Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Unveiling mechanochemistry: Kinematic-kinetic approach for the prediction of mechanically induced reactions
Gil-González, E.; Rodríguez-Laguna, M.d.R.; Sánchez-Jiménez, P.E.; Perejón, A.; Pérez-Maqueda, L.A.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 866 (2021) 158925
Show abstract ▽
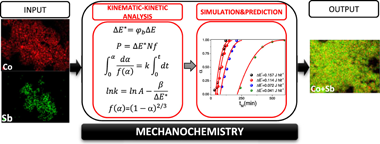
Mechanochemistry has attracted a lot of attention over the last few decades with a rapid growth in the number of publications due to its unique features. However, very little is known about how mechanical energy is converted into chemical energy. Most of the published works using mechanochemistry neglect the required attention to the experimental parameters and their effect over the resulting products, what makes extremely difficult to reproduce the results from lab to lab. Moreover, if it is taken into consideration the broad range of experimental conditions used in different studies, it is quite difficult to compare results and set optimum conditions. As a result, mechanochemistry is generally viewed as a "black box". The aim of this work is to provide some insight into mechanochemistry. Thus, a simple kinematic-kinetic approach that allows the full parametrization of mechanically induced reactions is proposed. In an analogous way to thermally activated process, it is shown that kinetic modeling can serve to parametrize and model mechanically induced reactions as a function of the milling parameters with great reliability, thereby gaining prediction capability. As a way of example, this methodology has been applied for the first time to the mechanochemical reaction of Co and Sb to form CoSb3, a skutterudite-type thermoelectric material. Moreover, the universality of this methodology has also been validated with data from the literature. A key feature of the proposed kinematic-kinetic approach is that it can be extrapolated to other mechanically induced reactions, either inorganic or organic.
June, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.158925
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Self-preserving ice layers on CO2 clathrate particles: Implications for Enceladus, Pluto, and similar ocean worlds
Bostrom, M; Esteso, V; Fiedler, J; Brevik, I; Buhmann, SY; Persson, C; Carretero-Palacios, S; Parsons, DF; Corkey, RWAstronomy & Astrophysics, 650 (2021) A54
Show abstract ▽
Context. Gas hydrates can be stabilised outside their window of thermodynamic stability by the formation of an ice layer - a phenomenon termed self-preservation. This can lead to a positive buoyancy for clathrate particles containing CO2 that would otherwise sink in the oceans of Enceladus, Pluto, and similar oceanic worlds.Aims. Here we investigate the implications of Lifshitz forces and low occupancy surface regions on type I clathrate structures for their self-preservation through ice layer formation, presenting a plausible model based on multi-layer interactions through dispersion forces.Methods. We used optical data and theoretical models for the dielectric response for water, ice, and gas hydrates with a different occupancy. Taking this together with the thermodynamic Lifshitz free energy, we modelled the energy minima essential for the formation of ice layers at the interface between gas hydrate and liquid water.Results. We predict the growth of an ice layer between 0.01 and 0.2 mu m thick on CO, CH4, and CO2 hydrate surfaces, depending on the presence of surface regions depleted in gas molecules. Effective hydrate particle density is estimated, delimiting a range of particle size and compositions that would be buoyant in different oceans. Over geological time, the deposition of floating hydrate particles could result in the accumulation of kilometre-thick gas hydrate layers above liquid water reservoirs and below the water ice crusts of their respective ocean worlds. On Enceladus, the destabilisation of near-surface hydrate deposits could lead to increased gas pressures that both drive plumes and entrain stabilised hydrate particles. Furthermore, on ocean worlds, such as Enceladus and particularly Pluto, the accumulation of thick CO2 or mixed gas hydrate deposits could insulate its ocean against freezing. In preventing freezing of liquid water reservoirs in ocean worlds, the presence of CO2-containing hydrate layers could enhance the habitability of ocean worlds in our Solar System and on the exoplanets and exomoons beyond.
