Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Biogas Conversion to Syngas Using Advanced Ni-Promoted Pyrochlore Catalysts: Effect of the CH4/CO2 Ratio
le Sache, E; Moreno, AA; Reina, TRFrontiers in Chemistry, 9 (2021) 672419
Show abstract ▽
Biogas is defined as the mixture of CH4 and CO2 produced by the anaerobic digestion of biomass. This particular mixture can be transformed in high valuable intermediates such as syngas through a process known as dry reforming (DRM). The reaction involved is highly endothermic, and catalysts capable to endure carbon deposition and metal particle sintering are required. Ni-pyrochlore catalysts have shown outstanding results in the DRM. However, most reported data deals with CH4/CO2 stoichiometric ratios resulting is a very narrow picture of the overall biogas upgrading via DRM. Therefore, this study explores the performance of an optimized Ni-doped pyrochlore, and Ni-impregnated pyrochlore catalysts in the dry reforming of methane, under different CH4/CO2 ratios, in order to simulate various representatives waste biomass feedstocks. Long-term stability tests showed that the ratio CH4/CO2 in the feed gas stream has an important influence in the catalysts' deactivation. Ni doped pyrochlore catalyst, presents less deactivation than the Ni-impregnated pyrochlore. However, biogas mixtures with a CH4 content higher than 60%, lead to a stronger deactivation in both Ni-catalysts. These results were in agreement with the thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of the post reacted samples that showed a very limited carbon formation when using biogas mixtures with CH4 content <60%, but CH4/CO2 ratios higher than 1.25 lead to an evident carbon deposition. TGA analysis of the post reacted Ni impregnated pyrochlore, showed the highest amount of carbon deposited, even with lower stoichiometric CH4/CO2 ratios. The later result indicates that stabilization of Ni in the pyrochlore structure is vital, in order to enhance the coke resistance of this type of catalysts.
April, 2021 | DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.672419
Reactividad de Sólidos
Enhancing the electrical conductivity of in-situ reduced graphene oxide-zirconia composites through the control of the processing routine
Lopez-Pernia, C; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, RCeramics International, 47 (2021) 9382-9391
Show abstract ▽
Graphene oxide (GO) was mixed with 3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (3YTZP) using two powder processing routines: a colloidal method in an aqueous solution and a combination of ultrasonication with highenergy planetary ball milling in wet conditions. Highly densified 3YTZP composites with reduced GO (rGO) were consolidated by Spark Plasma Sintering. The in-situ reduction of GO was successfully achieved during the high temperature sintering process and a detailed study of the restoration of the graphene structure in the sintered composites has been made by Raman spectroscopy. Although no differences between the composites prepared by the two processing methods were found in the distribution of the rGO throughout the 3YTZP matrix for high rGO contents (i.e. the composites with 5 and 10 vol% rGO), a better distribution of the graphene phase was found in the composites with 1 and 2.5 vol% rGO prepared by planetary ball milling. This result, together with a better reduction of the GO in these composites, led to the obtaining of rGO/3YTZP composites with a better behavior in terms of electrical conductivity: an electrical percolation threshold below 2.5 vol% rGO and a high electrical conductivity value (-610 S/m for 10 vol% rGO).
April, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.069
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Form Birefringence in Resonant Transducers for the Selective Monitoring of VOCs under Ambient Conditions
Oliva-Ramirez, Manuel; Lopez-Santos, Carmen; Berthon, Hermine; Goven, Mathilde; Portoles, Jose; Gil-Rostra, Jorge; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Yubero, FranciscoACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 13 (2021) 19148-19158
Show abstract ▽
In this work, we have developed a new kind of nanocolumnar birefringent Bragg microcavity (BBM) that, tailored by oblique angle deposition, behaves as a selective transducer of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Unlike the atomic lattice origin of birefringence in anisotropic single crystals, in the BBM, it stems from an anisotropic self-organization at the nanoscale of the voids and structural elements of the layers. The optical adsorption isotherms recorded upon exposure of these nanostructured systems to water vapor and VOCs have revealed a rich yet unexplored phenomenology linked to their optical activity that provides both capacity for vapor identification and partial pressure determination. This photonic response has been reproduced with a theoretical model accounting for the evolution of the form birefringence of the individual layers upon vapor condensation in nanopores and internanocolumnar voids. BBMs that repel water vapor but are accessible to VOCs have been also developed through grafting of their internal surfaces with perfluorooctyltriethoxysilane molecules. These nanostructured photonic systems are proposed for the development of transducers that, operating under environmental conditions, may respond specifically to VOCs without any influence by the degree of humidity of the medium.
April, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acsami.1c02499
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Organophilization of acid and thermal treated sepiolite for its application in BTEX adsorption from aqueous solutions
Varela, CF; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDJournal of Water Process Engineering, 40 (2021) 101949
Show abstract ▽
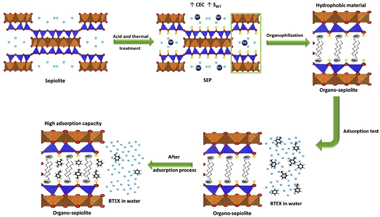
Acid and thermal treated sepiolite was organophilized by cationic exchange with several alkylammonium cations (octylammonium, hexadecylammonium, tetradecyltrimethylammonium, and hexadecyltrimethylammonium). The adsorption capacity of BTEX from aqueous solutions was evaluated through the adsorption isotherms performed in batch. The results were analysed using three isotherm models: Freundlich, Langmuir and Dubinin-Radushkevich (D-R model). The behaviour of adsorption isotherm suggested the multilayer coverage on a heterogeneous surface, which is according to the Freundlich isotherm model. The thermodynamic analyse using the D-R model show that physical mechanisms govern the process. The maximum adsorption capacity of BTEX on the obtained materials was in the range values of 81.19 mg g(-1) - 1448.42 mg g(-)(1), which are higher than those reported up to now. The organo-sepiolite materials exhibit a high potential in the adsorption of BTEX compounds from aqueous solutions.
April, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.101949
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Rietveld Refinement, mu-Raman, X-ray Photoelectron, and Mossbauer Studies of Metal Oxide-Nanoparticles Growth on Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Oxide
Ramos-Guivar, JA; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, JC; Litterst, FJ; Passamani, ECCrystal Growth & Design, 21 (2021) 2128-2141
Show abstract ▽
Applying a modified coprecipitation method, maghemite and anatase nanoparticles embedded in graphene oxide and multiwall carbon nanotube frameworks were prepared, and a detailed structural characterization is presented. Transmission electron images have revealed that the multiwall carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide act as substrates to reduce the nanoparticle agglomeration with narrow sizes of ca. 9-20 nm, in agreement with the results of the Rietveld refinement, which have also indicated their crystallite apparent size and shapes using the spherical harmonics approach. In structural studies of maghemite nanoparticles by Raman spectroscopy, it was found that the effect of optical density and laser power intensity plays a significant role. When no optical filter was located between the powder sample and the laser source, a transformation from the gamma-Fe2O3 to the alpha-Fe2O3 phase was observed, as demonstrated by the disappearance of the characteristic broad Raman peak (A(1g)) of the gamma-Fe2O3 phase when increasing the laser power. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy has also brought insights into the functionalization mechanism, suggesting that the one-pot reduction of the graphene oxide is favored by the alkaline gamma-Fe2O3 nanoparticle growth. The temperature dependence of the Fe-57 Mossbauer spectra has indicated that the effective anisotropy constant of Fe oxide-based nanoparticles is similar to that of bulk maghemite, and magnetic relaxation of Fe3+ spins depends on particle sizes.
April, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.0c01551
- ‹ previous
- 79 of 410
- next ›














