Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Electrical and reaction performances of packed-bed plasma reactors moderated with ferroelectric or dielectric materials
Gomez-Ramirez, A; Alvarez, R; Navascues, P; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Palmero, A; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Processes and Polymers, (2021) e2000193
Show abstract ▽
The operational behavior of packed-bed plasma reactors depends on the dimension, shape, and chemical properties of the pellets used as moderators, but little information exists about the influence of their specific dielectric properties. Herein, we comparatively study the electrical behavior of a packed-bed reactor filled with pellets of either dielectric (Al2O3 and glass) or ferroelectric (BaTiO3 and lead zirconate titanate) materials. We found that plasma current was higher for ferroelectrics and presented a nonlineal dependence on voltage. Moreover, for BaTiO3, we found a drastic decrease at around its relatively low Curie temperature. Differences in electrical behavior have a direct effect on the reactor performance, as illustrated for the ammonia synthesis, demonstrating the importance of moderator material dielectric properties and their dependence on temperature.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202000193
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synergizing carbon capture and utilization in a biogas upgrading plant based on calcium chloride: Scaling-up and profitability analysis
Baena-Moreno, FM; Reina, TR; Rodriguez-Galan, M; Navarrete, B; Vilches, LFScience of The Total Environment, 758 (2021) 143645
Show abstract ▽
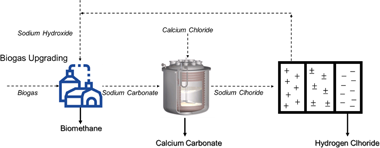
Herein we analyze the profitability of a novel regenerative process to synergize biogas upgrading and carbon dioxide utilization. Our proposal is a promising alternative which allows to obtain calcium carbonate as added value product while going beyond traditional biogas upgrading methods with high thermal energy consumption. Recently we have demonstrated the experimental viability of this route. In this work, both the scale-up and the profitability of the process are presented. Furthermore, we analyze three representative scenarios to undertake a techno-economic study of the proposed circular economy process. The scale-up results demonstrate the technical viability of our proposal. The precipitation efficiency and the product quality are still remarkable with the increase of the reactor size. The techno-economic analysis reveals that the implementation of this circular economy strategy is unprofitable without subsidies. Nonetheless, the results are somehow encouraging as the subsides needed to reach profitability are lower than in other biogas upgrading and carbon dioxide utilization proposals. Indeed, for the best-case scenario, a feed-in tariff incentive of 4.3 (sic)/MWh makes the approach profitable. A sensitivity study through tornado analysis is also presented, revealing the importance of reducing bipolar membrane electrodialysis energy consumption. Overall our study envisages the big challenge that the EU faces during the forthcoming years. The evolution towards bio-based and circular economies requires the availability of economic resources and progress on engineering technologies.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143645
Materiales Avanzados
Mining Wastes of an Albite Deposit as Raw Materials for Vitrified Mullite Ceramics
Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Garzon, E; Perez-Villarejo, L; Angelopoulos, GN; Eliche-Quesada, DMinerals, 11 (2021) 232
Show abstract ▽
In this work, an examination of mining wastes of an albite deposit in south Spain was carried out using X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), particle size analysis, thermodilatometry and Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) and Thermogravimetric (TG) analysis, followed by the determination of the main ceramic properties. The albite content in two selected samples was high (65-40 wt. %), accompanied by quartz (25-40 wt. %) and other minor minerals identified by XRD, mainly kaolinite, in agreement with the high content of silica and alumina determined by XRF. The content of Na2O was in the range 5.44-3.09 wt. %, being associated with albite. The iron content was very low (<0.75 wt. %). The kaolinite content in the waste was estimated from similar to 8 to 32 wt. %. The particle size analysis indicated values of 11-31 wt. % of particles <63 mu m. The ceramic properties of fired samples (1000-1350 degrees C) showed progressive shrinkage by the thermal effect, with water absorption and open porosity almost at zero at 1200-1250 degrees C. At 1200 ffiC, the bulk density reached a maximum value of 2.38 g/cm(3). An abrupt change in the phase evolution by XRD was found from 1150 to 1200 degrees C, with the disappearance of albite by melting in accordance with the predictions of the phase diagram SiO2-Al2O3-Na2O and the system albite-quartz. These fired materials contained as main crystalline phases quartz and mullite. Quartz was present in the raw samples and mullite was formed by decomposition of kaolinite. The observation of mullite forming needle-shape crystals was revealed by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). The formation of fully densified and vitrified mullite materials by firing treatments was demonstrated.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/min11030232
