Scientific Papers in SCI
2019
2019
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Dry Reforming of Ethanol and Glycerol: Mini-Review
Yu, J; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TRCatalysts, 9 (2019) art. 1015
Show abstract ▽
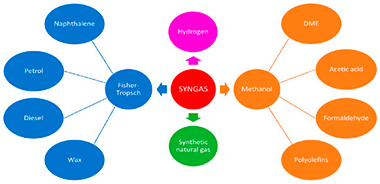
Dry reforming of ethanol and glycerol using CO2 are promising technologies for H-2 production while mitigating CO2 emission. Current studies mainly focused on steam reforming technology, while dry reforming has been typically less studied. Nevertheless, the urgent problem of CO2 emissions directly linked to global warming has sparked a renewed interest on the catalysis community to pursue dry reforming routes. Indeed, dry reforming represents a straightforward route to utilize CO2 while producing added value products such as syngas or hydrogen. In the absence of catalysts, the direct decomposition for H-2 production is less efficient. In this mini-review, ethanol and glycerol dry reforming processes have been discussed including their mechanistic aspects and strategies for catalysts successful design. The effect of support and promoters is addressed for better elucidating the catalytic mechanism of dry reforming of ethanol and glycerol. Activity and stability of state-of-the-art catalysts are comprehensively discussed in this review along with challenges and future opportunities to further develop the dry reforming routes as viable CO2 utilization alternatives.
December, 2019 | DOI: 10.3390/catal9121015
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Silver effect on the tribological and antibacterial properties of a-C:Ag coatings
Dominguez-Meister, S; Rojas, TC; Frias, JE; Sanchez-Lopez, JCTribology International, 140 (2019) UNSP 105837
Show abstract ▽
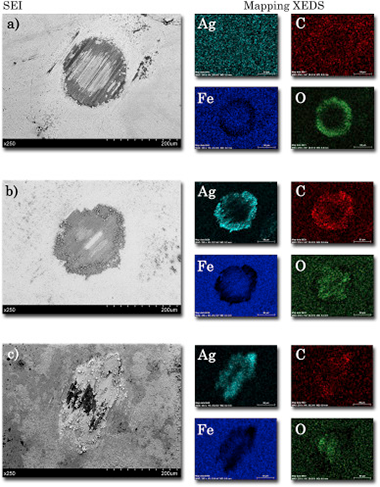
a-C:Ag coatings (1.2-23.4 at.% of Ag) were deposited using magnetron sputtering. Ag nanoparticles appear embedded in the carbon matrix or segregated to the column boundaries or surface. The silver doping has not promoted significant changes of the sp(2)/sp(3) ratio although a decrease of the hardness is observed (from 17 to 7 GPa). The tribological behavior did not show a clear dependence on the silver concentration in unlubricated or lubricated conditions (fetal bovinum serum) against alumina or UHMWPE balls. Ag nanoparticle dispersion enhanced the bactericide behavior as determined by the released Ag+ ion in the fluid media. There is no clear effect of friction rubbing on the released silver indicating that diffusion and top segregation are prevalent mechanisms for its dissolution.
December, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.triboint.2019.06.030
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
3D Organic Nanofabrics: Plasma-Assisted Synthesis and Antifreezing Behavior of Superhydrophobic and Lubricant-Infused Slippery Surfaces
Alcaire, M; Lopez-Santos, C; Aparicio, FJ; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Obrero, JM; Saghi, Z; Rico, VJ; de la Fuente, G; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, A; Borras, ALangmuir, 35 (2019) 16876-16885
Show abstract ▽
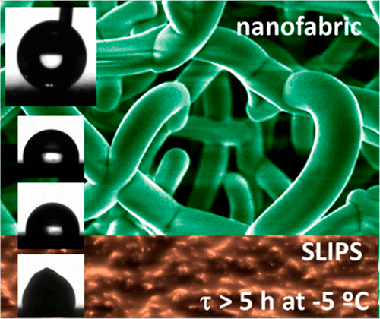
Herein, we present the development of supported organic nanofabrics formed by a conformal polymer-like interconnection of small-molecule organic nanowires and nanotrees. These organic nanostructures are fabricated by a combination of vacuum and plasma-assisted deposition techniques to generate step by step, single-crystalline organic nanowires forming one-dimensional building blocks, organic nanotrees applied as three-dimensional templates, and the polymer-like shell that produces the final fabric. The complete procedure is carried out at low temperatures and is compatible with an ample variety of substrates (polymers, metal, ceramics; either planar or in the form of meshes) yielding flexible and low solid-fraction three-dimensional nanostructures. The systematic investigation of this progressively complex organic nanomaterial delivers key clues relating their wetting, nonwetting, and anti-icing properties with their specific morphology and outer surface composition. Water contact angles higher than 150° are attainable as a function of the nanofabric shell thickness with outstanding freezing-delay times (FDT) longer than 2 h at −5 °C. The role of the extremely low roughness of the shell surface is settled as a critical feature for such an achievement. In addition, the characteristic interconnected microstructure of the nanofabrics is demonstrated as ideal for the fabrication of slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces (SLIPS). We present the straightforward deposition of the nanofabric on laser patterns and the knowledge of how this approach provides SLIPS with FDTs longer than 5 h at −5 °C and 1 h at −15 °C.
December, 2019 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b03116
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Design swelling micas: Insights on heavy metals cation exchange reaction
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 182 (2019) 105298
Show abstract ▽
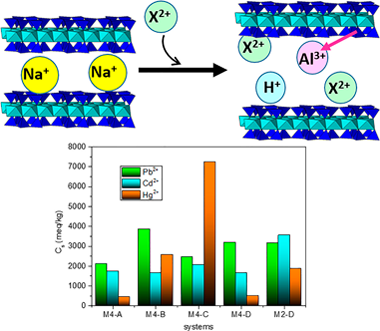
Heavy metal pollution has become one of the most serious environmental problems, demanding specialized remediation mechanisms. Among the studied treatments, ion-exchange processes have been widely used due to their high remediation capacity, efficiency and fast kinetic. Here, the potential use of a new family of design micas as cation exchanger has been analysed. Micas with a layer charge in the range of brittle micas have been synthesized and their heavy metals cation exchange capacity analysed as a function of the nature of the heavy metal cations (Pb2+, Cd2+ or Hg2+), the nature of the counterions (Cl− or NO3−), concentration of the solutions and the micas layer charge. A cation exchange ratio between 35% and 154% of their cation exchange capacity (CEC) was achieved, being more efficient when mica layer charge diminished. In general, the maximum adsorption capacity followed the trend: Hg2+ > Pb2+ > Cd2+. The efficiency of the cation exchange and adsorption mechanism of the synthetic micas depended on the experimental conditions and they were more efficient than raw and modified natural clay minerals.
December, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2019.105298
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Understanding segregation processes in SAMs formed by mixtures of hydroxylated and non-hydroxylated fatty acids
Bueno, OVM; Benitez, JJ; San-Miguel, MARSC Advances, 9 (2019) 39252-39263
Show abstract ▽
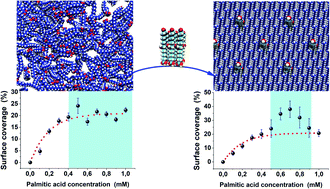
In this paper, we focus on the segregation processes emerging when preparing mixtures with different compositions of aleuritic (9,10,16 trihydroxyhexadecanoic) (ALE) and palmitic (hexadecanoic) (PAL) acids. The combination of atomic force microscopy (AFM) and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations enabled us to prove the role of the functional groups in the formation of self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) on muscovite mica surfaces. MD simulations indicate that segregation processes are favored in high ALE composition mixtures in agreement with the experimental evidence, whereas low ALE compositions promote the co-existence between segregated and dispersed systems. The secondary hydroxyl groups play a central role in the self-assembling mechanism because they control the formation of hydrogen bonding networks guarantying system stability.
December, 2019 | DOI: 10.1039/c9ra06799j
- ‹ previous
- 111 of 410
- next ›














