Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemically synthesized ternary chalcogenide Cu3SbS4 powders in a laboratory and an industrial mill
Dutkova, E; Sayagues, MJ; Fabian, M; Balaz, M; Achimovicova, MMaterials Letters, 291 (2021) 129566
Show abstract ▽
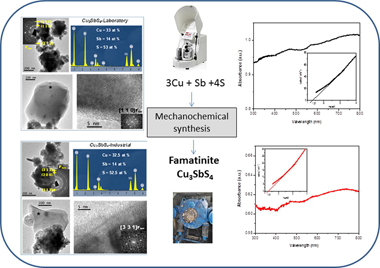
In this work, we demonstrate the use of elemental precursors (Cu, Sb, S) to synthesize famatinite Cu3SbS4 using a laboratory planetary ball milling and an industrial eccentric vibratory milling. Cu3SbS4 was prepared for 120 min and 180 min in laboratory and industrial mill, respectively, with the utilization of protective atmosphere. The Cu3SbS4 prepared in the laboratory and industrial mill with crystallite size 14 nm and 10 nm, respectively, was confirmed by both LeBail refinement of the X-ray powder diffraction data and transmission electron microscopy. The determined band gap energy 1.31 eV and 1.24 eV is blue-shifted relative to the bulk Cu3SbS4. The synthesis of Cu3SbS4 by a scalable milling process represents a prospective route for mass production of material with potential photovoltaic properties. In this work, we demonstrate the use of elemental precursors (Cu, Sb, S) to synthesize famatinite Cu3SbS4 using a laboratory planetary ball milling and an industrial eccentric vibratory milling. Cu3SbS4 was prepared for 120 min and 180 min in laboratory and industrial mill, respectively, with the utilization of protective atmosphere. The Cu3SbS4 prepared in the laboratory and industrial mill with crystallite size 14 nm and 10 nm, respectively, was confirmed by both LeBail refinement of the X-ray powder diffraction data and transmission electron microscopy. The determined band gap energy 1.31 eV and 1.24 eV is blue-shifted relative to the bulk Cu3SbS4. The synthesis of Cu3SbS4 by a scalable milling process represents a prospective route for mass production of material with potential photovoltaic properties.
May, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2021.129566
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Toward Commercialization of Stable Devices: An Overview on Encapsulation of Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Perovskite Solar Cells
Aranda, Clara A.; Calio, Laura; Salado, ManuelCrystals, 11 (2021) 519
Show abstract ▽
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) represent a promising technology for energy harvesting due to high power conversion efficiencies up to 26%, easy manufacturing, and convenient deposition techniques, leading to added advantages over other contemporary competitors. In order to promote this technology toward commercialization though, stability issues need to be addressed. Lately, many researchers have explored several techniques to improve the stability of the environmentally-sensitive perovskite solar devices. Challenges posed by environmental factors like moisture, oxygen, temperature, and UV-light exposure, could be overcome by device encapsulation. This review focuses the attention on the different materials, methods, and requirements for suitable encapsulated perovskite solar cells. A depth analysis on the current stability tests is also included, since accurate and reliable testing conditions are needed in order to reduce mismatching involved in reporting the efficiencies of PSC.
May, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/cryst11050519
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
New Insights on the Conversion Reaction Mechanism in Metal Oxide Electrodes for Sodium-Ion Batteries
Mosa, J; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Aparicio, MNanomaterials, 11 (2021) 966
Show abstract ▽
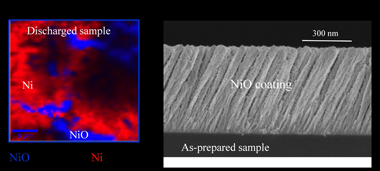
Due to the abundance and low cost of exchanged metal, sodium-ion batteries have attracted increasing research attention for the massive energy storage associated with renewable energy sources. Nickel oxide (NiO) thin films have been prepared by magnetron sputtering (MS) deposition under an oblique angle configuration (OAD) and used as electrodes for Na-ion batteries. A systematic chemical, structural and electrochemical analysis of this electrode has been carried out. The electrochemical characterization by galvanostatic charge-discharge cycling and cyclic voltammetry has revealed a certain loss of performance after the initial cycling of the battery. The conversion reaction of NiO with sodium ions during the discharge process to generate sodium oxide and Ni metal has been confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) and micro-Raman analysis. Likewise, it has been determined that the charging process is not totally reversible, causing a reduction in battery capacity.
April, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/nano11040966
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Novel procedure for studying laser-surface material interactions during scanning laser ablation cleaning processes on Cu-based alloys
Di Francia, E; Lahoz, R; Neff, D; Rico, V; Nuns, N; Angelini, E; Grassini, SApplied Surface Science, 544 (2021) art. 178820
Show abstract ▽
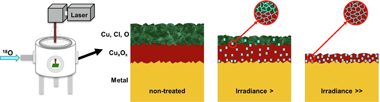
Laser ablation is an effective method to clean Cu-based alloys. A novel procedure of characterisation was developed involving O-18 isotopes evaluated by ToF-SIMS spectroscopy to assess the driving mechanisms of laser-surface interactions. The presence of re-oxidised compounds was detected, discerning between the oxygen from the corrosion layer and the one introduced by the interaction with the laser (that was generated in a controlled atmosphere of O-18 diluted in N-2). A set of samples treated with different laser conditions were characterised by FESEM and mu Raman. The results have shown that re-oxidation phenomenon can occur and its selectivity depends on the laser conditions.
April, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148820
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Fluorinated and platinized Titania for Glycerol oxidation
Murcia, J.J.; Bautista, E; Ávila Martínez, E.G.; Rangel R.N.; Romero, R.; Cubillos Lobo, J.A.; Rojas Sarmiento, H.A.; Hernández, J.S.; Cárdenas, O.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Navío, J.A.; Baeza, R.Materials Proceedings, 4 (2021) 37
Show abstract ▽
In this research, photocatalysts based on TiO2 modified by fluorination and platinum addition were evaluated in the glycerol oxidation. These materials were characterized by different instrumental analysis techniques to determine the physicochemical properties. It was found that the surface modification lead to improve the materials absorption in the Visible region of the electromagnetic spectra and to increase the surface area of TiO2. By HPLC analysis was possible to observed that the photocatalysts 0.5% Pt-F-TiO2 showed the highest yield and selectivity towards glyceraldehyde (GAL). It was also observed that the increase in the platinum content until values of 2% had a negative effect in the effectiveness of fluorinated Titania in the glycerol photo-oxidation. The fluorination and platinum addition modify some physicochemical properties of TiO2, leading also to modify the reaction mechanism and selectivity during glycerol partial photo-oxidation and the dose of photocatalysts is an important reaction condition to obtain GAL and Dyhidroxyacetone (DHA) with yields above to 70%.
April, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/IOCN2020-07792
- ‹ previous
- 78 of 410
- next ›














