Scientific Papers in SCI
2022
2022
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Au and Pt Remain Unoxidized on a CeO2-Based Catalyst during the Water-Gas Shift Reaction
Reina, TR; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Lopez-Flores, V; Martinez, LMT; Zitolo, A; Ivanova, S; Xu, WQ; Centeno, MA; Rodriguez, JA; Odriozola, JAJournal of the American Chemical Society, 144 (2022) 446-453
Show abstract ▽
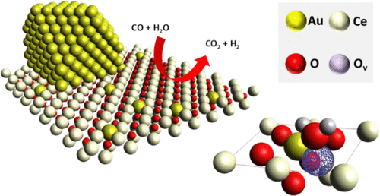
The active forms of Au and Pt in CeO2-based catalysts for the water-gas shift (WGS) reaction are an issue that remains unclear, although it has been widely studied. On one hand, ionic species might be responsible for weakening the Ce-O bonds, thus increasing the oxygen mobility and WGS activity. On the other hand, the close contact of Au or Pt atoms with CeO2 oxygen vacancies at the metal-CeO2 interface might provide the active sites for an efficient reaction. In this work, using in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy, we demonstrate that both Au and Pt remain unoxidized during the reaction. Remarkable differences involving the dynamics established by both species under WGS atmospheres were recognized. For the prereduced Pt catalyst, the increase of the conversion coincided with a restructuration of the Pt atoms into cuboctahedrical metallic particles without significant variations on the overall particle size. Contrary to the relatively static behavior of Pt-0, Au-0 nanoparticles exhibited a sequence of particle splitting and agglomeration while maintaining a zero oxidation state despite not being located in a metallic environment during the process. High WGS activity was obtained when Au atoms were surrounded by oxygen. The fact that Au preserves its unoxidized state indicates that the chemical interaction between Au and oxygen must be necessarily electrostatic and that such an electrostatic interaction is fundamental for a top performance in the WGS process.
January, 2022 | DOI: 10.1021/jacs.1c10481
Materiales Avanzados
Study of a Waste Kaolin as Raw Material for Mullite Ceramics and Mullite Refractories by Reaction Sintering
Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Eliche-Quesada, D; Martinez-Martinez, S; Perez-Villarejo, L; Garzon, EMaterials, 15 (2022) 583
Show abstract ▽
A deposit of raw kaolin, located in West Andalusia (Spain), was studied in this work using a representative sample. The methods of characterization were X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), particle size analysis by sieving and sedimentation, and thermal analysis. The ceramic properties were determined. A sample of commercial kaolin from Burela (Lugo, Spain), with applications in the ceramic industry, was used in some determinations for comparison purposes. The kaolin deposit has been produced by alteration of feldspar-rich rocks. This raw kaolin was applied as an additive in local manufactures of ceramics and refractories. However, there is not previous studies concerning its characteristics and firing properties. Thus, the meaning of this investigation was to conduct a scientific study on this subject and to evaluate the possibilities of application. The raw kaolin was washed for the beneficiation of the rock using water to increase the kaolinite content of the resultant material. The results indicated that the kaolinite content of the raw material was 20 wt % as determined by XRD, showing ~23 wt % of particles lower than 63 mu m. The kaolinite content of the fraction lower than 63 mu m was 50 wt %. Thus, an improvement of the kaolinite content of this raw kaolin was produced by wet separation. However, the kaolin was considered as a waste kaolin, with microcline, muscovite and quartz identified by XRD. Thermal analyses by Thermo-Dilatometry (TD), Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) and Thermo-Gravimetry (TG) allowed observe kaolinite thermal decomposition, quartz phase transition and sintering effects. Pressed samples of this raw kaolin, the fraction lower than 63 mu m obtained by water washing and the raw kaolin ground using a hammer mill were fired at several temperatures in the range 1000-1500 & DEG;C for 2 h. The ceramic properties of all these samples were determined and compared. The results showed the progressive linear firing shrinkage by sintering in these samples, with a maximum value of ~9% in the fraction lower than 63 mu m. In general, water absorption capacity of the fired samples showed a decrease from ~18-20% at 1050 & DEG;C up to almost zero after firing at 1300 & DEG;C, followed by an increase of the experimental values. The open porosity was almost zero after firing at 1350 & DEG;C for 2 h and the bulk density reached a maximum value of 2.40 g/cm(3) as observed in the ground raw kaolin sample. The XRD examination of fired samples indicated that they are composed by mullite, from kaolinite thermal decomposition, and quartz, present in the raw sample, as main crystalline phases besides a vitreous phase. Fully-densified or vitrified materials were obtained by firing at 1300-1350 & DEG;C for 2 h. In a second step of this research, it was examined the promising application of the previous study to increase the amount of mullite by incorporation of alumina (alpha-alumina) to this kaolin sample. Firing of mixtures, prepared using this kaolin and alpha-alumina under wet processing conditions, produced the increase of mullite in relative proportion by reaction sintering at temperatures higher than 1500 & DEG;C for 2 h. Consequently, a mullite refractory can be prepared using this kaolin. This processing of high-alumina refractories is favoured by a previous size separation, which increases the kaolinite content, or better a grinding treatment of the raw kaolin.
