Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Catalytic Performance of Bulk and Al2O3-Supported Molybdenum Oxide for the Production of Biodiesel from Oil with High Free Fatty Acids Content
Navajas, A; Reyero, I; Jimenez-Barrera, E; Romero-Sarria, F; Llorca, J; Gandia, LMCatalysts, 10 (2020) 158
Show abstract ▽
Non-edible vegetable oils are characterized by high contents of free fatty acids (FFAs) that prevent from using the conventional basic catalysts for the production of biodiesel. In this work, solid acid catalysts are used for the simultaneous esterification and transesterification with methanol of the FFAs and triglycerides contained in sunflower oil acidified with oleic acid. Molybdenum oxide (MoO3), which has been seldom considered as a catalyst for the production of biodiesel, was used in bulk and alumina-supported forms. Results showed that bulk MoO3 is very active for both transesterification and esterification reactions, but it suffered from severe molybdenum leaching in the reaction medium. When supported on Al2O3, the MoO3 performance improved in terms of active phase utilization and stability though molybdenum leaching remained significant. The improvement of catalytic performance was ascribed to the establishment of MoO3-Al2O3 interactions that favored the anchorage of molybdenum to the support and the formation of new strong acidic centers, although this effect was offset by a decrease of specific surface area. It is concluded that the development of stable catalysts based on MoO3 offers an attractive route for the valorization of oils with high FFAs content.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/catal10020158
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Mesoporous Matrices as Hosts for Metal Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals
Rubino, A; Calio, L; Garcia-Bennett, A; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, (2020) 201901868
Show abstract ▽
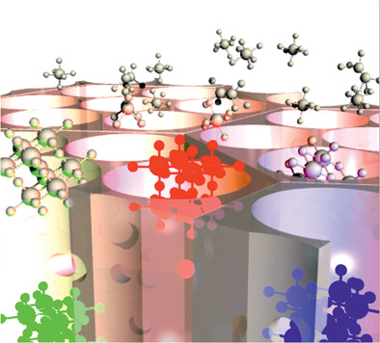
Several works have recently demonstrated that perovskite nanocrystals can be controllably formed within a variety of porous matrices employing diverse synthetic strategies. By means of the fine tuning of the pore size distribution, the thickness and composition of the walls, the geometry of the void network and its topology, strict control over the structural and morphological parameters of the hosted semiconductor can be achieved, determining its optical absorption and emission properties. Furthermore, porous hosts provide the guest semiconductor with enhanced stability and versatility in terms of processing, which favors its integration in devices. This article provides a comprehensive review of the different approaches proposed, as well as a discussion on the relevance they may have for the development of nanostructured perovskite-based optoelectronics. A critical assessment of the optical quality of the hybrid perovskite nanomaterials so obtained is presented, as well as an analysis of the fundamental and applied aspects of the nanocrystal-matrix interaction and a projected prospect of their impact in the fields of artificial lighting and renewable energy.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.201901868
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of Gold Particles Size over Au/C Catalyst Selectivity in HMF Oxidation Reaction
Megias-Sayago, C; Lolli, A; Bonincontro, D; Penkova, A; Albonetti, S; Cavani, F; Odriozola, JA; Ivanova, SChemcatchem, 12 (2020) 1177-1183
Show abstract ▽
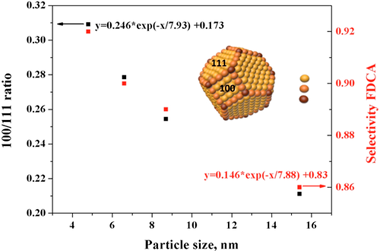
A series of gold nanoparticles in the 4-40 nm range were prepared, immobilized on activated carbon and further tested, at low base concentration, in the catalytic oxidation of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural (HMF) to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA). Gold particles size variation has no influence on HMF conversion but significantly affects product selectivity and carbon balance. This behavior is ascribed to the thermodynamically favorable oxygen reduction reaction on Au(100) faces. As the gold particle size decreases the Au(100)/Au(111) exposure ratio, estimated by using the van Hardeveld-Hartog model, increases as well as the FDCA selectivity. The smaller the gold particle size the smaller the 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furancarboxylic acid (HMFCA) to FDCA ratio pointing to the gold size dependent behavior of the oxidation of the alcohol function of the HMF molecule.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201901742
