Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Reactividad de Sólidos
Graphene-coated Ti-Nb-Ta-Mn foams: A promising approach towards a suitable biomaterial for bone replacement
Lascano, S; Chavez-Vasconez, R; Munoz-Rojas, D; Aristizabal, J; Arce, B; Parra, C; Acevedo, C; Orellana, N; Reyes-Valenzuela, M; Gotor, FJ; Arevalo, C; Torres, YSurface & Coatings Technology, 401 (2020) 126250
Show abstract ▽
The design of bone implants with proper biological and mechanical properties remains a challenge in medical implantology. The use of bioactive coatings has been shown to improve the biocompatibility of the implant surface. In this study, a new approach including porous scaffolds, beta-Ti alloys and nanocoatings to design new bone implants is presented. Porous Ti-Nb-Ta-xMn alloys (x: 2, 4, and 6 wt%) substrates were obtained by powder metallurgy and the effect of the porosity and Mn content on mechanical properties was studied. CVD single-layer graphene was transferred onto the porous substrates that presented the best mechanical response (x: 4 wt%) for further evaluation of in vitro cell behavior (biocompatibility and cell adhesion). Cytotoxicity and biocompatibility tests confirmed that cell adhesion and proliferation were successfully achieved on graphene-coated porous substrates, confirming these systems are potential candidates for using in partial bone tissue replacement.
November, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126250
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Unraveling Discharge and Surface Mechanisms in Plasma-Assisted Ammonia Reactions
Navascues, P; Obrero-Perez, JM; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Gomez-Ramirez, AACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 8 (2020) 14855-14866
Show abstract ▽
Current studies on ammonia synthesis by means of atmospheric pressure plasmas respond to the urgent need of developing less environmentally aggressive processes than the conventional Haber-Bosch catalytic reaction. Herein, we systematically study the plasma synthesis of ammonia and the much less investigated reverse reaction (decomposition of ammonia into nitrogen and hydrogen). Besides analyzing the efficiency of both processes in a packed-bed plasma reactor, we apply an isotope-exchange approach (using D-2 instead of H-2) to study the reaction mechanisms. Isotope labeling has been rarely applied to investigate atmospheric plasma reactions, and we demonstrate that this methodology may provide unique information about intermediate reactions that, consuming energy and diminishing the process efficiency, do not effectively contribute to the overall synthesis/decomposition of ammonia. In addition, the same methodology has demonstrated the active participation of the interelectrode material surface in the plasma-activated synthesis/decomposition of ammonia. These results about the involvement of surface reactions in packed-bed plasma processes, complemented with data obtained by optical emission spectroscopy analysis of the plasma phase, have evidenced the occurrence of inefficient intermediate reaction mechanisms that limit the efficiency and shown that the rate-limiting step for the ammonia synthesis and decomposition reactions are the formation of NH* species in the plasma phase and the electron impact dissociation of the molecule, respectively.
October, 2020 | DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c04461
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Multiple pollutants removal by functionalized heterostructures based on Na-2-Mica
Pazos, MC; Bravo, LR; Ramos, SE; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 196 (2020) 105749
Show abstract ▽
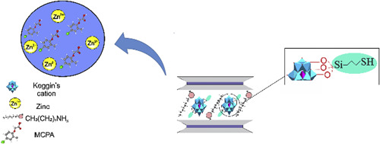
Organomica, C8-2-Mica, was obtained from a high charged synthetic mica, Na-2-Mica, by cation exchange reaction with octylammonium cations and these were used to host other bulky guest species such as polyhydroxy aluminium cations, Al(13)20. The hydrolization of 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane (MPTMS) allowed the covalent attachment with hydroxyl groups of the oligomeric cation, providing thiol groups that create specific adsorption sites, Al(13)20/SH. The structure of the adsorbents was analysed by XRD and Infrared spectroscopy and these were tested as an adsorbent for the removal of zinc and herbicide MCPA from aqueous solutions. C8-2-Mica was the best adsorbent for MCPA and thiol groups favoured the adsorption of Zn2+. Moreover, Al(13)20/SH showed excellent adsorptive properties for the simultaneous adsorption of MCPA and Zn2+.
October, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2020.105749
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Internal quantum efficiency and time signals from intensity-modulated photocurrent spectra of perovskite solar cells
Riquelme, A; Galvez, FE; Contreras-Bernal, L; Miguez, H; Anta, JAJournal of Applied Physics, 128 (2020) 133103
Show abstract ▽
Intensity Modulated Photocurrent Spectroscopy (IMPS) is a small-perturbation optoelectronic technique that measures the quantum efficiency of a photoelectrochemical device as a function of optical excitation frequency. Metal Halide Perovskites (MHPs) are mixed electronic-ionic semiconductors with an extraordinary complex optoelectronic behavior and a record efficiency surpassing 25%. In this paper, we propose a simplified procedure to analyze IMPS data in MHPs based on the analysis of the internal quantum efficiency and the time signals featuring in the frequency spectra. In this procedure, we look at the change of each signal when optical excitation wavelength, photon flux, and temperature are varied for an archetypical methyl ammonium lead iodide solar cell. We use drift-diffusion modeling and comparison with relatively simpler dye-sensitized solar cells (DSC) with viscous and non-viscous electrolytes to help us to understand the origin of the three signals appearing in MHP cells and the measurement of the internal quantum efficiency.
October, 2020 | DOI: 10.1063/5.0013317
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Upgrading the PtCu intermetallic compounds: The role of Pt and Cu in the alloy
Castillo, R; Garcia, ED; Santos, JL; Centeno, MA; Sarria, FR; Daturi, M; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 356 (2020) 390-398
Show abstract ▽
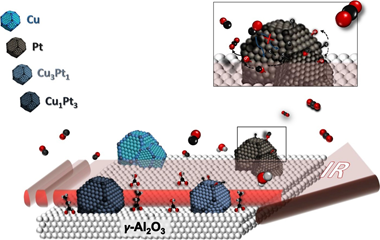
This work is devoted to the study of the role of both metals in the intermetallic PtxCuy/ γ Al2O3 catalysts commonly employed in CO-PROX reaction. Therefore, monometallic Pt and Cu based catalysts and PtCu intermetallic compound with different molar ratios (Pt3Cu1 and Pt1Cu3) supported catalysts were carefully synthesized and deeply characterized. Room temperature CO adsorptions by FTIR spectroscopy were carried out on the mono- and intermetallic catalysts being the monometallic catalyst determinant for the study. From the analysis of the nature of the platinum surface in Pt/ γ Al2O3, we have demonstrated that the role of Pt sites is based in the CO dissociation for the CO2 formation and also how the platinum surface is partially blocked by leftovers from the synthesis. Moreover, the study of the Cu/ γ Al2O3 and the bimetallic catalysts PtxCuy/ γ Al2O3 allowed elucidating the effect of the copper in the metallic site and support interphase as well as the role of copper in the hydrocarbon oxidation.
October, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2019.11.026
- ‹ previous
- 92 of 410
- next ›