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Long-term low friction maintenance and wear reduction on the ventral scales in snakes
Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Schaber, CF; Gorb, SNMaterials Letters, 285 (2021) 129011
Show abstract ▽
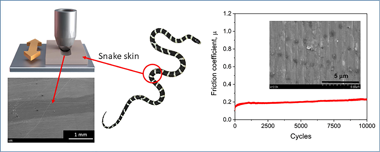
Snake skins evolved to withstand permanent friction and wear during sliding. Here, the microstructure of ventral scales of the snake Lampropeltis getula californiae was analyzed using scanning electron microscopy, and the long-term dynamic friction behavior was investigated by reciprocating sliding friction tests. A smooth epoxy resin with similar elasticity modulus and hardness was used for comparison purposes. Strong differences in frictional and wear mechanisms between the two materials were revealed in spite of similar mechanical properties. Snake skin showed a considerably lower frictional coefficient that kept stable over several thousands of sliding cycles. A reduction of the stick-slip behavior was also denoted by analyzing the variation of the friction coefficient in the forward and reverse motion influencing the wear mechanism. This frictional behavior can be explained by three different but complementary mechanisms: fibrous layered composite material of the skin with a gradient of material properties, surface microstructure, and the presence of ordered layers of lipid molecules at the skin surface.
February, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.129011
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Impact of Tb4+ and morphology on the thermal evolution of Tb-doped TiO2 nanostructured hollow spheres and nanoparticles
Colomer, MT; Rodriguez, E; Moran-Pedroso, M; Vattier, F; de Andres, AJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 853 (2021) 156973
Show abstract ▽
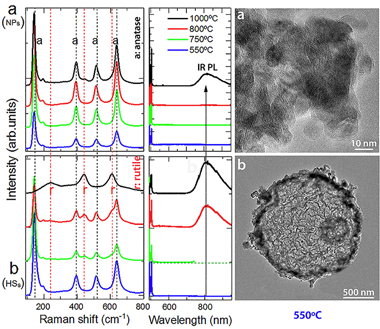
Tb-doped TiO2 hollow spheres (HSs) in the range 0.0-2.0 at.% have been synthesized by the first time to the best of our knowledge. The HSs are compared with nanoparticles (NPs) to evaluate the impact of morphology on their physicochemical and photoluminescence (PL) behavior upon increasing calcination temperature. After calcination at 550 degrees C, the particles are anatase with a primary average size of 10.0 +/- 0.2 nm for the NPs and 12.0 +/- 0.2 nm for those that form the micron sized hollow spheres of 1.8 +/- 0.2 mu m diameter and ca. 64 nm shell thickness. The temperature of the anataseerutile transition is found to be strongly dependent on the presence of Tb as well as on morphology. Contrarily to the usual stabilization of anatase when doping with trivalent rare-earth ions, the transition temperature is reduced when doping with Tb. The rutile phase is further favored for the HSs compared to the NPs probably related to the low density of the HSs and/or a more efficient packing density and/or a bigger crystal size of the nanoparticles that form those spheres with respect to the packing and the size of the NPs and/or the crystal size of the nanoparticles of the HSs with respect to the size of the NPs. Only a slight unit-cell volume increase for the anatase structure is observed upon Tb doping, in both the NPs and in the HSs, contrary to the expected increment due to the larger ionic radius of Tb3+ compared to Ti4+. In addition, the intensity of the characteristic f-f Tb3+ emission bands is extremely weak both in the anatase and rutile phases. The transition is accompanied with the emergence of an infrared emission band centered at 810 nm related to the formation of defects during the structural transformation providing deep levels in the gap that partly quench the f-f emissions in the rutile phase. The results are consistent with the presence of Tb in both +3 and +4 valence states. XPS measurements confirmed the presence of Tb3+ as well as of Tb4+ in both HSs and NPs. The large fraction of Tb4+ present in the samples originates the weak f-f emission intensity, an only slight increase of the cell parameters and the destabilization of the anatase phase.
February, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156973
- ‹ previous
- 84 of 410
- next ›














