Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Light-Harvesting Properties of a Subphthalocyanine Solar Absorber Coupled to an Optical Cavity
Esteso, V; Calio, L; Espinos, H; Lavarda, G; Torres, T; Feist, J; Garcia-Vidal, FJ; Bottari, G; Míguez, HSOLAR RRL, (2021) 2100308
Show abstract ▽
Herein, both from the experimental and theoretical point of view, the optical absorption properties of a subphthalocyanine (SubPc), an organic macrocycle commonly used as a sunlight harvester, coupled to metallic optical cavities are analyzed. How different electronic transitions characteristic of this compound and specifically those that give rise to excitonic (Q band) and charge transfer (CT band) transitions couple to optical cavity modes is investigated. It is observed that whereas the CT band couples weakly to the cavity, the Q band transitions show evidence of hybridization with the photon eigenstates of the resonator, a distinctive trait of the strong coupling regime. As a result of the different coupling regimes of the two electronic transitions, very different spectral and directional light-harvesting features are observed, which for the weakly coupled CT transitions are mainly determined by the highly dispersive cavity modes and for the strongly coupled Q band by the less angle-dependent exciton-polariton bands. Modeling also allows discriminating parasitic from productive absorption in each case, enabling the estimation of the expected losses in a solar cell acting as an optical resonator.
July, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/solr.202100308
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Mechanistic Considerations on the H-2 Production by Methanol Thermal-assisted Photocatalytic Reforming over Cu/TiO2 Catalyst
Platero, F; Lopez-Martin, A; Caballero, A; Colon, GCHEMCATCHEM, 13 (2021) 3878-3888
Show abstract ▽
We have studied the gas phase H-2 production by methanol thermo-photoreforming using Cu-modified TiO2. Metal co-catalyst has been deposited by means of photodeposition method. The concentration of methanol in the steam was also considered. It appears that H-2 production is notably higher as temperature increases. Moreover, the optimum H-2 yield is achieved using methanol concentration of 10 % v/v. CO and CO2 were monitored as side products of the overall reaction. It has been stated that CO evolution is significant at lower temperatures. As temperature increases, CO evolution is hindered and H-2 appeared boosted. We have demonstrated that other reactions such water-gas-shift or formate dehydration would participate in the overall process. On this basis, optimal operational condition for H-2 production is attained for thermo-photocatalytic reforming of methanol solution 10 % v/v at 200 degrees C.
July, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/cctc.202100680
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Dehydration of glucose to 5-Hydroxymethlyfurfural on bifunctional carbon catalysts
Bounoukta, CE; Megias-Sayago, C; Ammari, F; Ivanova, S; Monzon, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 286 (2021) 119938
Show abstract ▽
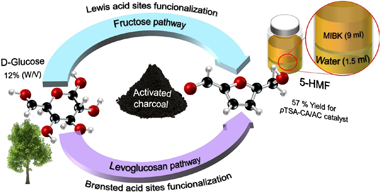
The proposed study tries to reply on one important question concerning glucose dehydration: What is the role of bare or tandem Lewis/Bronsted acid sites in the reaction and which are better? A series of mono and bifunctional catalyst are designed and screened for the glucose dehydration reaction. The results clearly reveal that catalyst activity is a function of catalyst composition. The presence of Lewis sites the reaction toward first step isomerization, while the Brunsted acid dehydrate directly glucose to HMF via levoglucosane intermediate. This study proposed also a kinetic modelling of the included reactions and their contrast with the empirical observations.
June, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.119938
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales - Materiales Coloidales
Highly Versatile Upconverting Oxyfluoride-Based Nanophosphor Films
Ngo, TT; Cabello-Olmo, E; Arroyo, E; Becerro, AI; Ocana, M; Lozano, G; Miguez, HACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 13 (2021) 30051-30060
Show abstract ▽
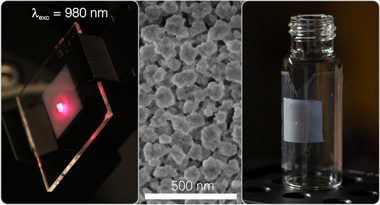
Fluoride-based compounds doped with rare-earth cations are the preferred choice of materials to achieve efficient upconversion, of interest for a plethora of applications ranging from bioimaging to energy harvesting. Herein, we demonstrate a simple route to fabricate bright upconverting films that are transparent, self-standing, flexible, and emit different colors. Starting from the solvothermal synthesis of uniform and colloidally stable yttrium fluoride nanoparticles doped with Yb3+ and Er3+, Ho3+, or Tm3+, we find the experimental conditions to process the nanophosphors as optical quality films of controlled thickness between few hundreds of nanometers and several micrometers. A thorough analysis of both structural and photophysical properties of films annealed at different temperatures reveals a tradeoff between the oxidation of the matrix, which transitions through an oxyfluoride crystal phase, and the efficiency of the upconversion photoluminescence process. It represents a significant step forward in the understanding of the fundamental properties of upconverting materials and can be leveraged for the optimization of upconversion systems in general. We prove bright multicolor upconversion photoluminescence in oxyfluoride-based phosphor transparent films upon excitation with a 980 nm laser for both rigid and flexible versions of the layers, being possible to use the latter to coat surfaces of arbitrary shape. Our results pave the way toward the development of upconverting coatings that can be conveniently integrated in applications that demand a large degree of versatility.
June, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acsami.1c07012
Reactividad de Sólidos
Paving the Way to Establish Protocols: Modeling and Predicting Mechanochemical Reactions
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, AJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 12 (2021) 5540-5546
Show abstract ▽
Parametrization of mechanochemical reactions, or relating the evolution of the reaction progress to the supplied input power, is required both to establish protocols and to gain insight into mechanochemical reactions. Thus, results could be compared, replicated, or scaled up even under different milling conditions, enlarging the domains of application of mechanochemistry. Here, we propose a procedure that allows the parametrization of mechanochemical reactions as a function of the supplied input power from the direct analysis of the milling experiments in a model-free approach, where neither the kinetic model function nor the rate constant equation are previously assumed. This procedure has been successfully tested with the mechanochemical reaction of CH3NH3PbCl3, enabling the possibility to make predictions regardless of the milling device as well as gaining insight into the reaction dynamic. This methodology can work for any other mechanical reaction and definitely paves the way to establish mechanochemistry as a standard synthetic procedure.
June, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c01472
- ‹ previous
- 73 of 410
- next ›














