Scientific Papers in SCI
2024
2024
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
CuO-TiO2 pilot-plant system performance for solar photocatalytic hydrogen production
Villachica-Llamosas, JG; Ruiz-Aguirre, A; Colón, G; Peral, J; Malato, SInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 51 (2024) 1069-1077
Show abstract ▽
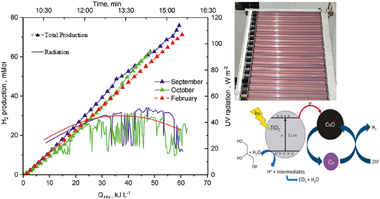
The main goal of the present study was to explore photocatalytic performance of the TiO2 -CuO mixture, for solar to hydrogen conversion at pilot plant scale under two different irradiation conditions (sunny and partly cloudy), focusing on high-temperature pretreat-ment of the catalyst mixture to try to improve TiO2 doping with copper. P25-TiO2 and commercial CuO were used with different amounts of Cu (2 wt% or 7 wt% Cu) calcined at 200-400 degrees C during several hours. Catalysts were tested at pilot plant scale using solar compound parabolic collectors, with glycerol as the sacrificial agent. The photocatalyst prepared after heating at 200 degrees C for 3 h and with 7 wt% Cu, resulted in higher hydrogen production than under the other heating conditions, and results were slightly better (5 -10%) than the reference values with the untreated catalysts. Photocatalytic efficiency was slightly lower at the higher calcination temperature (400 degrees C). CO2 production and formation of formate and glycolate clearly demonstrated glycerol photoreforming. The Cu from the calcined catalyst remaining on the solid was significantly less (2.5%) than on the non -calcined catalyst (4.2%), with an important fraction of lixiviated copper and copper deposition on the reactor walls. This is a critical drawback that must be considered for large-scale applications.
January, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.07.149
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Switchable catalysis for methanol and synthetic natural gas synthesis from CO2: A techno-economic investigation
Merkouri, LP; Mathew, J; Jacob, J; Reina, TR; Duyar, MSJournal of CO2 Utilization, 79 (2024) 102652
Show abstract ▽
The oil and gas sector produces a considerable volume of greenhouse gas emissions, mainly generated from flaring and venting natural gas. Herein, a techno-economic analysis has been performed of a switchable catalytic process to convert the CH4 and CO2 in flared/vented natural gas into syngas or methanol. Specifically, it was shown that depending on greenhouse gas composition, dry methane reforming (DRM), reverse water-gas shift (RWGS), and CO2 methanation could be chosen to valorise emissions in an overall profitable and flexible operation scenario. The switchable process produced methanol and synthetic natural gas as its products, resulting in an annual income of €687m and annual operating expenses of €452m. The pre-tax profit was calculated at €234m, and at the end of the project, the net present value was calculated as €1.9b with a profitability index of 4.7€/€. The expected payback time of this process was ca. 4 years, and with a 35% internal rate of return (IRR). Most importantly, this process consumed 42.8m tonnes of CO2 annually. The sensitivity analysis revealed that variations in operation time, green hydrogen price, and products' prices significantly impacted the profitability of the process. Overall, this techno-economic analysis demonstrated that switchable catalysis in greenhouse gas utilisation processes is profitable, and thus it could play an important role in achieving net zero emissions.
January, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2023.102652
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
A review on high-pressure heterogeneous catalytic processes for gas-phase CO2 valorization
Villora-Picó, J.J; González-Arias, J; Pastor-Pérez, L; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TREnvironmental Research, 240 (2024) 117520
Show abstract ▽
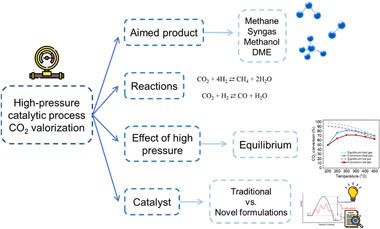
This review discusses the importance of mitigating CO2 emissions by valorizing CO2 through high-pressure catalytic processes. It focuses on various key processes, including CO2 methanation, reverse water-gas shift, methane dry reforming, methanol, and dimethyl ether synthesis, emphasizing pros and cons of high-pressure operation. CO2 methanation, methanol synthesis, and dimethyl ether synthesis reactions are thermodynami-cally favored under high-pressure conditions. However, in the case of methane dry reforming and reverse water -gas shift, applying high pressure, results in decreased selectivity toward desired products and an increase in coke production, which can be detrimental to both the catalyst and the reaction system. Nevertheless, high-pressure utilization proves industrially advantageous for cost reduction when these processes are integrated with Fischer-Tropsch or methanol synthesis units. This review also compiles recent advances in heterogeneous catalysts design for high-pressure applications. By examining the impact of pressure on CO2 valorization and the state of the art, this work contributes to improving scientific understanding and optimizing these processes for sustainable CO2 management, as well as addressing challenges in high-pressure CO2 valorization that are crucial for industrial scaling-up. This includes the development of cost-effective and robust reactor materials and the development of low-cost catalysts that yield improved selectivity and long-term stability under realistic working environments.
January, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.117520
2023
2023
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Photoreforming of glycerol to produce hydrogen from natural water in a compound parabolic collector solar photoreactor
Villachica-Llamosas, JG; Sowik, J; Ruiz-Aguirre, A; Colón, G; Peral, J; Malato, SJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 11 (2023) 111216
Show abstract ▽
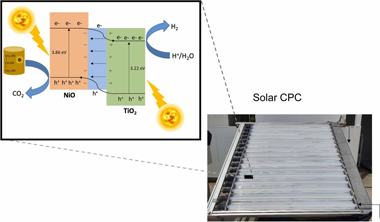
To improve TiO2 for H2 generation, one strategy for the separation of photogenerated charges is the formation of heterostructures with other materials. In particular, NiO is a photocatalyst known for its good stability and low cost. However, no studies at pilot scale using solar energy have been described. Consequently, an evaluation of a physical NiO:TiO2 mixture at pilot scale (25 L) with natural irradiation (2.10 m2 of sun-exposed surface) and with simultaneous glycerol photoreforming was explored. NiO:TiO2 50 mg & sdot;L- 1 resulted in the highest hydrogen production, showing an STH = 1.44%, considering only the UV fraction of the solar irradiation. H2 and CO2 production were analysed by on-line GC; Glycerol, dissolved organic carbon, carboxylic acids and nickel leaching were also evaluated. The NiO:TiO2 mixtures rendered a systematically lower H2 production in natural water than in high-purity water. The increase of ionic strength increased the mean size of particle clusters, promoting rapid sedimentation. All this indicates the importance of testing under real field conditions for attaining reliable solar to hydrogen (STH) efficiency.
December, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.111216
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of zeolite topological structure in bifunctional catalyst on direct conversion of syngas to light olefins
Meng, FH; Gong, ZY; Yang, LL; Wang, Q; Xing, MQ; Nawaz, MA; Li, ZMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 362 (2023) 112792
Show abstract ▽
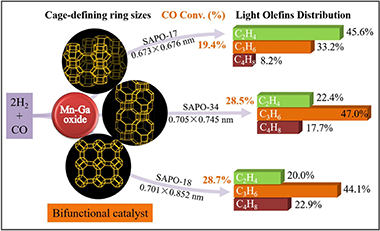
Bifunctional catalyst composed of metal oxide and zeolite (OX-ZEO) is a promising strategy for the direct conversion of syngas to light olefins (STO), where the structure of zeolite plays a vital role in determining the selectivity of product. Herein, three kinds of silicoaluminophosphate zeolites with different topological structures, i.e., the ERI(SP17), AEI(SP18) and CHA(SP34), were hydrothermally synthesized, after the combination with Mn-Ga oxide, the prepared OX-ZEO was applied for STO reaction. The variation in the crystallization time for SP17 synthesis has a great impact on the generation of impurity phase of SAPO-5, where a crystallization time of 48-96 h is found to be beneficial in synthesizing SP17 zeolite with pure phase. SP17 zeolite with a crystallization time of 96 h, possesses the micropores and columnar morphology, where the small cage-defining 8-ring size of SP17 shows the olefins selectivity of 87.0% at a low CO conversion of 19.4%, significantly deviating towards the major fraction of ethylene (45.6%) than that of butene (8.2%). In a contrast, SP18 and SP34 zeolites with the same and large cage-defining 8-ring size, are richer in propylene and butene fractions than that of ethylene in overall similar olefins selectivity of 87.0% and 87.1% at CO conversion of 28.7% and 28.5%, respectively. Interestingly, it is further interpreted that the SP17 sample generated more carbon species during the reaction due to the small 8-ring size, while those amounts of carbon species were restricted in the hierarchical pore structure and plate-like morphology in SP18 and SP34 samples.
December, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2023.112792
- ‹ previous
- 6 of 410
- next ›














