Artículos SCI
2020
2020
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Low gas consumption fabrication of He-3 solid targets for nuclear reactions
Fernandez, A; Hufschmidt, D; Colaux, JL; Valiente-Dobon, JJ; Godinho, V; de Haro, MCJ; Feria, D; Gadea, A; Lucas, SMaterials & Design, 186 (2020) 108337
Show abstract ▽
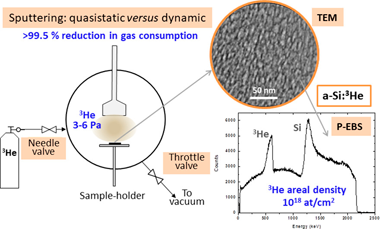
Nanoporous solids that stabilize trapped gas nanobubbles open new possibilities to fabricate solid targets for nuclear reactions. A methodology is described based on the magnetron sputtering (MS) technique operated under quasistatic flux conditions to produce such nanocomposites films with He-3 contents of up to 16 at.% in an amorphous-silicon matrix. In addition to the characteristic low pressure (3-6 Pa) needed for the gas discharge, the method ensures almost complete reduction of the process gas flow during film fabrication. The method could produce similar materials to those obtained under classical dynamic flux conditions for MS. The drastic reduction (>99.5%) of the gas consumption is fundamental for the fabrication of targets with scarce and expensive gases. Si:He-3 and W:He-3 targets are presented together with their microstructural (scanning and transmission electron microscopy, SEM and TEM respectively) and compositional (Ion Beam Analysis, IBA) characterization. The He-3 content achieved was over 1 x 10(18) at/cm(2) for film thicknesses between 1.5 and 3 mu m for both Si and W matrices. First experiments to probe the stability of the targets for nuclear reaction studies in inverse kinematics configurations are presented.
Enero, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108337
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Platinum nanoparticles stabilized by N-heterocyclic thiones. Synthesis and catalytic activity in mono- and di-hydroboration of alkynes
Moraes, LCC; Figueiredo, RCC; Espinos, JPP; Vattier, F; Franconetti, A; Jaime, C; Lacroix, B; Rojo, J; Lara, P; Conejero, SNanoscale, 12 (2020) 6821-6831
Show abstract ▽
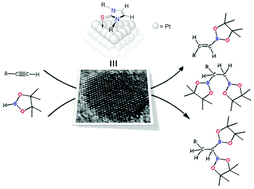
N-Heterocyclic Thiones (NHT) proved to be efficient ligands for the stabilization of small platinum nanoparticles (1.3-1.7 nm), synthesized by decomposition of [Pt(dba)(2)], under a H-2 atmosphere, in the presence of variable sub-stoichiometric amounts of the NHT. Full characterization by means of TEM, HR-TEM, NMR, ICP, TGA and XPS have been carried out, providing information about the nature of the metal nanoparticles and the interaction of the NHT ligands to the metal surface. Importantly, DFT calculations indicate that some NHT ligands interact with the metal through the C & xe001;C double bond of the imidazole fragment in addition to the sulfur atom, thus providing additional stabilization to the nanoparticles. According to XPS, TGA and ICP techniques, the surface coverage by the ligand increases by decreasing the size of the substituents on the nitrogen atom. The platinum nanoparticles have been used as catalyst in the hydroboration of alkynes. The most active system is that with a less covered surface area lacking an interaction of the ligand by means of the C & xe001;C double bond. This catalyst hydroborates alkynes with excellent selectivities towards the monoborylated anti-Markovnikov product (vinyl-boronate) when one equiv. of borane is used. Very interestingly, aliphatic alkynes undergo a second hydroborylation process leading to the corresponding 1,1- and 1,2-diboroylated species with good selectivities towards the former.