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Evaluation of Au–ZnO, ZnO/Ag2CO3 and Ag–TiO2 as Photocatalyst for Wastewater Treatment
Murcia, J.J.; Hernández, J.S.;Rojas, H.; Moreno-Cascante, J.; Sánchez-Cid, P.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Navío, J.A.; Jaramillo-Páez, C.Topics in Catalysis, (2020)
Show abstract ▽
In this work series of photocatalysts based on ZnO modified by Au and Ag2CO3 addition and Ag–TiO2 materials were synthesized and evaluated in the treatment of handicrafts factories wastewater and water samples taken from a highly polluted river. In general, it was found that ZnO series were more effective in the bacteria elimination than the commonly used TiO2 semiconductor. It was also observed that the metal (Au, Ag) or silver carbonate addition significantly increases the photocatalytic activity of ZnO and TiO2. It was determined that the content of the metal or carbonate added is an important factor to take into account in order to obtain suitable efficiency in the photocatalytic process, so, for example in the case of the river water samples the increase of Ag2CO3 content from 1 to 5%, had a detrimental effect over the bacteria elimination. The optimal conditions for dyes photodegradation and bacteria elimination were found by using a response surface study and the Au–ZnO (1%) photocatalyst. From this study it was determined that even after recycling this material leads to obtain a removal percentage of these pollutants over than 94%.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1007/s11244-020-01232-z
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Hybrid ZnO/Ag3PO4 photocatalysts, with low and high phosphate molar percentages
Martín-Gómez, A.N.;Navío, J.A.;Jaramillo-Páeza, C.;Sánchez-Cid, P.;Hidalgo, M.C.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, (2020) 112196
Show abstract ▽
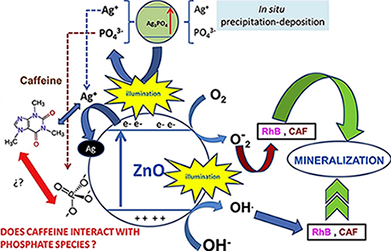
In this work, a previously optimized synthesized ZnO photocatalyst was modified with different molar percentages of Ag3PO4 through a facile in situ precipitation–deposition method and then characterized by different techniques (XRD, XRF, BET, UV–vis DRS, SEM, TEM and XPS). The incorporation of Ag3PO4 produces important changes in the light absorption properties with a significant absorbance in the visible region observed for ZnO modified with different amounts of Ag3PO4; the optical absorption intensity in the visible region of the coupled ZnO/Ag3PO4 increases as the molar percentages of Ag3PO4 increases, evidencing a clear dependence on the content of Ag3PO4. However, this work shows that the incorporation of Ag3PO4 in almost all cases reduces the photocatalytic capacity of ZnO, except when it is used in a specific percentage of 10 % and only being more active against rhodamine B and not on the Caffeine. SEM images and elemental mapping indicate that Ag3PO4 disperses very well in the ZnO particles, exhibiting an almost homogeneous distribution, showing zones with cumulus of Ag3PO4 (rich in P-Ag) in contact with ZnO-zones (rich in Zn). All the prepared photocatalysts were tested in the photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B as a dye, and caffeine as a toxic and persistent emerging compound under UV and visible light illumination. It is reported that not only the ZnO:Ag3PO4 ratio is an important factor that influences the photocatalytic process of substrate degradation, but also the nature of the substrate has an important influence on the photocatalytic behavior of the materials under both UV and visible illumination. Thus, pristine Ag3PO4 showed high photocatalytic degradation for rhodamine B, while for caffeine negligible photocatalytic degradation was found in both the UV and visible regions. The thermal- and photo-stability of the coupled system was also studied. At least, for rhodamine B no loss of photocatalytic activity has been observed after five recycles although the mineralization degree progressively diminished along the recycles.
February, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112196
- ‹ previous
- 106 of 410
- next ›














