ; Osbild, S; Guzman-Puyol, S; Heredia, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAPolymers, 12 (2020) 942
Show abstract ▽
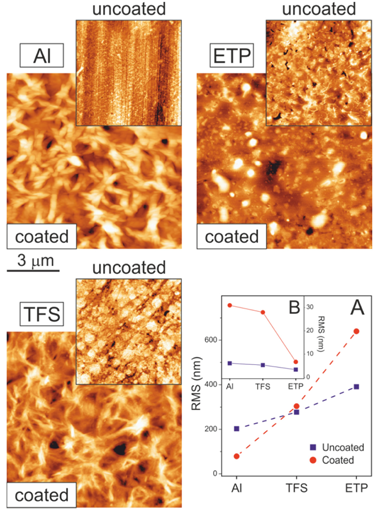
Metals used for food canning such as aluminum (Al), chromium-coated tin-free steel (TFS) and electrochemically tin-plated steel (ETP) were coated with a 2-3-mu m-thick layer of polyaleuritate, the polyester resulting from the self-esterification of naturally-occurring 9,10,16-trihydroxyhexadecanoic (aleuritic) acid. The kinetic of the esterification was studied by FTIR spectroscopy; additionally, the catalytic activity of the surface layer of chromium oxide on TFS and, in particular, of tin oxide on ETP, was established. The texture, gloss and wettability of coatings were characterized by AFM, UV-Vis total reflectance and static water contact angle (WCA) measurements. The resistance of the coatings to solvents was also determined and related to the fraction of unreacted polyhydroxyacid. The occurrence of an oxidative diol cleavage reaction upon preparation in air induced a structural modification of the polyaleuritate layer and conferred upon it thermal stability and resistance to solvents. The promoting effect of the tin oxide layer in such an oxidative cleavage process fosters the potential of this methodology for the design of effective long-chain polyhydroxyester coatings on ETP.
April, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/polym12040942
- ‹ previous
- 101 of 410
- next ›














