Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Reactividad de Sólidos
A first insight into the microstructure and crack propagation in novel boron nitride nanosheet/3YTZP composites
Munoz-Ferreiro, C; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, RBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 60 (2021) 128-136
Show abstract ▽
In this work, novel 3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycristalline (3YTZP) ceramic composites with boron nitride nanosheets (BNNS) are investigated for the first time. Highly densified composites with 1 and 4 vol% BNNS were obtained by spark plasma sintering (SPS) after BNNS synthesis using a solution exfoliation method and BNNS dispersion into the ceramic powder by ultrasonication. The BNNS presented homogeneous distribution throughout the ceramic matrix and preferential alignment in the plane perpendicular to the pressing axis during SPS. The BNNS incorporation had practically no effect on the Vickers hardness of the material nor on the Young's modulus. Anisotropy in crack development was found in the composite with 4% vol BNNS, together with a mechanism of extensive microcracking. Several energy-absorbing mechanisms during crack propagation, such as crack deflection, crack bridging, crack branching, BNNS pull-out and BNNS debonding, were identified in the composites by a close observation of the indentation-induced fracture paths.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.bsecv.2020.02.003
Reactividad de Sólidos
EGFR-targeting antitumor therapy: Neuregulins or antibodies?
de Lavera, I; Merkling, PJ; Oliva, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Cotan, D; Sanchez-Alcazar, JA; Infante, JJ; Zaderenko, A.P.European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 158 (2021) 105678
Show abstract ▽
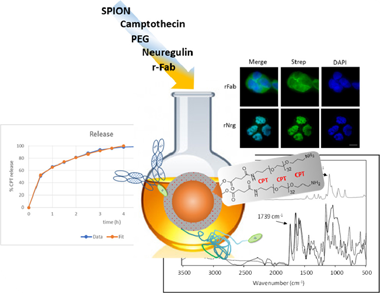
Malignancies such as lung, breast and pancreatic carcinomas are associated with increased expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR, and its role in the pathogenesis and progression of tumors has made this receptor a prime target in the development of antitumor therapies. In therapies targeting EGFR, the development of resistance owing to mutations and single nucleotide polymorphisms, and the expression of the receptor ligands themselves are very serious issues. In this work, both the ligand neuregulin and a bispecific antibody fragment to EGFR are conjugated separately or together to the same drug-delivery system to find the most promising candidate. Camptothecin is used as a model chemotherapeutic drug and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a delivery system. Results show that the lowest LD50 is achieved by formulations conjugated to both the antibody and the ligand, demonstrating a synergy. Additionally, the ligand location in the nucleus favors the antitumor activity of Camptothecin. The high loading capacity and efficiency convert these systems into a good alternative for administering Camptothecin, a drug whose use is otherwise severely limited by its chemical instability and poor solubility. Our choice of targeting agents allows treating tumors that express ErbB2 (Her2+ tumors) as well as Her2- tumors expressing EGFR.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105678
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Cation-driven electrical conductivity in Ta-doped orthorhombic zirconia ceramics
Moshtaghioun, BM; Laguna-Bercero, MA; Pena, JI; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, ACeramics International, 47 (2021) 7248-7522
Show abstract ▽
This paper is devoted to the study of the electrical conductivity of tantalum-doped zirconia ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering. In this study, the temperature dependence of conductivity in as-prepared specimens and in those previously annealed in air is determined and compared. A semi-empirical model, which is based on the oxidation states of the cations, has been developed and successfully assessed. According to this, the conductivity is basically controlled by the diffusion of tetravalent zirconium cations in both cases, although the concentration of these species varies drastically with the amount of induced oxygen vacancies. This is a quite unexpected fact, since conductivity is normally controlled by anionic diffusion in zirconia ceramics. This option is forbidden here due to the presence of substitutional pentavalent cations. Therefore, conductivity values are much lower than those reported in trivalent or divalent substitutional cation doped zirconia ceramics.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.10.227
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Insights into the role of the layer architecture of Cr-Ti-N based coatings in long-term high temperature oxidation experiments in steam atmosphere
Mato, S; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Barriga, J; Perez, FJ; Alcala, GCeramics International, 47 (2021) 4257-4266
Show abstract ▽
Knowledge on hard coatings has been applied in the energy field extending their use as protecting coatings of steam power generation plants components. The role of the layer architecture of Cr-Ti-N based coatings deposited by reactive cathodic arc evaporation on P92 steel substrates was studied with the focus on their oxidation resistance at 650 degrees C in 100% steam atmosphere up to 2000 h. Characterization of the coatings was performed by gravimetry, scanning electron microscopy, electron probe microanalysis, glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, thermodynamic simulations using the CALPHAD method, Rockwell C indentation and nanoindentation. The layered arrangement improves the oxidation resistance of TiN under the working conditions of steam power plants, as well as the mechanical properties of CrN. The produced architectures performance under the described working conditions boosts the understanding of the processes taking place at high temperature, making possible the design of optimal coatings combining the best behavior of both nitrides for each specific application, reaching a corrosion protection at high temperature in water vapor comparable to that of CrN and a hardness and Young's modulus as high as those of TiN.
February, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.10.003
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Active sites and optimization of mixed copper-cobalt oxide anodes for anion exchange membrane water electrolysis
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Gil-Rostra, J; Escudero, C; Villar-Garcia, IJ; Yubero, F; Consuegra, AD; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Power Sources, 485 (2021) 229217
Show abstract ▽
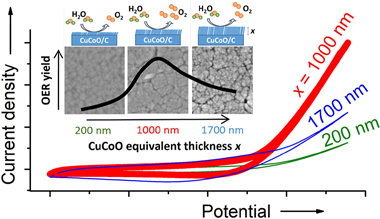
The optimization of the catalysts incorporated to the electrodes for anion exchange membrane water electmlysers is a key issue to maximize their performance through the improvement of the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) yield. In this work, we show that the modification of the microstructure and the chemical properties of a mixed copper-cobalt oxide anode may contribute to increase the activity of this reaction. For this purpose, the OER has been systematically studied, either in a half cell or in a membrane electrode assembly configuration, as a function of the load and agglomeration degree of the catalysts used as electrodes, as prepared on a carbon paper support by magnetron sputtering deposition in an oblique angle configuration. Chemical analysis by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and electrochemical analysis by cyclic voltammetry and impedance spectroscopy have shown that cobalt-copper mixed oxide catalysts with a 1.8 Co/Cu atomic ratio and about one micron equivalent thickness maximizes the cell performance. The chemical, structural and microstructural factors controlling the final behaviour of these anodes and accounting for this maximization of the reaction yield are discussed on the basis of these characterization results and as a function of preparation variables of the electrodes and operating conditions of the cell.
February, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.229217
- ‹ previous
- 84 of 410
- next ›














