Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Reactividad de Sólidos
Calcium-Looping Performance of Biomineralized CaCO3 for CO2 Capture and Thermochemical Energy Storage
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Valverde, JM; Chacartegui, R; Perez-Maqueda, LAIndustrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 59 (2020) 12924-12933
Show abstract ▽
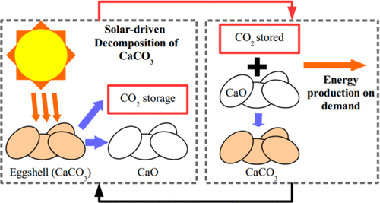
The commercial deployment of calcium-looping (CaL)-based technologies relies on the availability of nontoxic, widely available and cheap CaCO3 rich materials. Biomineralized CaCO3 from waste amply fulfills the aforementioned requirements. In the present work, we study the performance of eggshell and snail shell from food waste as CaO precursors for CaL applications. The results obtained suggest the feasible use of these waste materials. The multicyclic conversion exhibited by biomineralized CaCO3 was comparable to that demonstrated by limestone, which is a commonly proposed material for CaL applications. In addition, the temperature needed to completely calcine biomineralized CaCO3 in short residence times is lower than that required to fully calcine limestone. This would mitigate the energy cost of the technology.
July, 2020 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05997
Reactividad de Sólidos
ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for analysis of multi-step kinetics
Vyazovkin, S; Burnham, AK; Favergeon, L; Koga, N; Moukhina, E; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sbirrazzuoli, NThermochimica Acta, 689 (2020) 178597
Show abstract ▽
The present recommendations have been developed by the Kinetics Committee of the International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (ICTAC). The recommendations provide guidance on kinetic analysis of multi-step processes as measured by thermal analysis methods such as thermogravimetry (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Ways of detecting the multi-step kinetics are discussed first. Then, four different approaches to evaluation of kinetic parameters (the activation energy, the pre-exponential factor, and the reaction model) for individual steps are considered. The approaches considered include multi-step model-fitting as well as distributed reactivity, isoconversional, and deconvolution analyses. For each approach practical advice is offered on its effective usage. Due attention is also paid to the typical problems encountered and to the ways of resolving them. The objective of these recommendations is to help a non-expert with efficiently performing multi-step kinetic analysis and interpreting its results.
July, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2020.178597
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Influence of Sr-doping on structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of synthesized Ca3(PO4)2
Y.Naciri; A.Hsini; Z.Ajmal; A.Bouddouch; B.Bakiz; J.A.Navío; A.Albourine; J-C.Valmalette; M.Ezahri; A.BenlhachemiJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 572 (2020) 269-280
Show abstract ▽
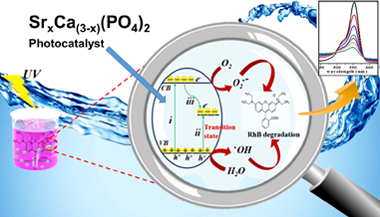
Well-crystallized Ca3(PO4)2 doped and un-doped nano-particles with the maximum strontium content (40 wt% Sr) followed by calcination at 800 °C for 3 h were synthesized via facile co-precipitation method. DTA/TGA, X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive scanning electron microscopy (SEM/EDX), UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectrum (UV–vis DRS), Raman spectroscopy and photoluminescence (PL) techniques were used for material characterization. The (XRD) patterns of as-synthesized Sr-doped Ca3(PO4)2 solid solution samples exhibited a systematic shift toward lower angles by possessing a single rhombohedral crystal structure without any secondary phases. The UV light driven photocatalytic activity was assessed for rhodamine B (RhB) degradation. As a result, ultrafast photodegradation activity was observed after Sr doping. Moreover, the 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 sample showed the highest photocatalytic degradation among the Sr-doped Ca3(PO4)2 samples toward RhB. It was further suggested that as-synthesized 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 superior photocatalytic performance is ascribed to the more proficient partition of photogenerated electron-hole pairs. Furthermore, the involved mechanism of superior photocatalytic performance of the 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 solid solution was also investigated. In addition, regeneration cycles indicated the higher stability of the photocatalyst to be effectively recycled up to four times without any considerable reduction in photocatalytic performance. Thus, these informations further provides us a scalable pathway to fabricate Sr doped Ca3(PO4)2 and its consequent use as an efficient photocatalyst for rhodamine B (RhB) contaminated wastewater treatment.
July, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.105
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Sustainable, High-Barrier Polyaleuritate/Nanocellulose Biocomposites
Tedeschi, G; Guzman-Puyol, S; Ceseracciu, L; Benitez, JJ; Cataldi, P; Bissett, M; Heredia, A; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAACS Sistainable Chemistry & Engineering, 8 (2020) 10682-10690
Show abstract ▽
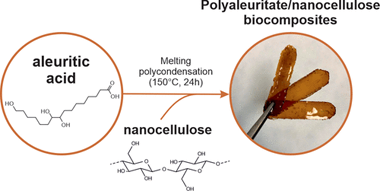
Free-standing and flexible biocomposite films formed by a polyaleuritate matrix and nanocellulose fillers (i.e., cellulose nanofibrils) have been fabricated by a sustainable process. For this, 9,10,16-trihydroxyhexadecanoic (aleuritic) acid from shellac and nanocellulose were blended at different ratios in water through a sonication process. Polymerization of the polyhydroxylated fatty acid into polyaleuritate was induced by a solvent-free, melting polycondensation reaction in the oven. These biocomposites were characterized to evaluate their chemical (by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy) and physical (e.g., density, thermal stability, rigidity, gas permeability, surface energy, etc.) properties. The compatibility between the polyester matrix and the polysaccharide fillers was excellent due to the interaction by H bonds of the polar groups of both components. The addition of nanocellulose increased all determined mechanical parameters as well as the wettability and the barrier properties, while the thermal stability and the water uptake were determined by the polyaleuritate matrix. The physical properties of these biocomposites were compared to those of petroleum-based plastics and bio-based polymers, indicating that the developed materials can represent a sustainable alternative for different applications such as packaging.
July, 2020 | DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00909
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
New biomorphic filters to face upcoming particulate emissions policies: A review of the FIL-BIO-DIESEL project
Orihuela, MP; Chacartegui, R; Martinez-Fernandez, JEnergy, 201 (2020) 117577
Show abstract ▽
With a high number of diesel vehicles worldwide, particulate emission control is an urgent issue with a global impact, from the health of citizens to commercial future of this technology in some transport segments. Particulate filters are widely used in automotive engines to comply emissions regulations, but current technologies have room for improvement as they add additional backpressure in the exhaust system, and efficient on-board regeneration process is challenging.
The Fil-Bio-Diesel Project is a R&D initiative to improve current particle filtration systems, based on the development of novel biomorphic substrates. By replicating the biologic tissue of a wood precursor, a biomorphic silicon carbide with hierarchic orthotropic microstructure can be produced. The porosity, the pore size, and pore orientation of this bioceramic material can be tailored through the selection of a suitable precursor, widening the initially narrow relationship between filtration efficiency and pressure drop that characterizes granular ceramic materials. In this paper the methodology and main results of the Fil-Bio-Diesel Project are presented. This work shows the peculiar advantages of biomorphic silicon carbide through several experimental studies. The results show the potential of this novel filter substrate to be used in future particulate abatement systems.
June, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.117577
- ‹ previous
- 97 of 410
- next ›














