Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Structural and surface considerations on Mo/ZSM-5 systems for methane dehydroaromatization reaction
Lopez-Martin, A; Caballero, A; Colon, GMolecular Catalysis, 486 (2020) 110787
Show abstract ▽
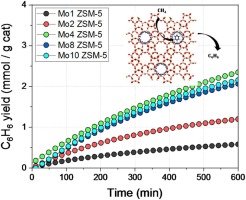
We have prepared a series of Mo/ZSM-5 systems by impregnation method with different metal loading. The optimum performance has been attained for 4% metal loading, yielding to ca. 2 mmol(benzene)/g(ca)(t) at the end of the reaction. The obtained catalysts were widely structural and surface characterized. As Mo content increases, the surface feature of the support is affected specially its mesoporosity. It has been stated the enormous complexity of Mo species present in the studied system. In situ characterization by XPS reveals different reduction and carburization behaviour depending on the Mo content.
May, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2020.110787
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Microwave-assisted sol-gel synthesis of TiO2 in the presence of halogenhydric acids. Characterization and photocatalytic activity
Puga,F.;Navío,J.A.;Jaramillo-Páez,C.;Sánchez-Cid,P.;Hidalgo,M.C.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 394 (2020) 112457
Show abstract ▽
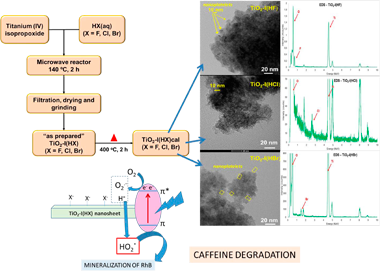
The synthesis of mesoporous TiO2 nanosheets is reported using Ti(IV) Isopropoxide as Ti(IV) precursor. A sol-gel process combined with microwave activation is used. Three different halogenhydric acids (HX), were used to peptise the sol: HF(ac), HCl (ac) and HBr (ac). The three obtained TiO2-I(HX) samples were characterized by XRD, XRF, N2-adsorption, SEM, TEM, DRS and XPS. The three synthesized samples have high values of specific surfaces (between 100 m2/g and 200 m2/g) and similar band gap values (3.2–3.3 eV). The analysis of the surface composition by XPS confirms the presence of the halogenated species (F, Cl or Br) on the surface of each ones of the samples. The nanometric size (ca 5 nm) of the particles for each of the three samples was confirmed by XRD and by TEM. On the other hand, the nature of the halogenated acid used plays a role in the composition of the phases. While the TiO2-I (HF) sample was 100 % anatase, the other samples turned out to be biphasic, showing anatase/rutile in the TiO2-I(HCl) sample and anatase/brookite in the TiO2-I(HBr) sample. The samples were tested under two illumination conditions (UV and visible light) using rhodamine B and caffeine. The indirect role of the halide agent on the photocatalytic activities thereof is discussed.
May, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112457
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optical properties of molybdenum in the ultraviolet and extreme ultraviolet by reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy
Pauly, N; Yubero, F; Tougaard, SApplied Optics, 59 (2020) 4527-4532
Show abstract ▽
Optical properties of polycrystalline molybdenum are determined from ultraviolet up to extreme ultraviolet by reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy (REELS). Calculations are performed within the dielectric response theory by means of the quantitative analysis of electron energy losses at surfaces QUEELS-epsilon (k, omega)-REELS software [Surf. Interface Anal. 36, 824 (2004)] that allows the simulation of inelastic scattering cross sections, using a parametric energy loss function describing the optical response of the material. From this energy loss function, the real and imaginary parts of the dielectric function, the refractive index, and the extinction coefficient are deduced and compared with previously published results.
May, 2020 | DOI: 10.1364/AO.391014
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Premelting of ice adsorbed on a rock surface
Esteso, V; Palacios, SC; MacDowell, LG; Fiedler, J; Parsons, DF; Spallek, F; Miguez, H; Persson, C; Buhmann, SY; Brevik, I; Bostrom, MPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 22 (2020) 11362-11373
Show abstract ▽
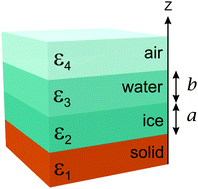
Considering ice-premelting on a quartz rock surface (i.e. silica) we calculate the Lifshitz excess pressures in a four layer system with rock-ice-water-air. Our calculations give excess pressures across (1) ice layer, (2) water layer, and (3) ice-water interface for different ice and water layer thicknesses. We analyse equilibrium conditions where the different excess pressures take zero value, stabilized in part by repulsive Lifshitz interactions. In contrast to previous investigations which considered varying thickness of only one layer (ice or water), here we present theory allowing for simultaneous variation of both layer thicknesses. For a given total thickness of ice and water, this allows multiple alternative equilibrium solutions. Consequently the final state of a system will depend on initial conditions and may explain variation in experimental measurements of the thicknesses of water and ice layers.
May, 2020 | DOI: 10.1039/c9cp06836h
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
In Vitro and In Vivo Study of Titanium Grade IV and Titanium Grade V Implants with Different Surface Treatments
Diaz-Sanchez, RM; de-Paz-Carrion, A; Serrera-Figallo, MA; Torres-Lagares, D; Barranco, A; Leon-Ramos, JR; Gutierrez-Perez, JLMetals, 10 (2020) 449
Show abstract ▽
The aim of our study is to evaluate different implant surface treatments using TiIV and TiV in in vitro and in vivo studies. An in vitro study was established comprising four study groups with treated and untreated TiIV titanium discs (TiIVT and TiIVNT) and treated and untreated TiV titanium discs (TiVT and TiVNT). The surface treatment consisted in a grit blasting treatment with alumina and double acid passivation to modify surface roughness. The surface chemical composition and the surface microstructure of the samples were analyzed. The titanium discs were subjected to cell cultures to determine cell adhesion and proliferation of osteoblasts on them. The in vivo study was carried out on the tibia of three New Zealand rabbits in which 18 implants divided into three experimental groups were placed (TiIVT, TiIVNT, and TiVT). Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) was performed to determine bone density around the implants. The results showed that cell culture had minor adhesion and cell proliferation in TiIVT and TiVT within the first 6 and 24 h. However, no differences were found after 48 h. No statistically significant differences were found in the in vivo micro-CT and histological study; however, there was a positive trend in bone formation in the groups with a treated surface. Conclusions: All groups showed a similar response to in vitro cell proliferation cultures after 48 h. No statistically significant differences were found in the in vivo micro-CT and histological study
April, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/met10040449
- ‹ previous
- 100 of 410
- next ›














