Artículos SCI
2021
2021
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
LaFeO3 Modified with Ni for Hydrogen Evolution Via Photocatalytic Glucose Reforming in Liquid Phase
G. Iervolino; V. Vaiano; D. Sannino; F. Puga; J.A. Navío; M.C. HidalgoCatalysts, 11 (2021) 1558
Show abstract ▽
In this work, the optimization of Ni amount on LaFeO3 photocatalyst was studied in the photocatalytic molecular hydrogen production from glucose aqueous solution under UV light irradiation. LaFeO3 was synthesized via solution combustion synthesis and different amount of Ni were dispersed on LaFeO3 surface through deposition method in aqueous solution and using NaBH4 as reducing agent. The prepared samples were characterized with different techniques: Raman spectroscopy, UltraViolet-Visible Diffuse Reflectance Spettroscopy (UV–Vis-DRS), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), Transmission Electron microscopy (TEM), and Scanning Electron microscopy (SEM) analyses. For all the investigated photocatalysts, the presence of Ni on perovskite surface resulted in a better activity compared to pure LaFeO3. In particular, it is possible to identify an optimal amount of Ni for which it is possible to obtain the best hydrogen production. Specifically, the results showed that the optimal Ni amount was equal to nominal 0.12 wt% (0.12Ni/LaFeO3), for which the photocatalytic H2 production was equal to 2574 μmol/L after 4 h of UV irradiation. The influence of different of photocatalyst dosage and initial glucose concentration was also evaluated. The results of the optimization of operating parameters indicated that the highest molecular hydrogen production was achieved on 0.12Ni/LaFeO3 sample with 1.5 g/L of catalyst dosage and 1000 ppm initial glucose concentration. To determine the reactive species that play the most significant role in the photocatalytic hydrogen production, photocatalytic tests in the presence of different radical scavengers were performed. The results showed that •OH radical plays a significant role in the photocatalytic conversion of glucose in H2. Moreover, photocatalytic tests carried out with D2O instead of H2O evidenced the role of water molecules in the photocatalytic production of molecular hydrogen in glucose aqueous solution.
Diciembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/catal11121558
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
In Situ DRIFTS-MS Methanol Adsorption Study onto Supported NiSn Nanoparticles: Mechanistic Implications in Methanol Steam Reforming
Bobadilla, LF; Azancot, L; Ivanova, S; Delgado, JJ; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Roger, ACNanomaterials, 11 (2021) 3234
Show abstract ▽
Methanol adsorption over both supported NiSn Nps and analogous NiSn catalyst prepared by impregnation was studied by in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) to gain insights into the basis of hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming. Different intermediate species such as methoxides with different geometry (bridge and monodentate) and formate species were identified after methanol adsorption and thermal desorption. It is proposed that these species are the most involved in the methanol steam reforming reaction and the major presence of metal-support interface sites in supported NiSn Nps leads to higher production of hydrogen. On the basis of these results, a plausible reaction mechanism was elucidated through the correlation between the thermal stability of these species and the evolution of the effluent gas released. In addition, it was demonstrated that DME is a secondary product generated by condensation of methoxides over the acid sites of alumina support in an acid-catalyzed reaction.
Diciembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/nano11123234
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Recent Advances in the Bronsted/Lewis Acid Catalyzed Conversion of Glucose to HMF and Lactic Acid: Pathways toward Bio-Based Plastics
Megias-Sayago, C; Navarro-Jaen, S; Drault, F; Ivanova, SCatalysts, 11 (2021) 1395
Show abstract ▽
One of the most trending topics in catalysis recently is the use of renewable sources and/or non-waste technologies to generate products with high added value. That is why, the present review resumes the advances in catalyst design for biomass chemical valorization. The variety of involved reactions and functionality of obtained molecules requires the use of multifunctional catalyst able to increase the efficiency and selectivity of the selected process. The use of glucose as platform molecule is proposed here and its use as starting point for biobased plastics production is revised with special attention paid to the proposed tandem Bronsted/Lewis acid catalysts.
Noviembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/catal11111395
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Polyaniline coated tungsten trioxide as an effective adsorbent for the removal of orange G dye from aqueous media
Hsini, A.; Naciri, Y.; Bouziani, A.; Aarab, N.; Essekri, A; Imgharn, A.; Laabd. M.; Navío, J.A.;Puga, F.; Lakhmirid, R.; Albourine, A.RSC Advances, 11 (2021) 31272-31283
Show abstract ▽

In this work, the core–shell PANI@WO3 composite was obtained from the reaction of aniline monomer polymerization with WO3 particles; sodium persulfate was used as an oxidant. Various analytical techniques such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM-EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were used to characterize the as-prepared PANI@WO3 adsorbent, which well confirmed that the WO3 particles were coated by polyaniline polymer. The PANI@WO3 composite was tested as an adsorbent to remove reactive orange G (OG) for the first time. pH, adsorbent dose, contact time, initial dye concentration, and temperature were systematically investigated in order to study their effect on the adsorption process. The experimental findings showed that the PANI@WO3 composite has considerable potential to remove an aqueous OG dye. Langmuir and Freundlich's models were used to analyze the equilibrium isotherms of OG dye adsorption on the PANI@WO3 composite. As a result, the best correlation of the experimental data was provided by the Langmuir model, and the maximum capacity of adsorption was 226.50 mg g−1. From a thermodynamic point of view, the OG dye adsorption process occurred spontaneously and endothermically. Importantly, PANI@WO3 still exhibited an excellent adsorption capability after four regeneration cycles, indicating the potential reusability of the PANI@WO3 composite. These results indicate that the as prepared PANI@WO3 composite could be employed as an efficient adsorbent and was much better than the parent material adsorption of OG dye.
Noviembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1039/D1RA04135E
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Ultrastrong Exciton-Photon Coupling in Broadband Solar Absorbers
Bujalance, C; Esteso, V; Calio, L; Lavarda, G; Torres, T; Feist, J; Garcia-Vidal, FJ; Bottari, G; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 12 (2021) 10706-10712
Show abstract ▽
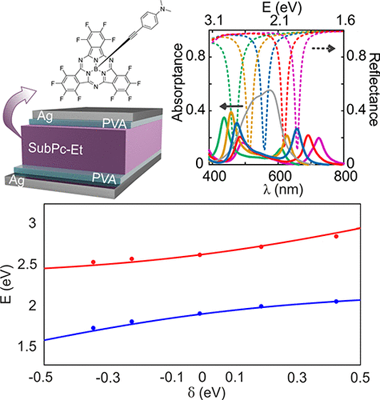
The recent development of organic polaritonic solar cells, in which sunlight absorbers and photon modes of a resonator are hybridized as a result of their strong coupling, has revealed the potential this interaction offers to control and enhance the performance of these devices. In this approach, the photovoltaic cell is built in such a way that it also behaves as an optical cavity supporting spectrally well-defined resonances, which match the broad absorption bands of the dyes employed. Herein we focus on the experimental and theoretical analysis of the specific spectral and angular optical absorption characteristics of a broadband light harvester, namely a subphthalocyanine, when operating in the ultrastrong coupling regime. We discuss the implications of having a broad distribution of oscillator strengths and demonstrate that rational design of the layered structure is needed to optimize both the spectral and the angular response of the sunlight harvester dye.
Noviembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c02898
- ‹ anterior
- 63 of 410
- siguiente ›