June, 2021 | DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202040181
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
New Trends in Nanoclay-Modified Sensors
Pavon, E; Martin-Rodriguez, R; Perdigon, AC; Alba, MDInorganics, 9 (2021) 43
Show abstract ▽
Nanoclays are widespread materials characterized by a layered structure in the nano-scale range. They have multiple applications in diverse scientific and industrial areas, mainly due to their swelling capacity, cation exchange capacity, and plasticity. Due to the cation exchange capacity, nanoclays can serve as host matrices for the stabilization of several molecules and, thus, they can be used as sensors by incorporating electroactive ions, biomolecules as enzymes, or fluorescence probes. In this review, the most recent applications as bioanalyte sensors are addressed, focusing on two main detection systems: electrochemical and optical methods. Particularly, the application of electrochemical sensors with clay-modified electrodes (CLME) for pesticide detection is described. Moreover, recent advances of both electrochemical and optical sensors based on nanoclays for diverse bioanalytes' detection such as glucose, H2O2, organic acids, proteins, or bacteria are also discussed. As it can be seen from this review, nanoclays can become a key factor in sensors' development, creating an emerging technology for the detection of bioanalytes, with application in both environmental and biomedical fields.
June, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/inorganics9060043
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Features of coupled AgBr/WO3 materials as potential photocatalysts
Puga, F.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 867 (2021) 159191
Show abstract ▽
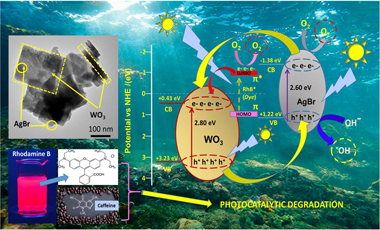
AgBr/WO3 composite photocatalysts with different selected molar AgBr/WO3 ratios were prepared and widely characterized by XRD, N2-adsorption, SEM, TEM, UV–visible/DRS and XPS techniques. The samples were tested using rhodamine B (RhB) or caffeine, under two illumination conditions (UV and visible light). Although AgBr and WO3 pristine materials have relatively low band gap values (2.6 eV and 2.8 eV, respectively), they exhibit low or no photocatalytic activity under visible light, at least for caffeine degradation. This fact may be mainly related to a high recombination rate of photogenerated charge carriers in these samples. However, the coupling of both leads to a substantial improvement in the degradation of caffeine and RhB under both UV and visible lighting conditions. The increased photocatalytic activity found in the coupled systems with respect to the pristine materials can be attributed to the formation of a type II heterostructure in the coupled AgBr/WO3 samples. Our results show that for AgBr/WO3 coupled systems, kinetic degradation profiles have clear dependence on the molar percentages of the coupled pristine materials, as well as on the nature (sensitizing or not sensitizing effect) of the substrate. For caffeine photodegradation, the best performance was obtained when AgBr/WO3(10–15%) catalysts were used. The AgBr/WO3(20%) sample showed the best photocatalytic activity for rhodamine B degradation, exhibiting also excellent dark adsorption capacity (40–45%). Additionally, studies of activity in five consecutive tests showed a good RhB degradation during the successive reuses being involving a N-de-ethylation mechanism with the main O2•− radicals participation; relatively low mineralization percentages were observed, both under UV and visible light conditions. In these successive runs, no silver leaching to the medium was observed but a change from AgBr towards Ag2CO3 and/or AgxO was produced at the catalyst surface. These features should be known in the use of these systems as potential photocatalysts for practical applications.
June, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159191
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Swelling layered minerals applications: A solid state NMR overview
Pavon, E; Alba, MDProgress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, 124 (2021) 99-128
Show abstract ▽
Swelling layered clay minerals form an important sub-group of the phyllosilicate family. They are characterized by their ability to expand or contract in the presence or absence of water. This property makes them useful for a variety of applications, ranging from environmental technologies to heteroge-neous catalysis, and including pharmaceutical and industrial applications. Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (SS-NMR) has been extensively applied in the characterization of these materials, providing useful information on their dynamics and structure that is inaccessible using other characterization methods such as X-ray diffraction. In this review, we present the key contributions of SS-NMR to the understanding of the mechanisms that govern some of the main applications associated to swelling clay minerals. The article is divided in two parts. The first part presents SS-NMR conventional applications to layered clay minerals, while the second part comprises an in-depth review of the information that SS-NMR can provide about the different properties of swelling layered clay minerals.
June, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2021.04.001
- ‹ previous
- 75 of 410
- next ›














