Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
An insight on the design of mercapto functionalized swelling brittle micas
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 561 (2020) 533-541
Show abstract ▽
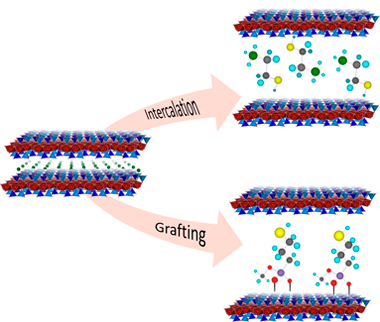
Surface modification of natural clay minerals with reagents containing metal chelating groups has great environmental value. The functionalization by adsorption or grafting guarantees a durable immobilization of the reactive organic groups, preventing their leaching when they are used in liquid media. The aim of this research was the designed mercapto functionalization of swelling brittle micas, Na-Mn, thorough both chemical and physical mechanisms. Na-Mn were functionalized with 2-mercaptoethylammonium (MEA), 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanol (BAL) and (3-mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane (MPTMS). The thiol concentration on swelling brittle micas is higher than the observed value for others adsorbents. The cation exchange reaction with MEA and one-step grafting with MPTMS in acid medium are the most efficient mercapto functionalization mechanism.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.028
Reactividad de Sólidos
Development by Mechanochemistry of La0.8Sr0.2Ga0.8Mg0.2O2.8 Electrolyte for SOFCs
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Tang, YQ; Gotor, FJ; Sayagues, MJMaterials, 13 (2020)
Show abstract ▽
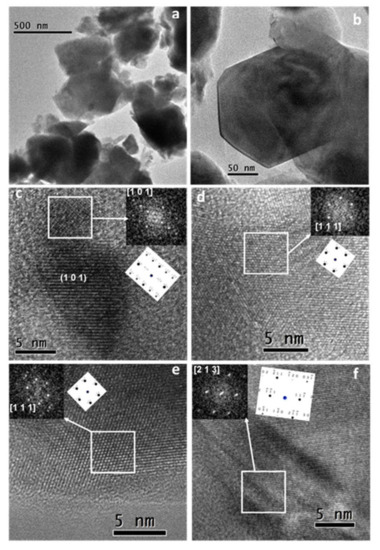
In this work, a mechanochemical process using high-energy milling conditions was employed to synthesize La0.8Sr0.2Ga0.8Mg0.2O3-δ (LSGM) powders from the corresponding stoichiometric amounts of La2O3, SrO, Ga2O3, and MgO in a short time. After 60 min of milling, the desired final product was obtained without the need for any subsequent annealing treatment. A half solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) was then developed using LSGM as an electrolyte and La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 (LSM) as an electrode, both obtained by mechanochemistry. The characterization by X-ray diffraction of as-prepared powders showed that LSGM and LSM present a perovskite structure and pseudo-cubic symmetry. The thermal and chemical stability between the electrolyte (LSGM) and the electrode (LSM) were analyzed by dynamic X-ray diffraction as a function of temperature. The electrolyte (LSGM) is thermally stable up to 800 and from 900 °C, where the secondary phases of LaSrGa3O7 and LaSrGaO4 appear. The best sintering temperature for the electrolyte is 1400 °C, since at this temperature, LaSrGaO4 disappears and the percentage of LaSrGa3O7 is minimized. The electrolyte is chemically compatible with the electrode up to 800 °C. The powder sample of the electrolyte (LSGM) at 1400 °C observed by HRTEM indicates that the cubic symmetry Pm-3m is preserved. The SOFC was constructed using the brush-painting technique; the electrode–electrolyte interface characterized by SEM presented good adhesion at 800 °C. The electrical properties of the electrolyte and the half-cell were analyzed by complex impedance spectroscopy. It was found that LSGM is a good candidate to be used as an electrolyte in SOFC, with an Ea value of 0.9 eV, and the LSM sample is a good candidate to be used as cathode
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/ma13061366
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Platinum nanoparticles stabilized by N-heterocyclic thiones. Synthesis and catalytic activity in mono- and di-hydroboration of alkynes
Moraes, LCC; Figueiredo, RCC; Espinos, JPP; Vattier, F; Franconetti, A; Jaime, C; Lacroix, B; Rojo, J; Lara, P; Conejero, SNanoscale, 12 (2020) 6821-6831
Show abstract ▽
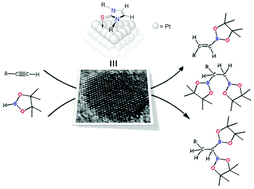
