Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Tribomechanical properties of hard Cr-doped DLC coatings deposited by low-frequency HiPIMS
Santiago, JA; Fernandez-Martinez, I; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Rojas, TC; Wennberg, A; Bellido-Gonzalez, V; Molina-Aldareguia, JM; Monclus, MA; Gonzalez-Arrabal, RSurface & Coatings Technology, 382 (2020) 124899
Show abstract ▽
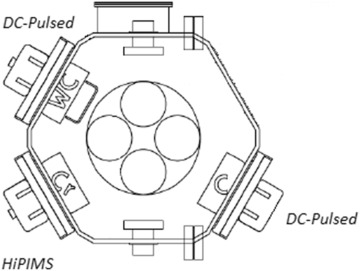
Cr-doped diamond-like carbon (Cr-DLC) films with Cr contents ranging from 3 up to 20 at. % were synthesised in a codeposition process with HiPIMS (Cr deposition) and DC-pulsed technology (C deposition). The application of HiPIMS at low frequencies was observed to significantly enhance the energy density during the Cr plasma discharge due to the interaction of Cr-C species. The higher energy bombardment at low HiPIMS frequencies allowed doping with Cr the DLC structure avoiding the graphitization of the carbon structure. EELS spectroscopy was used to evaluate sp(3) content and Raman was used for sp(2) structural characterization of the films. Enhanced mechanical properties (hardness up to 30 GPa) were observed with nanoindentation for Cr-doped DLC at low frequencies. High temperature nanoindentation tests were also performed from room temperature to 425 degrees C in order to evaluate the evolution of hardness and Young Modulus with temperature. The results showed that the mechanical properties at high temperature mainly depend on the initial sp(3)-sp(2) structure. Tribological tests were carried out in air from room temperature to 250 degrees C. Cr-doped DLC coatings deposited by low-frequency HiPIMS showed lower friction and wear compared to undoped DLC.
January, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.124899
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Dipole reorientation and local density of optical states influence the emission of light-emitting electrochemical cells
Jimenez-Solano, Alberto; Martinez-Sarti, Laura; Pertegas, Antonio; Lozano, Gabriel; Bolink, Henk J; Miguez, HernanPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 22 (2020) 92-96
Show abstract ▽
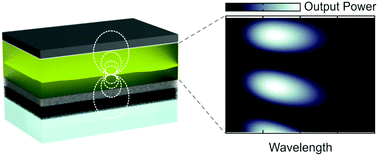
Herein, we analyze the temporal evolution of the electroluminescence of light-emitting electrochemical cells (LECs), a thin-film light-emitting device, in order to maximize the luminous power radiated by these devices. A careful analysis of the spectral and angular distribution of the emission of LECs fabricated under the same experimental conditions allows describing the dynamics of the spatial region from which LECs emit, i.e. the generation zone, as bias is applied. This effect is mediated by dipole reorientation within such an emissive region and its optical environment, since its spatial drift yields a different interplay between the intrinsic emission of the emitters and the local density of optical states of the system. Our results demonstrate that engineering the optical environment in thin-film light-emitting devices is key to maximize their brightness.
January, 2020 | DOI: 10.1039/c9cp05505c
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Effect of synthesis pH on the physicochemical properties of a synthesized Bi2WO6 and the type of substrate chosen, in assessing its photo-catalytic activities
Jaramillo-Páez, C.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 13 (2020) 431-443
Show abstract ▽

Crystalline orthorhombic Bi2WO6 powders were synthesized by a hydrothermal method from aqueous solutions of Bi(NO3)35H2O and Na2WO42H2O over a range of three selected pH values (2.0, 5.0 and 7.0), using NaOH as precipitating agent. The as-prepared catalysts were characterized by XRD, BET, FE-SEM, TEM, XPS and UV-vis spectroscopy. The effect of pH-synthesis on crystallinity, morphologies, surface area and optical absorption properties, were investigated.
Although the pH has a marked influence on morphology, the nature of the precipitating agent (NaOH or TEA) also influences the morphology and surface structure composition, as it is observed in the present work. Three different probe molecules were used to evaluate the photocatalytic properties under two illumination conditions (UV and Visible): Methyl Orange and Rhodamine B were chosen as dye substrates and Phenol as a transparent substrate. The photo-catalytic activities are strongly dependent not only on the pH used in the synthesis but also on the nature of the chosen substrate in assessing the photo-catalytic activities. Results were compared with those obtained when using TiO2(P25, Evonik) in the same experimental conditions. The photocatalytic activity of one of the synthesised samples has been evaluated by exposing a mixture of Rhodamine B and Phenol in water, to different illumination conditions. Our results provide new evidences about the issue of whether dyes are suitable substrates to assess the activity of a photo-catalyst.
January, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.014
Reactividad de Sólidos
Development of Ti(C,N)-based cermets with (Co,Fe,Ni)-based high entropy alloys as binder phase
de la Obra, AG; Sayagues, MJ; Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 814 (2020) 152218
Show abstract ▽
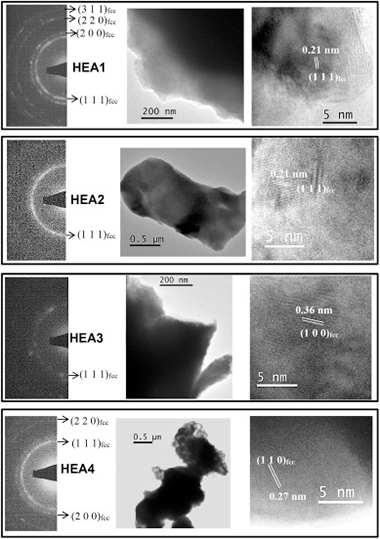
High entropy alloys have been proposed as novel binder phases in cemented carbides and cermets. Many aspects related to the stability of these alloys during the liquid phase sintering process are still unclear and were addressed in this work. Consolidated Ti(C,N)-based cermets using four different (Co,Fe,Ni)based high entropy alloys as the binder phase were obtained. The chosen alloys - CoCrCuFeNi, CoCrFeNiV, CoCrFeMnNi and CoFeMnNiV - were previously synthesized through mechanical alloying and a single alloyed solid solution phase with fcc structure and nanometric character was always obtained. The powdered alloys and the consolidated cermets were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray energy dispersive spectrometry and transmission electron microscopy. Differential thermal analysis was employed to determine the melting point of the four high entropy alloys that ranged between 1310 degrees C and 1375 degrees C. Although a high temperature of 1575 degrees C was required to obtain the highest cermet densification by pressureless sintering, porosity still remained in most of the cermets. Best densification was achieved when CoCrFeNiV was used as the binder phase. During liquid phase sintering, different compositional changes were observed in the ceramic and binder phases. A core-rim microstructure was observed in cermets containing V in the alloys (CoCrFeNiV and CoFeMnNiV), since this element was incorporated to the carbonitride structure during sintering. A slight Cr segregation was detected in cermets containing Cr, leading to CrTi-rich alloys in small binder regions. However, a great Cu segregation was produced when CoCrCuFeNi was used, and the formation of two different fcc alloys -a Cu-rich and a Cu-depleted- was observed. Finally, a loss of Mn was also evidenced in CoCrFeMnNi and CoFeMnNiV, probably due to its sublimation at the sintering temperature.
January, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152218
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Preparation and Characterization of Bio-Based PLA/PBAT and Cinnamon Essential Oil Polymer Fibers and Life-Cycle Assessment from Hydrolytic Degradation
Correa-Pacheco, ZN; Black-Solis, JD; Ortega-Gudino, P; Sabino-Gutierrez, MA; Benitez-Jimenez, JJ; Barajas-Cervantes, A; Bautista-Banos, S; Hurtado-Colmenares, LBPolymers, 12 (2020) 38
Show abstract ▽

Nowadays, the need to reduce the dependence on fuel products and to achieve a sustainable development is of special importance due to environmental concerns. Therefore, new alternatives must be sought. In this work, extruded fibers from poly (lactic acid) (PLA) and poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) added with cinnamon essential oil (CEO) were prepared and characterized, and the hydrolytic degradation was assessed. A two-phase system was observed with spherical particles of PBAT embedded in the PLA matrix. The thermal analysis showed partial miscibility between PLA and PBAT. Mechanically, Young's modulus decreased and the elongation at break increased with the incorporation of PBAT and CEO into the blends. The variation in weight loss for the fibers was below 5% during the period of hydrolytic degradation studied with the most important changes at 37 degrees C and pH 8.50. From microscopy, the formation of cracks in the fiber surface was evidenced, especially for PLA fibers in alkaline medium at 37 degrees C. This study shows the importance of the variables that influence the performance of polyester-cinnamon essential oil-based fibers in agro-industrial applications for horticultural product preservation.
January, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/polym12010038
- ‹ previous
- 108 of 410
- next ›