Marzo, 2020 | DOI: 10.1039/d0nr00251h
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Robust label-free CuxCoyOz electrochemical sensors for hexose detection during fermentation process monitoring
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez, R; Yubero, F; de Lucas-Consuegra, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSensors and Actuators B-Chemical, 304 (2020) 127360
Show abstract ▽

Label free electrochemical sensors of glucose are used whenever long-term operation and stable response are required. For this purpose, various metals and oxides of the first transition series have been proposed as alternative to more expensive noble metal electrochemical sensors. In this work we propose a new formulation consisting of copper-cobalt mixed oxides which, in the form of porous and nanostructured thin films with well controlled Co/Cu ratio, are prepared at room temperature in one step by a modification of the magnetron sputtering oblique angle deposition procedure. Films with various compositions were electrochemically characterized by cyclic voltammetry to determine their amperometric response to glucose as a function of voltage and NaOH electrolyte concentration. This analysis showed that films with a Co/Cu atomic ratio equal 3.4 presented a maximum sensitivity (0.710 A M−1 cm−2), a small limit of detection (0.105 μM) and a resilient behaviour upon cycling operation and long storage periods that clearly overpassed the performance of copper and cobalt single oxides. The CuxCoyO electrocatalysts also presented a good selectivity towards glucose and fructose in the presence of common interference compounds found in biological fluids (e.g., ascorbic acid, acetaminophen and uric acid), sucrose and ethanol, this latter present in many agrofood liquids. The possibilities of this sensor electrocatalyst have been tested for the analysis of a wine synthetic fermentation process. The comparison of the electrochemical results with conventional analytical methods showed a lineal amperometric response with respect hexose contents in a must at different stages of its transformation into wine.
Febrero, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.127360
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Localized surface plasmon effects on the photophysics of perovskite thin films embedding metal nanoparticles
Bayles, A; Carretero-Palacios, S; Calio, L; Lozano, G; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 8 (2020) 916-921
Show abstract ▽
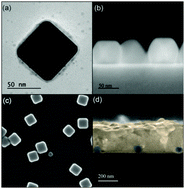
Herein we provide direct experimental evidence that proves that the photophysical properties of thin methylammonium lead iodide perovskite films are significantly enhanced by localized surface plasmon resonances (SPRs). Observations are well supported by rigorous calculations that prove that improved light harvesting can be unequivocally attributed to plasmonic scattering and near field reinforcement effects around silver nanoparticles embedded within the semiconductor layer. Adequate design of the localized SPR allows raising the absorptance of a 300 nm thick film at well-defined spectral regions while minimizing the parasitic absorption from the metallic inclusions. Measured enhancements can be as large as 80% at specific wavelengths and 20% when integrated over the whole range at which SPR occurs, in agreement with theoretical estimations. Simultaneously, the characteristic quenching effect that the vicinity of metals has on the photoluminescence of semiconductors is largely compensated for by the combined effect of the enhanced photoexcitation and the higher local density of photon states occurring at SPR frequencies, with a two fold increase of the perovskite photoemission efficiency being measured.
Marzo, 2020 | DOI: 10.1039/c9tc05785d
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Efficient third harmonic generation from FAPbBr(3) perovskite nanocrystals
Rubino, A; Huq, T; Dranczewski, J; Lozano, G; Calvo, ME; Vezzoli, S; Miguez, H; Sapienza, RJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 8 (2020) 15990-15995
Show abstract ▽
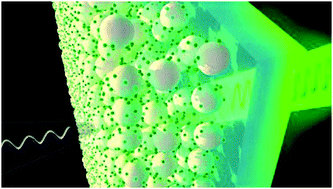
The development of versatile nanostructured materials with enhanced nonlinear optical properties is relevant for integrated and energy efficient photonics. In this work, we report third harmonic generation from organic lead halide perovskite nanocrystals, and more specifically from formamidinium lead bromide nanocrystals, ncFAPbBr(3), dispersed in an optically transparent silica film. Efficient third order conversion is attained for excitation in a wide spectral range in the near infrared (1425 nm to 1650 nm). The maximum absolute value of the modulus of the third order nonlinear susceptibility of ncFAPbBr(3), chi((3)NC), is derived from modelling both the linear and nonlinear behaviour of the film and is found to be chi((3)NC) = 1.46 x 10(-19) m(2) V-2 (or 1.04 x 10(-11) esu) at 1560 nm excitation wavelength, which is of the same order as the highest previously reported for purely inorganic lead halide perovskite nanocrystals (3.78 x 10(-11) esu for ncCsPbBr(3)). Comparison with the experimentally determined optical constants demonstrates that maximum nonlinear conversion is attained at the excitonic resonance of the perovskite nanocrystals where the electron density of states is largest. The ease of synthesis, the robustness and the stability provided by the matrix make this material platform attractive for integrated nonlinear devices.
Diciembre, 2020 | DOI: 10.1039/d0tc04790b
- ‹ anterior
- 93 of 410
- siguiente ›
icms











