Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Functionalized biochars as supports for Pd/C catalysts for efficient hydrogen production from formic acid
Santos, JL; Megias-Sayago, C; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 282 (2021) 119615
Show abstract ▽

Biomass waste product was used to generate biochars as catalytic supports for selective hydrogen production from formic acid. The supports were obtained after pyrolysis in CO2 atmosphere of non-pretreated and che-mically ZnCl2 activated raw materials (vine shoot and crystalline cellulose). The support series includes materials with different textural properties and surface chemistry. The support nature and especially textural properties firstly affects significantly Pd size and dispersion and its interaction with the support and secondly influence in a great extent the catalytic behavior of the final material. The presence of prevailing mesoporous character appeared to be the most important parameter influencing formic acid dehydrogenation and overall hydrogen production.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119615
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales - Materiales Coloidales
Persistent luminescence of transparent ZnGa2O4:Cr3+ thin films from colloidal nanoparticles of tunable size
Arroyo, E; Medran, B; Castaing, V; Lozano, G; Ocana, M; Becerro, AIJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 9 (2021) 4474-4485
Show abstract ▽
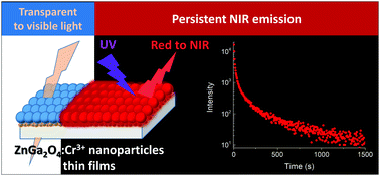
We report on the fabrication of ZnGa2O4:Cr3+ transparent thin films and the evaluation, for the first time in the literature, of their persistent red to NIR emission. For this purpose, we have used a simple and economic global strategy based on wet processing methods from colloidal nanospheres with uniform size. A microwave-assisted hydrothermal method was first developed for the synthesis of precursor particles, which allows size tuning from 300 nm to 30 nm through simple modification of the Zn2+ precursor and the Cr3+ content of the starting solutions. ZnGa2O4:Cr3+ transparent thin films over quartz substrates were then easily fabricated by spin coating, and their structural and optical characteristics were analyzed in detail after annealing at high temperature to elucidate the effect of processing temperature and particle size on the properties of the films. Indeed, our results indicate that high temperature annealing does not compromise the transparency of the films but improves their photoluminescence. In addition, the analysis reveals that persistence luminescence in our films is rather independent of the size of the precursor nanoparticles. Due to their transparency and persistent emission properties, films fabricated from colloidal suspensions of ZnGa2O4:Cr3+ nanoparticles show great potential for application in the fields of chemical sensing, information storage, labelling, and anti-counterfeiting technology.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1039/d1tc00258a
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Zirconium retention for minimizing environmental risk: Role of counterion and clay mineral
Montes, L; Pavon, E; Cota, A; AlbaChemosphere, 267 (2021) 128914
Show abstract ▽
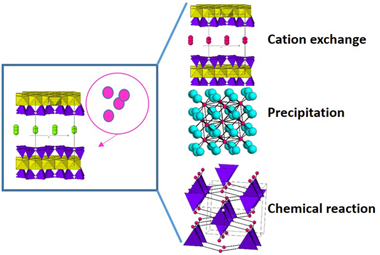
Zr(IV) together with U(IV) are the major components of high-level radionuclide waste (HLRW) and spent nuclear fuel (SNF) from nuclear power plants. Thus, their retention in the waste disposal is of great importance for the environmental risk control. Here, the influence of clay minerals on the retention of Zr(IV), as component of the nuclear waste and as chemical analogues of U(IV), has been evaluated. Three clay minerals, two bentonites and one saponite, were hydrothermally treated with three zirconium salts. A structural study at long-range order by X-ray diffraction and short-range order by NMR was performed to evaluate the generation of new zirconium phases and degradation of the clay minerals. Three immobilization mechanisms were observed: i) cation exchange of ZrO2+ or Zr4+ by clay minerals, ii) the precipitation/crystallization of ZrO2, and, iii) the chemical interaction of zirconium with the clay minerals, with the formation of zirconium silicates.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128914
