Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Elucidating the Promotional Effect of Cerium in the Dry Reforming of Methane
Rodriguez-Gomez, A; Lopez-Martin, A; Ramirez, A; Gascon, J; Caballero, AChemcatchem, 13 (2021) 553-563
Show abstract ▽
A series of Ni-Ce catalysts supported on SBA-15 has been prepared by co-impregnation, extensively characterized and evaluated in the carbon dioxide reforming of methane (DRM). The characterization by TEM, XRD and TPR has allowed us to determine the effect of metal loading on metal dispersion. Cerium was found to improve nickel location inside the mesopores of SBA-15 and to suppress coke formation during the DRM reaction. The analysis by XPS allowed us to associate the high cerium dispersion with the presence of low-coordinated Ce3+ sites, being main responsible for its promotional effect. A combination of XAS and XPS has permitted us to determine the physicochemical properties of metals under reduction conditions. The low nickel coordination number determined by XAS in N-Ce doped systems after reduction suggests the generation of very small nickel particles which showed greater catalytic activity and stability in the reaction, and a remarkable resistance to coke formation.
January, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/cctc.202001527
Materiales Coloidales
Dysprosium and Holmium Vanadate Nanoprobes as High-Performance Contrast Agents for High-Field Magnetic Resonance and Computed Tomography Imaging
Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Nunez, NO; Caro, C; Garcia-Martin, ML; Fernandez-Afonso, Y; de la Fuente, JM; Balcerzyk, M; Ocana, MInorganic Chemistry, 60 (2021) 152-160
Show abstract ▽
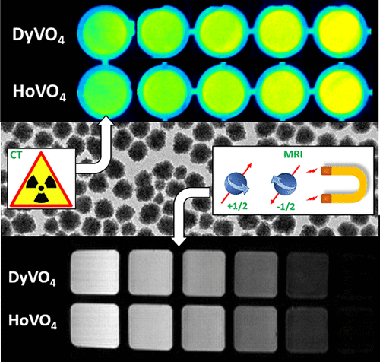
We describe a wet chemical method for the synthesis of uniform and well-dispersed dysprosium vanadate (DyVO4) and holmium vanadate (HoVO4) nanoparticles with an almost spherical shape and a mean size of ∼60 nm and their functionalization with poly(acrylic acid). The transverse magnetic relaxivity of both systems at 9.4 T is analyzed on the basis of magnetic susceptibility and magnetization measurements in order to evaluate their potential for application as high-field MRI contrast agents. In addition, the X-ray attenuation properties of these systems are also studied to determine their capabilities as computed tomography contrast agent. Finally, the colloidal stability under physiological pH conditions and the cytotoxicity of the functionalized NPs are also addressed to assess their suitability for bioimaging applications.
January, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c02601
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Enhanced Directional Light Extraction from Patterned Rare-Earth Phosphor Films
Cabello-Olmo, E; Molet, P; Mihi, A; Lozano, G; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, 9 (2021) 2001611
Show abstract ▽
The combination of light‐emitting diodes (LEDs) and rare earth (RE) phosphors as color‐converting layers comprises the basis of solid‐state lighting. Indeed, most LED lamps include a photoluminescent coating made of phosphor material, i.e., crystalline matrix suitably doped with RE elements, to produce white light from a blue or ultraviolet LED chip. Transparent phosphor‐based films constitute starting materials for new refined emitters that allow different photonic designs to be implemented. Among the different photonic strategies typically employed to tune or enhance emission, surface texturing has proved its versatility and feasibility in a wide range of materials and devices. However, most of the nanofabrication techniques cannot be applied to RE phosphors directly because of their chemical stability or because of their cost. The first monolithic patterned structure of down‐shifting nanophosphors with square arrays of nanoholes with different lattice parameters is reported in this study. It is shown that a low‐cost soft‐nanolithography procedure can be applied to red‐emitting nanophosphors (GdVO4:Eu3+ nanocrystals) to tune their emission properties, attaining a twofold directional enhancement of the emitted light at predesigned emission wavelengths in specific directions.
January, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.202001611
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Disentangling Electron–Phonon Coupling and Thermal Expansion Effects in the Band Gap Renormalization of Perovskite Nanocrystals
Rubino, A; Francisco-Lóprez, A.; Baker, A.J., Petrozza, A.; Calvo, M.E.; Goñi, A.R.; Míguez, H.Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 12 (2021) 569-575
Show abstract ▽
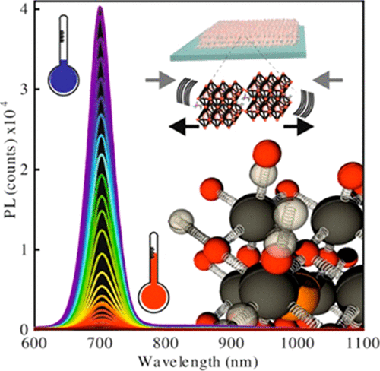
The complex electron–phonon interaction occurring in bulk lead halide perovskites gives rise to anomalous temperature dependences, like the widening of the electronic band gap as temperature increases. However, possible confinement effects on the electron–phonon coupling in the nanocrystalline version of these materials remain unexplored. Herein, we study the temperature (ranging from 80 K to ambient) and hydrostatic pressure (from atmospheric to 0.6 GPa) dependence of the photoluminescence of ligand-free methylammonium lead triiodide nanocrystals with controlled sizes embedded in a porous silica matrix. This analysis allowed us to disentangle the effects of thermal expansion and electron–phonon interaction. As the crystallite size decreases, the electron–phonon contribution to the gap renormalization gains in importance. We provide a plausible explanation for this observation in terms of quantum confinement effects, showing that neither thermal expansion nor electron–phonon coupling effects may be disregarded when analyzing the temperature dependence of the optoelectronic properties of perovskite lead halide nanocrystals.
January, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c03042
2020
2020
Reactividad de Sólidos
Control of experimental conditions in reaction flash-sintering of complex stoichiometry ceramics
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Roman-Gonzalez, D; Perez-Maqueda, LACeramics International, 46 (2020) 29413-29420
Show abstract ▽
The inherent potential of reaction flash-sintering for the preparation of complex oxides is evidenced by the one-step synthesis and densification of a ceramic of complex stoichiometry. The system Bi0.93La0.07FeO3, a multi-ferroic ceramic with promising technological applications, has been chosen. This system presents three different metals in its composition and it is extremely challenging to prepare by conventional procedures. Non-stoichiometric materials with unwilling secondary phases are usually obtained by conventional methods, due to the high volatility of bismuth oxide at the temperatures required for inducing the solid-solid reactions. Here, it is demonstrated that a careful control of the experimental flash conditions (applied electric field and selected current density limit) is required to obtain a high quality ceramic. Small deviations from the optimum conditions result in either non-stoichometric or poorly densified samples.
December, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.091
- ‹ previous
- 88 of 410
- next ›














