Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
An electrochemical evaluation of nitrogen-doped carbons as anodes for lithium ion batteries
Gomez-Martin, A; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Ruttert, M; Winter, M; Placke, T; Ramirez-Rico, JCarbon, 164 (2020) 261-271
Show abstract ▽
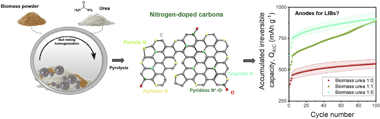
New anode materials beyond graphite are needed to improve the performance of lithium ion batteries (LIBs). Chemical doping with nitrogen has emerged as a simple strategy for enhancing lithium storage in carbon-based anodes. While specific capacity and rate capability are improved by doping, little is known about other key electrochemical properties relevant to practical applications. This work presents a systematic evaluation of electrochemical characteristics of nitrogen-doped carbons derived from a biomass source and urea powder as anodes in LIB half- and full-cells. Results show that doped carbons suffer from a continuous loss in capacity upon cycling that is more severe for higher nitrogen contents. Nitrogen negatively impacts the voltage and energy efficiencies at low charge/discharge current densities. However, as the charge/discharge rate increases, the voltage and energy efficiencies of the doped carbons outperform the non-doped ones. We provide insights towards a fundamental understanding of the requirements needed for practical applications and reveal drawbacks to be overcome by novel doped carbon-based anode materials in LIB applications. With this work, we also want to encourage other researchers to evaluate electrochemical characteristics besides capacity and cycling stability which are mandatory to assess the practicality of novel materials.
August, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.04.003
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Performance trends in wall-flow diesel particulate filters: Comparative analysis of their filtration efficiency and pressure drop
Orihuela, MP; Chacartegui, R; Gomez-Martin, A; Ramirez-Rico, J; Villanueva, JABJournal of Cleaner Production, 60 (2020) 12063
Show abstract ▽
Soot and particulate emissions from the transport sector are a major concern worldwide, given their harmful effects on public health and the environment. On-road vehicles are the main contributing source to this kind of pollution. They are strictly regulated in many countries, with limitations on the number and concentration of released particles, and they must be equipped with particle abatement systems. Wall-flow particulate filters are the most popular and effective devices to reduce particulate emissions from diesel and gasoline vehicles. Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs) have been a recurrent research topic since the last century. There are different research studies analysing different aspects of these systems, at different levels, using different methodologies and different approaches. Their results are not always comparable. This work analyses the latest advances and trends in this technology by comparing two relevant performance parameters: their filtration efficiency and pressure drop. The findings of this study suggest that, in order to be competitive, upcoming DPFs should have filtration efficiencies above 80%, and pressure drops below 10 kPa, for space velocities of 1.5.10(5) h(-1) or more at the clean state. They should reach similar to 100% efficiency after a short operation period, before the soot load reaches 0.2 g/L. Later, they should keep a low pressure drop for a longer time, with a reference of no more than 13 kPa for 6 g/L of soot load. Based on this analysis, this work proposes some test criteria and suggestions for the main parameters.
July, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120863
Reactividad de Sólidos
Calcium-Looping Performance of Biomineralized CaCO3 for CO2 Capture and Thermochemical Energy Storage
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Valverde, JM; Chacartegui, R; Perez-Maqueda, LAIndustrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 59 (2020) 12924-12933
Show abstract ▽
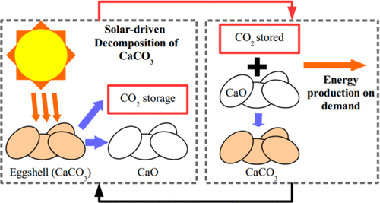
The commercial deployment of calcium-looping (CaL)-based technologies relies on the availability of nontoxic, widely available and cheap CaCO3 rich materials. Biomineralized CaCO3 from waste amply fulfills the aforementioned requirements. In the present work, we study the performance of eggshell and snail shell from food waste as CaO precursors for CaL applications. The results obtained suggest the feasible use of these waste materials. The multicyclic conversion exhibited by biomineralized CaCO3 was comparable to that demonstrated by limestone, which is a commonly proposed material for CaL applications. In addition, the temperature needed to completely calcine biomineralized CaCO3 in short residence times is lower than that required to fully calcine limestone. This would mitigate the energy cost of the technology.
July, 2020 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05997
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Influence of Sr-doping on structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of synthesized Ca3(PO4)2
Y.Naciri; A.Hsini; Z.Ajmal; A.Bouddouch; B.Bakiz; J.A.Navío; A.Albourine; J-C.Valmalette; M.Ezahri; A.BenlhachemiJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 572 (2020) 269-280
Show abstract ▽
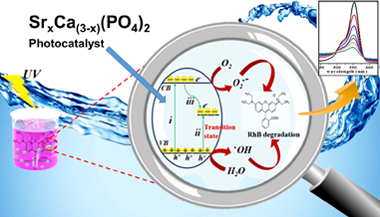
Well-crystallized Ca3(PO4)2 doped and un-doped nano-particles with the maximum strontium content (40 wt% Sr) followed by calcination at 800 °C for 3 h were synthesized via facile co-precipitation method. DTA/TGA, X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive scanning electron microscopy (SEM/EDX), UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectrum (UV–vis DRS), Raman spectroscopy and photoluminescence (PL) techniques were used for material characterization. The (XRD) patterns of as-synthesized Sr-doped Ca3(PO4)2 solid solution samples exhibited a systematic shift toward lower angles by possessing a single rhombohedral crystal structure without any secondary phases. The UV light driven photocatalytic activity was assessed for rhodamine B (RhB) degradation. As a result, ultrafast photodegradation activity was observed after Sr doping. Moreover, the 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 sample showed the highest photocatalytic degradation among the Sr-doped Ca3(PO4)2 samples toward RhB. It was further suggested that as-synthesized 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 superior photocatalytic performance is ascribed to the more proficient partition of photogenerated electron-hole pairs. Furthermore, the involved mechanism of superior photocatalytic performance of the 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 solid solution was also investigated. In addition, regeneration cycles indicated the higher stability of the photocatalyst to be effectively recycled up to four times without any considerable reduction in photocatalytic performance. Thus, these informations further provides us a scalable pathway to fabricate Sr doped Ca3(PO4)2 and its consequent use as an efficient photocatalyst for rhodamine B (RhB) contaminated wastewater treatment.
July, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.105
Reactividad de Sólidos
ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for analysis of multi-step kinetics
Vyazovkin, S; Burnham, AK; Favergeon, L; Koga, N; Moukhina, E; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sbirrazzuoli, NThermochimica Acta, 689 (2020) 178597
Show abstract ▽
The present recommendations have been developed by the Kinetics Committee of the International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (ICTAC). The recommendations provide guidance on kinetic analysis of multi-step processes as measured by thermal analysis methods such as thermogravimetry (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Ways of detecting the multi-step kinetics are discussed first. Then, four different approaches to evaluation of kinetic parameters (the activation energy, the pre-exponential factor, and the reaction model) for individual steps are considered. The approaches considered include multi-step model-fitting as well as distributed reactivity, isoconversional, and deconvolution analyses. For each approach practical advice is offered on its effective usage. Due attention is also paid to the typical problems encountered and to the ways of resolving them. The objective of these recommendations is to help a non-expert with efficiently performing multi-step kinetic analysis and interpreting its results.
July, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2020.178597
- ‹ previous
- 96 of 410
- next ›