N-Heterocyclic Thiones (NHT) proved to be efficient ligands for the stabilization of small platinum nanoparticles (1.3-1.7 nm), synthesized by decomposition of [Pt(dba)(2)], under a H-2 atmosphere, in the presence of variable sub-stoichiometric amounts of the NHT. Full characterization by means of TEM, HR-TEM, NMR, ICP, TGA and XPS have been carried out, providing information about the nature of the metal nanoparticles and the interaction of the NHT ligands to the metal surface. Importantly, DFT calculations indicate that some NHT ligands interact with the metal through the C & xe001;C double bond of the imidazole fragment in addition to the sulfur atom, thus providing additional stabilization to the nanoparticles. According to XPS, TGA and ICP techniques, the surface coverage by the ligand increases by decreasing the size of the substituents on the nitrogen atom. The platinum nanoparticles have been used as catalyst in the hydroboration of alkynes. The most active system is that with a less covered surface area lacking an interaction of the ligand by means of the C & xe001;C double bond. This catalyst hydroborates alkynes with excellent selectivities towards the monoborylated anti-Markovnikov product (vinyl-boronate) when one equiv. of borane is used. Very interestingly, aliphatic alkynes undergo a second hydroborylation process leading to the corresponding 1,1- and 1,2-diboroylated species with good selectivities towards the former.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1039/d0nr00251h
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optofluidic liquid sensing on electromicrofluidic devices
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Wang, SL; Rico-Gavira, V; Lopez-Santos, C; Fan, SK; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARMaterials Research Express, 7 (2020) 036407
Show abstract ▽
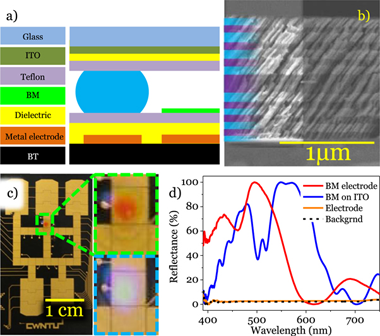
Electromicrofluidic (EMF) devices are used to handle and move tiny amounts of liquids by electrical actuation, including electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD) and dielectrophoresis (DEP). Monitoring the liquid characteristics in one of these devices requires suitable sensing transducers incorporated within the microfluidic structure. In the present work, we describe the incorporation of an optofluidic photonic transducer in an EMF device to monitor the refractive index of a liquid during its manipulation. The incorporated transducer consists of a responsive porous Bragg Microcavity (BM) deposited via physical vapor oblique angle deposition. Besides reporting the manufacturing procedure of the sensing-EMF device combining liquid handling and monitoring, the performance of the BM is verified by infiltrating several liquids dripped on its surface and comparing the responses with those of liquid droplets electrically moved from the delivery part of the chip to the BM location. This study proved that modified EMF devices can incorporate photonic structures to analyze very low liquid volumes (similar to 0.2 mu L) during its handling.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab7fdf
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Localized surface plasmon effects on the photophysics of perovskite thin films embedding metal nanoparticles
Bayles, A; Carretero-Palacios, S; Calio, L; Lozano, G; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 8 (2020) 916-921
Show abstract ▽
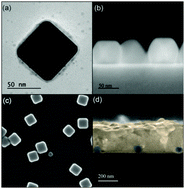
Herein we provide direct experimental evidence that proves that the photophysical properties of thin methylammonium lead iodide perovskite films are significantly enhanced by localized surface plasmon resonances (SPRs). Observations are well supported by rigorous calculations that prove that improved light harvesting can be unequivocally attributed to plasmonic scattering and near field reinforcement effects around silver nanoparticles embedded within the semiconductor layer. Adequate design of the localized SPR allows raising the absorptance of a 300 nm thick film at well-defined spectral regions while minimizing the parasitic absorption from the metallic inclusions. Measured enhancements can be as large as 80% at specific wavelengths and 20% when integrated over the whole range at which SPR occurs, in agreement with theoretical estimations. Simultaneously, the characteristic quenching effect that the vicinity of metals has on the photoluminescence of semiconductors is largely compensated for by the combined effect of the enhanced photoexcitation and the higher local density of photon states occurring at SPR frequencies, with a two fold increase of the perovskite photoemission efficiency being measured.
March, 2020 | DOI: 10.1039/c9tc05785d
- ‹ previous
- 103 of 410
- next ›














