Artículos SCI
2021
2021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Mesoporous Carbon Production by Nanocasting Technique Using Boehmite as a Template
Ortega-Franqueza, M; Ivanova, S; Dominguez, MI; Centeno, MACatalysts, 11 (2021) 1132
Show abstract ▽
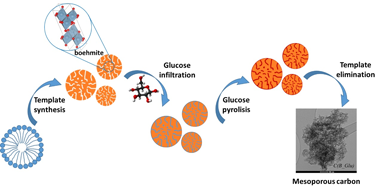
A series of mesoporous carbonaceous materials were synthesized by the nanocasting technique using boehmite as a template and glucose as a carbon precursor. After pyrolysis and template removal, the resulting material is a mesoporous carbon that can be additionally doped with N, B and K during prepyrolysis impregnation. In addition, the influence of doping on the morphology, crystallinity and stability of the synthesized carbons was studied using X-ray diffraction, nitrogen physisorption, thermogravimetry, Raman and IR spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy. While the nanocasting process is effective for the formation of mesopores, KOH and urea do not modify the textural properties of carbon. The use of H3PO4 as a dopant, however, led to the formation of an AlPO4 compound and resulted in a solid with a lower specific surface area and higher microporosity. All doped solids present higher thermal stability as a positive effect of the introduction of heteroatoms to the carbon skeleton. The phosphorus-doped sample has better oxidation resistance, with a combustion temperature 120-150 degrees C higher than those observed for the other materials.
Septiembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/catal11091132
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Effect of Al content on the hardness and thermal stability study of AlTiN and AlTiBN coatings deposited by HiPIMS
Mendez, A; Monclus, MA; Santiago, JA; Fernandez-Martinez, I; Rojas, TC; Garcia-Molleja, J; Avella, M; Dams, N; Panizo-Laiz, M; Molina-Aldareguia, JMSurface & Coatings Technology, 422 (2021) 127513
Show abstract ▽
The microstructure, mechanical properties and thermal stability of AT(x)Ti(1-x)N and Al1Ti1-xBN coatings grown by reactive high-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) have been analyzed as a function of Al/(Al + Ti) ratio (x) between 0.5 and 0.8. The coatings were predominantly formed by a face-centered cubic Ti(Al)N crystalline phase, both with and without B, even for x ratios as high as 0.6, which is higher than the ratio typically encountered for AlxTi1-xN coatings deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering. B doping, in combination with the highly energetic deposition conditions offered by HiPIMS, results in the suppression of the columnar grain morphology typically encountered in AlxTi1-xN coatings. On the contrary, the AlxTi1-xN coatings grown by HiPIMS present a dense nanocomposite type microstructure, formed by nanocrystalline Ti(Al) N domains and amorphous regions composed of Ti(Al)B 2 and BN. As a result, high-Al content (x approximate to 0.6) AlxTi1-xN coatings grown by HiPIMS offer higher hardness, elasticity and fracture toughness than AlxTi1-xN coatings. Moreover, the thermal stability and the hot hardness are substantially enhanced, delaying the onset of formation of the detrimental hexagonal AlN phase from 850 degrees C in the case of Al0.6Ti0.4N, to 1000 degrees C in the case of Al0.6Ti0.4N.
Septiembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127513
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic production of hydrogen and methane from glycerol reforming over Pt/TiO2–Nb2O5
Iervolino, G; Vaiano, V; Murcia, JJ; Lara, AE; Hernández, JS; Rojas, H; Navío, JA; Hidalgo, MCInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy
Show abstract ▽
In this study, platinized mixed oxides (TiO2–Nb2O5) were tested on photocatalytic hydrogen production from a glycerol solution under UV light. Different samples with different Ti:Nb ratios were prepared by using a simple method that simultaneously combined a physical mixture and a platinum photochemical reduction. This method led to improved physicochemical properties such as low band gap, better Pt nanoparticle distribution on the surface, and the formation of different Pt species. Niobia content was also found to be an important factor in determining the overall efficiency of the Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 photocatalyst in the glycerol reforming reaction. The photocatalytic results showed that Pt on TiO2–Nb2O5 enhanced hydrogen production from the aqueous glycerol solution at a 5 wt% initial glycerol concentration. The influence of different operating conditions such as the catalyst dosage and initial glycerol concentration was also evaluated. The results indicated that the best hydrogen and methane production was equal to 6657 μmol/L and 194 μmol/L, respectively after 4 h of UV radiation using Pt/Ti:Nb (1:2) sample and with 3 g/L of catalyst dosage. Moreover, the role of water in photocatalytic hydrogen production was studied through photocatalytic activity tests in the presence of D2O. The obtained results confirmed the role of water molecules on the photocatalytic production of hydrogen in an aqueous glycerol solution.
Septiembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.09.111
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Nb-C thin films prepared by DC-MS and HiPIMS: Synthesis, structure, and tribomechanical properties
Sala, N; Abad, MD; Sánchez-López, JC; Caro, J; Colominas, CSurface & Coatings Technology, 422 (2021) 127569
Show abstract ▽
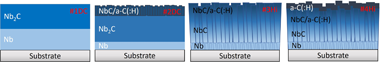
Nanostructured Nb-C thin films were prepared by direct current magnetron sputtering (DC-MS) and high-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS). The films were characterized in depth by X-ray diffraction (XRD), grazing incidence X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, electron probe microanalysis, and Raman spectroscopy. The mechanical properties were measured by nanoindentation, and the tribological properties were measured by pin-on-disk tests in ambient air. The wear tracks and ball scars were analyzed by Raman spectroscopy to elucidate the tribochemical reactions that occurred at the contact area and to determine the wear mechanism for each specimen type. The thermal stability of the coatings was studied up to 1000 degrees C using Raman spectroscopy and XRD. The samples prepared by DC-MS were very dense, and the phase composition changed from purely nanocrystalline (Nb2C and NbC) to a mixture of NbC crystals embedded in an amorphous carbon-based matrix (NbC/a-C(:H)). However, the samples prepared by HiPIMS developed a marked columnar morphology with a NbC/a-C(:H) nanocomposite structure. The hardness values ranged from 11 to 20 GPa depending on the deposition technique and the amount of the soft a-C(:H) phase present in the sample. The tribological properties of all the coatings were remarkably good when the carbon content was approximately 50 at.%. The formation of a lubricating sp(2)-rich C tribofilm between the ball and coating during the pin-on-disk tests was observed by Raman spectroscopy. The tribofilm formed preferentially on the samples prepared by HiPIMS, which had higher C contents. At 750 degrees C, the degradation of the NbC phases resulted in the formation of an additional a-C phase and niobium oxides.
Septiembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127569
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
One-reactor vacuum and plasma synthesis of transparent conducting oxide nanotubes and nanotrees: from single wire conductivity to ultra-broadband perfect absorbers in the NIR
Castillo-Seoane, J; Gil-Rostra, J; Lopez-Flores, V; Lozano, G; Ferrer, FJ; Espinos, JP; Ostrikov, K; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Borras, ANanoscale, 13 (2021) 13882-13895
Show abstract ▽
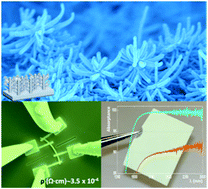
The eventual exploitation of one-dimensional nanomaterials needs the development of scalable, high yield, homogeneous and environmentally friendly methods capable of meeting the requirements for fabrication of functional nanomaterials with properties on demand. In this article, we demonstrate a vacuum and plasma one-reactor approach for the synthesis of fundamental common elements in solar energy and optoelectronics, i.e. the transparent conducting electrode but in the form of nanotube and nanotree architectures. Although the process is generic and can be used for a variety of TCOs and wide-bandgap semiconductors, we focus herein on indium doped tin oxide (ITO) as the most previously researched in previous applications. This protocol combines widely applied deposition techniques such as thermal evaporation for the formation of organic nanowires serving as 1D and 3D soft templates, deposition of polycrystalline layers by magnetron sputtering, and removal of the templates by simply annealing under mild vacuum conditions. The process variables are tuned to control the stoichiometry, morphology, and alignment of the ITO nanotubes and nanotrees. Four-probe characterization reveals the improved lateral connectivity of the ITO nanotrees and applied on individual nanotubes shows resistivities as low as 3.5 +/- 0.9 x 10(-4) omega cm, a value comparable to that of single-crystalline counterparts. The assessment of diffuse reflectance and transmittance in the UV-Vis range confirms the viability of the supported ITO nanotubes as random optical media working as strong scattering layers. Their further ability to form ITO nanotrees opens a path for practical applications as ultra-broadband absorbers in the NIR. The demonstrated low resistivity and optical properties of these ITO nanostructures open a way for their use in LEDs, IR shields, energy harvesting, nanosensors, and photoelectrochemical applications.
Agosto, 2021 | DOI: 10.1039/d1nr01937f
- ‹ anterior
- 69 of 410
- siguiente ›