January, 2022 | DOI: 10.3390/ma15020583
2021
2021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
In Situ DRIFTS-MS Methanol Adsorption Study onto Supported NiSn Nanoparticles: Mechanistic Implications in Methanol Steam Reforming
Bobadilla, LF; Azancot, L; Ivanova, S; Delgado, JJ; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Roger, ACNanomaterials, 11 (2021) 3234
Show abstract ▽
Methanol adsorption over both supported NiSn Nps and analogous NiSn catalyst prepared by impregnation was studied by in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) to gain insights into the basis of hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming. Different intermediate species such as methoxides with different geometry (bridge and monodentate) and formate species were identified after methanol adsorption and thermal desorption. It is proposed that these species are the most involved in the methanol steam reforming reaction and the major presence of metal-support interface sites in supported NiSn Nps leads to higher production of hydrogen. On the basis of these results, a plausible reaction mechanism was elucidated through the correlation between the thermal stability of these species and the evolution of the effluent gas released. In addition, it was demonstrated that DME is a secondary product generated by condensation of methoxides over the acid sites of alumina support in an acid-catalyzed reaction.
December, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/nano11123234
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Mechanical Performances of Isolated Cuticles Along Tomato Fruit Growth and Ripening
Benitez, JJ; Guzman-Puyol, S; Vilaplana, F; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Dominguez, E; Heredia, AFrontiers in Chemistry, 12 (2021) 787839
Show abstract ▽
The cuticle is the most external layer that protects fruits from the environment and constitutes the first shield against physical impacts. The preservation of its mechanical integrity is essential to avoid the access to epidermal cell walls and to prevent mass loss and damage that affect the commercial quality of fruits. The rheology of the cuticle is also very important to respond to the size modification along fruit growth and to regulate the diffusion of molecules from and toward the atmosphere. The mechanical performance of cuticles is regulated by the amount and assembly of its components (mainly cutin, polysaccharides, and waxes). In tomato fruit cuticles, phenolics, a minor cuticle component, have been found to have a strong influence on their mechanical behavior. To fully characterize the biomechanics of tomato fruit cuticle, transient creep, uniaxial tests, and multi strain dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) measurements have been carried out. Two well-differentiated stages have been identified. At early stages of growth, characterized by a low phenolic content, the cuticle displays a soft elastic behavior. Upon increased phenolic accumulation during ripening, a progressive stiffening is observed. The increment of viscoelasticity in ripe fruit cuticles has also been associated with the presence of these compounds. The transition from the soft elastic to the more rigid viscoelastic regime can be explained by the cooperative association of phenolics with both the cutin and the polysaccharide fractions.
December, 2021 | DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.787839
Reactividad de Sólidos
Unravelling the optimization of few-layer graphene crystallinity and electrical conductivity in ceramic composites by Raman spectroscopy
Muñoz-Ferreiro, C; Lopez-Pernia, C; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, RJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 41 (2021) 290-298
Show abstract ▽
Zirconia composites with few-layer graphene (FLG) were prepared by two powder processing routines-ultrasonic agitation or planetary ball milling-and spark plasma sintered at 1250 and 1300 degrees C. An in-depth study of the crystallinity of FLG, in terms of presence and nature of defects, was performed by Raman spectroscopy, revealing enhanced FLG crystallinity after sintering. This enhancement was more noticeable in the composites sintered at the highest temperature, with lower amount of structural defects and amorphous carbon. However, remaining amorphous carbon was detected in the composites prepared by planetary ball milling even after sintering at the highest temperature, resulting in lower electrical conductivities. Optimum results in terms of electrical conductivity were achieved for the composites prepared by ultrasonic agitation and sintered at 1300 degrees C, with electrical percolation limit below 2.5 vol% FLG and high electrical conductivity (678 S/m for 5 vol% FLG), as result of the enhanced FLG crystallinity after sintering.
December, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.09.025
- ‹ previous
- 63 of 412
- next ›