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Solid-State Dewetting of Gold on Stochastically Periodic SiO2 Nanocolumns Prepared by Oblique Angle Deposition
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Wang, D; Flock, D; Rico, V; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Schaaf, PACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 13 (2021) 11385-11395
Show abstract ▽
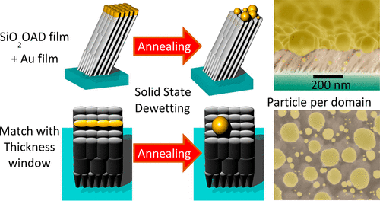
Solid-state dewetting (SSD) on patterned substrates is a straightforward method for fabricating ordered arrays of metallic nanoparticles on surfaces. However, a drawback of this procedure is that the patterning of substrates usually requires time-consuming and expensive two-dimensional (2D) fabrication methods. Nanostructured thin films deposited by oblique angle deposition (OAD) present at the surface a form of stochastically arranged periodic bundles of nanocolumns that might act as a patterned template for fabricating arrays of nanoparticles by SSD. In this work, we explore this concept and investigate the effect of three different types of OAD SiO2 thin films on the SSD of Au deposited on their surface. We demonstrate that the size and spatial distribution of the particles can be tailored through the surface morphology of these OAD film substrates. It has been found that the SSD of the evaporated Au layer gives rise to a bimodal size distribution of particles. A majority of them appeared as mesoparticles with sizes.100 nm and the rest as nanoparticles with similar to 10 nm, respectively, located either on top of the nanocolumns following their lateral distribution (i.e., resulting from a patterning effect) or incorporated inside the open mesopores existing among them. Moreover, on the SiO2-OAD thin films where interconnected nanocolumnar bundles arrange in the form of discrete motifs, the patterning effect gave rise to the formation of approximately one Au mesoparticle per motif, which is one of the assets of patterned SSD. The morphological, optical (i.e., plasmon resonance), and crystalline structural characteristics of Au mesoparticles suggest that the interplay between a discontinuous nanocolumnar surface acting as a template and the poor adhesion of Au onto SiO2 are key factors for the observed template effect controlling the SSD on the surface of OAD thin films.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acsami.0c19327
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Overcoming Pd-TiO2 Deactivation during H-2 Production from Photoreforming Using Cu@Pd Nanoparticles Supported on TiO2
Platero, F; Lopez-Martin, A; Caballero, A; Rojas, TC; Nolan, M; Colon, GACS Applied Nano Materials, 4 (2021) 3204-3219
Show abstract ▽
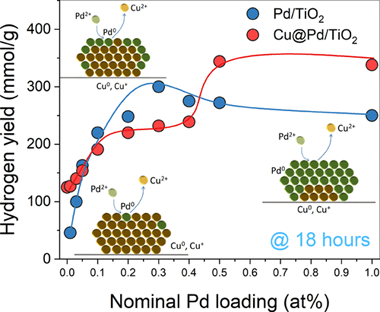
Different Cu@Pd-TiO2 systems have been prepared by a two-step synthesis to obtain a bimetallic co-catalyst for the H-2 photoreforming reaction. We find that the tailored deposition of Pd covering the Cu nanoclusters by a galvanic replacement process results in the formation of a core@shell structure. The photocatalytic H-2 production after 18 h is 350 mmol/g on the Cu@Pd-1.0-TiO2 bimetallic system, which is higher than that on the monometallic ones with a H-2 production of 250 mmol/g on Pd-supported TiO2. Surface characterization by highangle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy, H-2-temperatureprogramed reduction, CO-FTIR spectroscopy, and XPS gives clear evidence of the formation of a core@shell structure. With a Pd loading of 0.2-0.3 at. %, we propose a full coverage of the Cu nanoparticles with Pd. Long-time photoreforming runs show the enhanced performance of supported Cu@Pd with respect to bare palladium leading to a more stable catalyst and ultimately higher H-2 production.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.1c00345
- ‹ previous
- 82 of 410
- next ›














